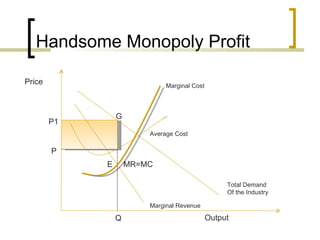
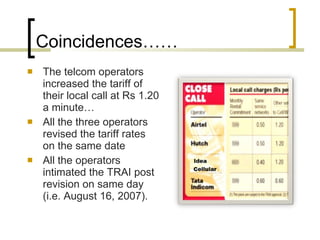
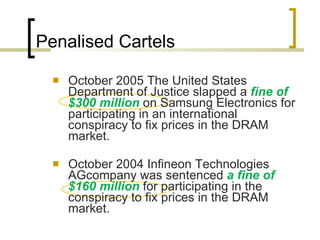
The document discusses cartelization, which refers to when independent firms work together to control competition and set prices. It provides examples of cartels that have formed in industries like cement production, trucking, and telecommunications in India. Cartels allow firms to fix prices higher than competitive levels and divide markets between participants. However, cartel behavior can harm consumers and the economy. The document argues that India needs stronger penalties and enforcement against cartels for the Competition Act to be an effective deterrent.