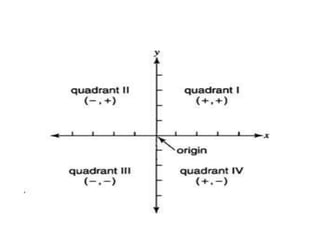
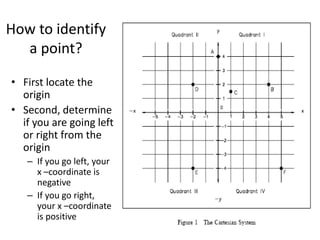
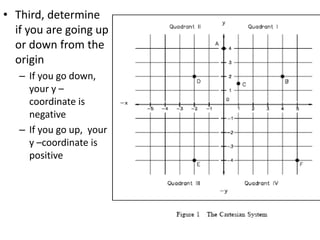
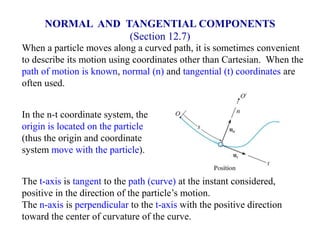
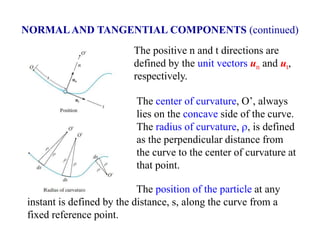
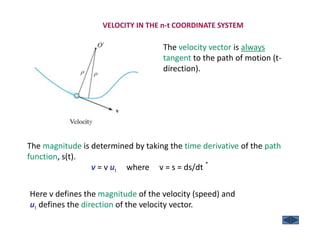
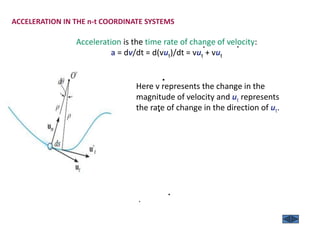
The document describes the Cartesian coordinate system and the normal-tangential coordinate system. The Cartesian system uses perpendicular x and y axes to locate points in a plane using ordered pairs (x,y). The normal-tangential system is used to describe motion along a curved path, with the t-axis tangent to the path and the n-axis perpendicular, pointing toward the center of curvature. In this system, a particle's position is defined by its distance s along the curve, and its velocity is always in the t-direction while its acceleration has components in both the t and n directions.