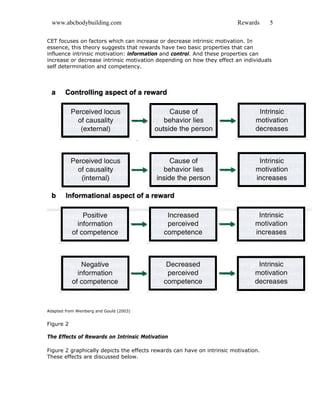
- External rewards can undermine intrinsic motivation depending on how the reward is framed and delivered. Rewards that are perceived as controlling undermine intrinsic motivation, while rewards seen as providing positive feedback can enhance intrinsic motivation.
- The effects of rewards on intrinsic motivation have been debated for over 30 years. Research has found that rewards focused on competence and autonomy, rather than control, tend to maintain and even increase intrinsic motivation.
- Self-determination theory posits that humans have innate psychological needs for competence, autonomy, and relatedness, and rewards perceived as controlling can undermine these needs and reduce intrinsic motivation for an activity.