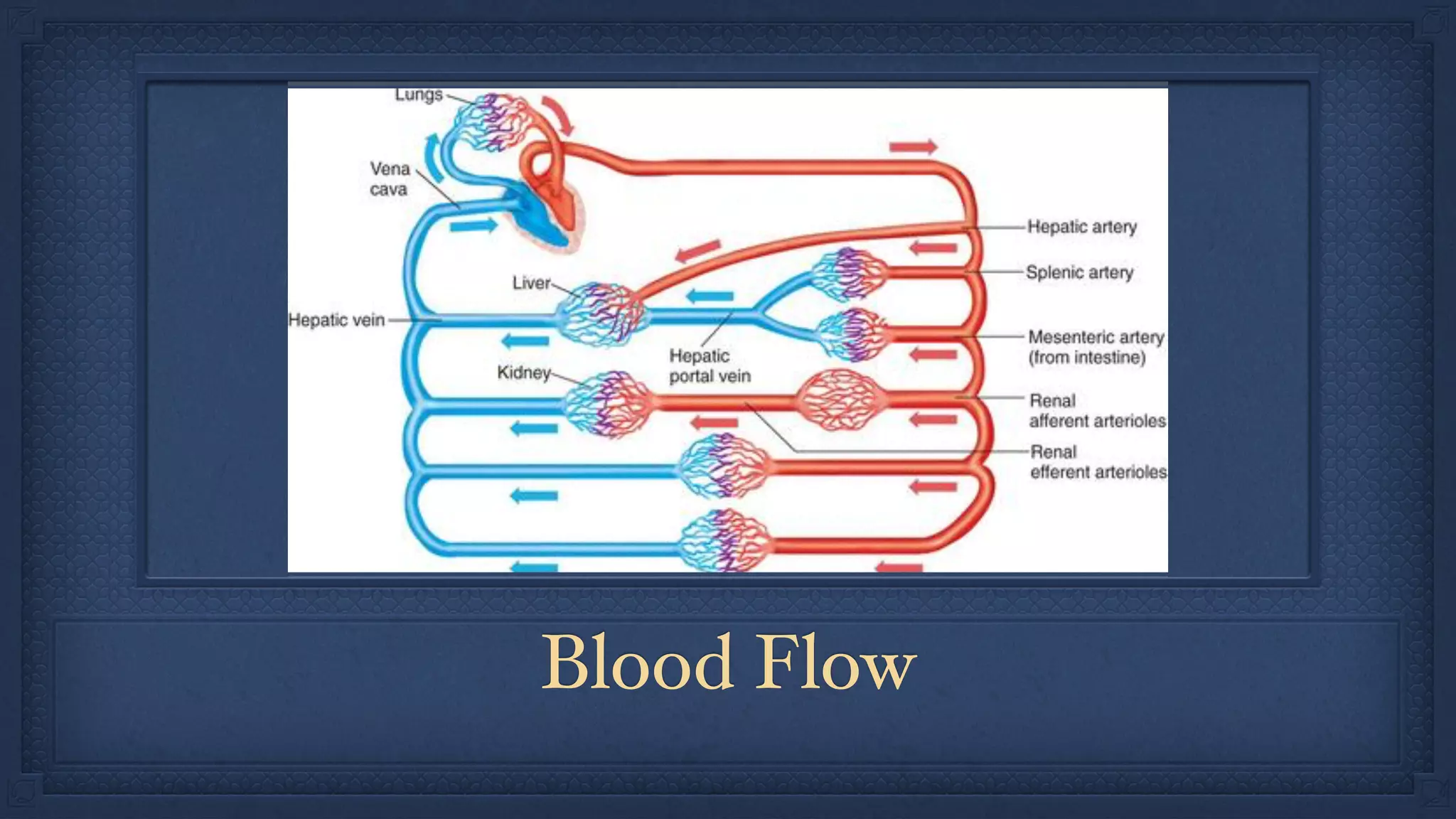
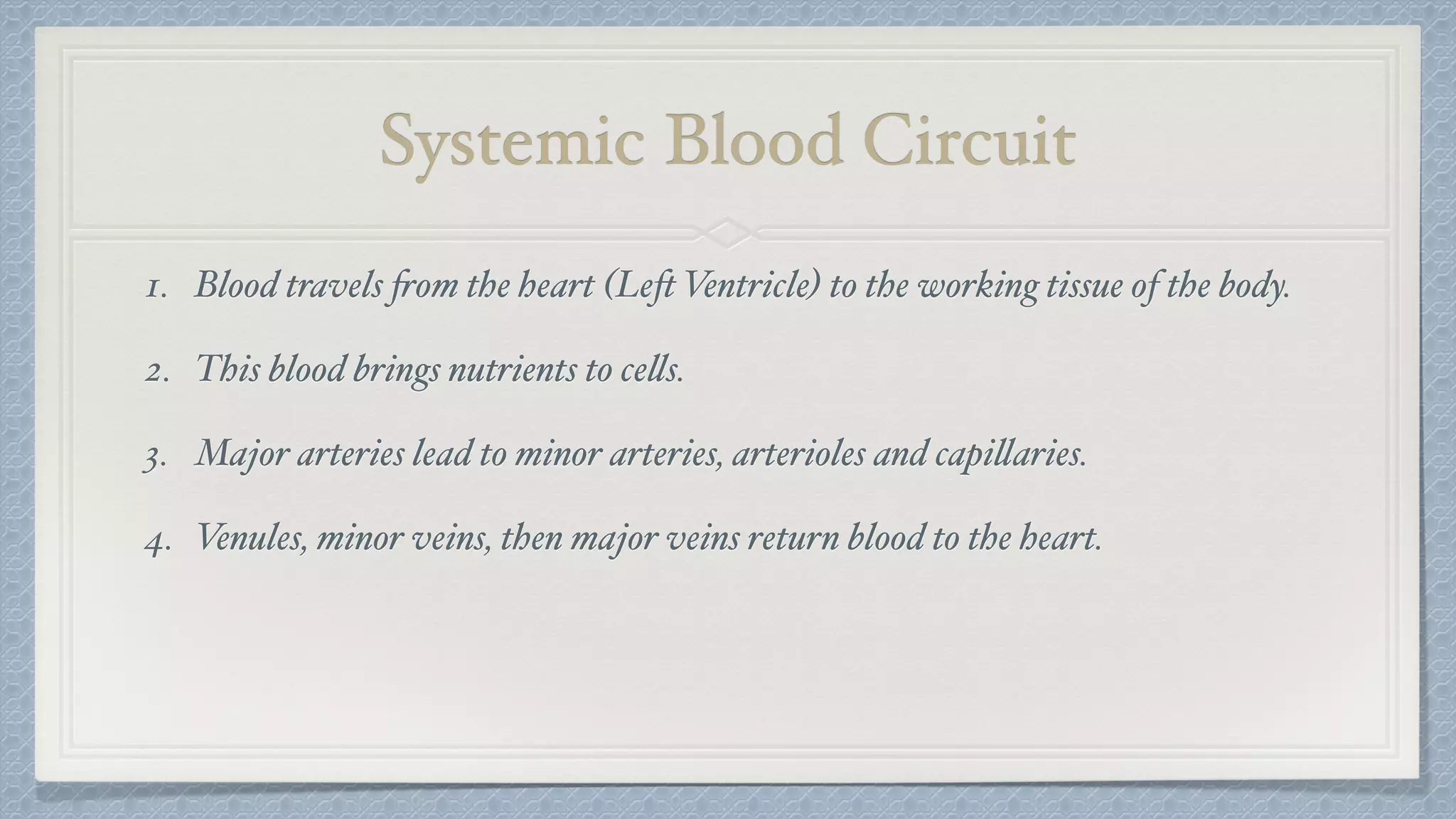
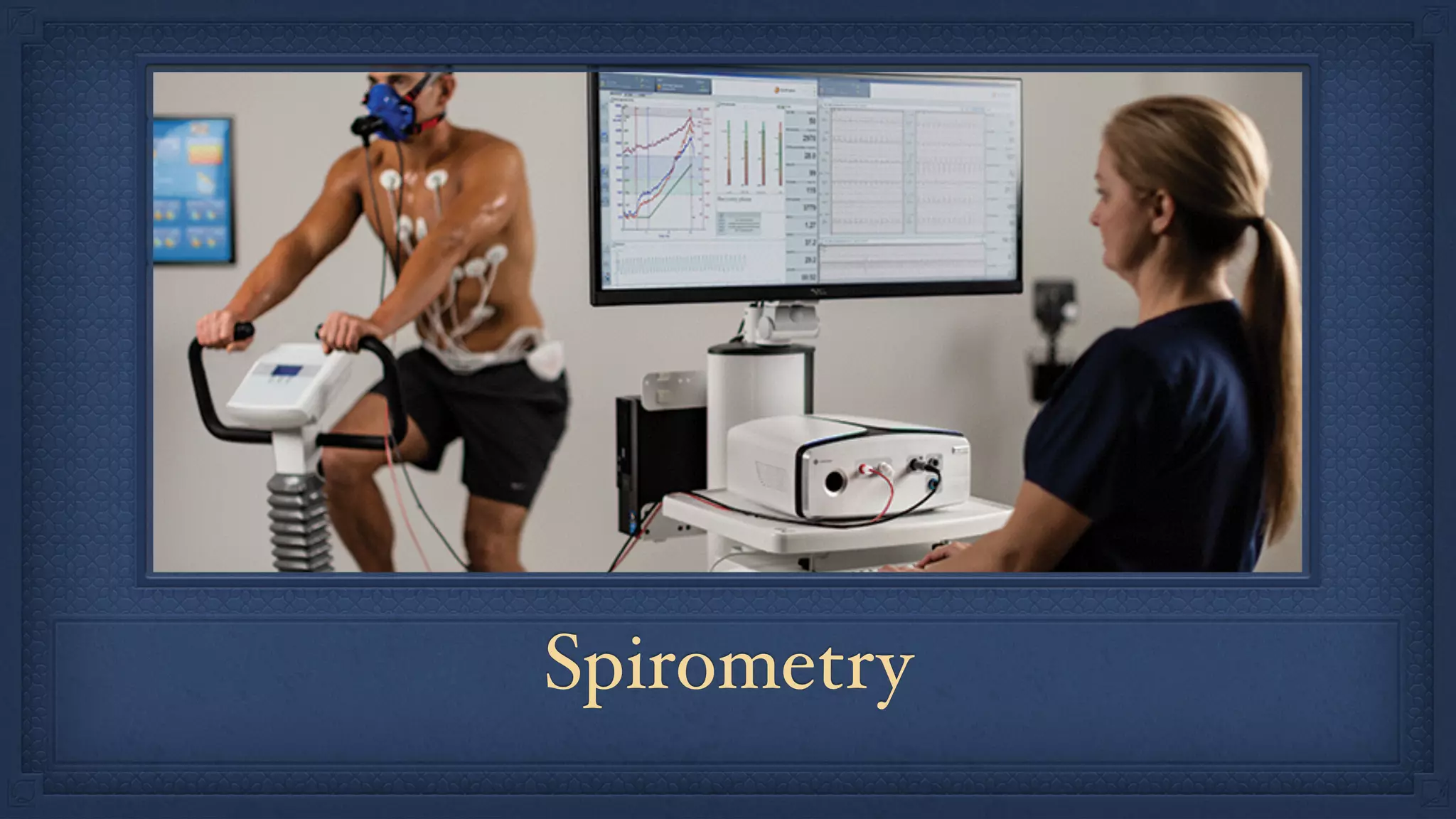
