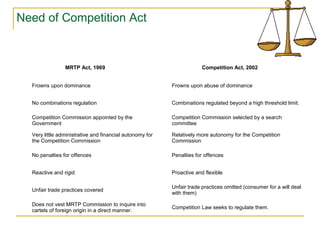
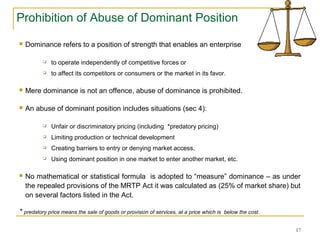
The document provides an overview of the Competition Act of 2002 in India. It discusses key aspects of the Act including its objectives to prevent anti-competitive practices and abuse of dominance. It outlines the prohibitions on anti-competitive agreements and abuse of dominant position. It also covers the regulation of combinations or mergers and acquisitions as well as the thresholds for notification. The document proposes some amendments to the Act including increasing pre-merger consultation and notification timelines.