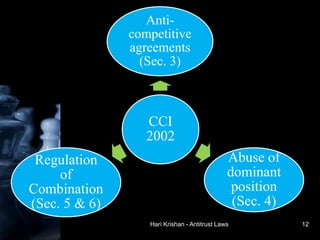
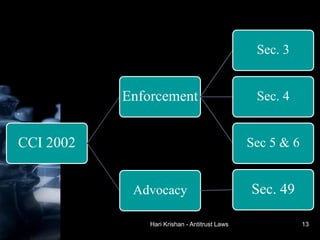
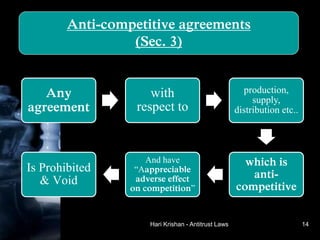
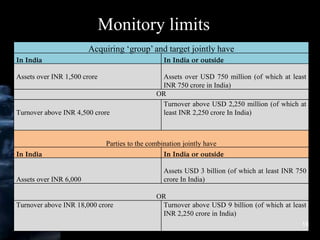
The document provides an overview of antitrust laws, beginning with their historical context in the 1800s when monopolistic 'trusts' dominated sectors like railroads and steel. Key legislation like the Sherman Act, Clayton Act, and the Competition Act in India aimed to promote fair competition and prevent anti-competitive practices, with regulatory bodies such as the FTC and CCI established to enforce these laws. It details specific provisions against anti-competitive agreements, abuse of dominance, and regulation of mergers in both the U.S. and Indian contexts.