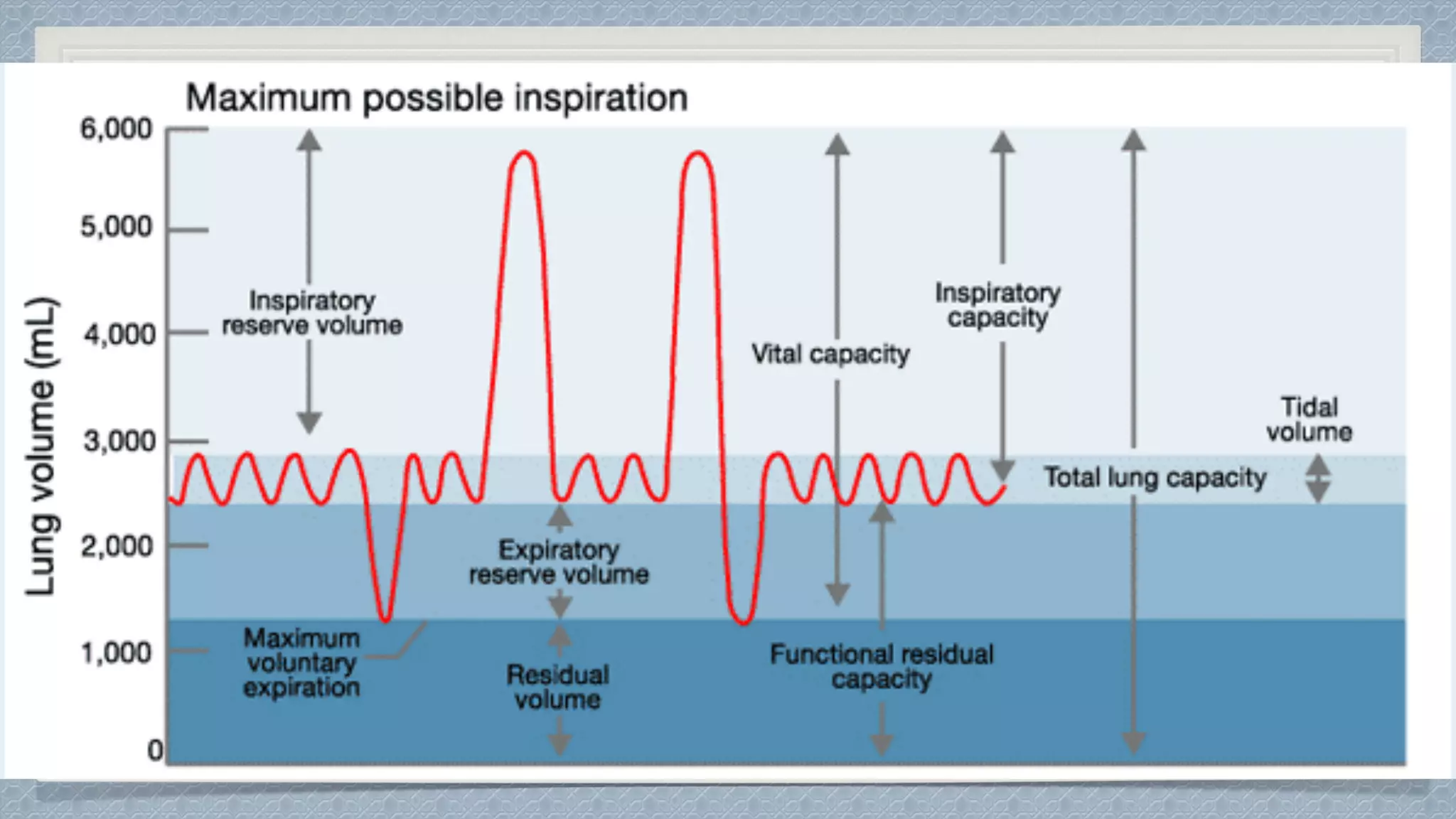
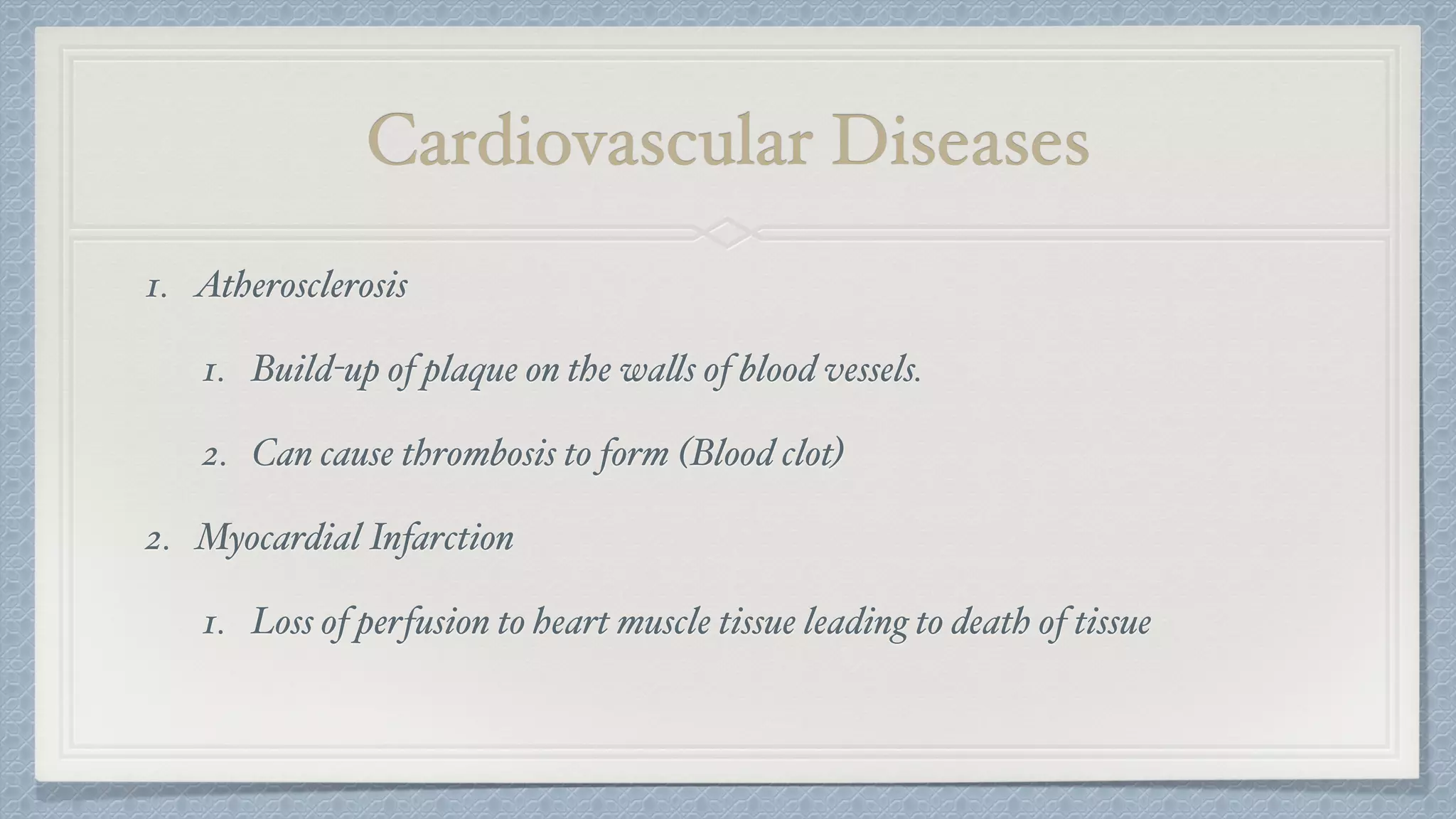
The circulatory and respiratory systems are closely linked. The circulatory system transports oxygen to tissues via blood flow and removes carbon dioxide through a dual circuit pathway. The respiratory system oxygenates blood in the lungs through gas exchange and is regulated to meet metabolic demands through controlled breathing. Diseases that impact these systems like COPD and heart attacks disrupt their functions and ability to effectively deliver oxygen and remove wastes.