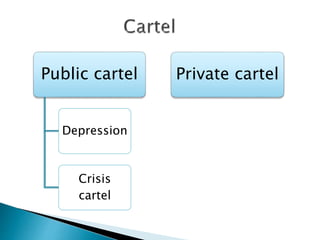
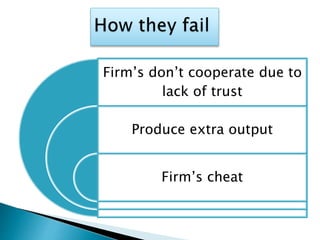
This document discusses cartels, including what they are, different types, how they can succeed or fail, and their impact. A cartel is a formal agreement between producers to regulate supply and prices in order to maximize profits. They aim to increase profits by fixing prices, limiting supply, or other means. While cartels can benefit members by avoiding price competition, they often fail due to cheating or lack of cooperation between firms and create inefficiencies in the market. The only legal cartel is OPEC, which restricts oil production through quotas.