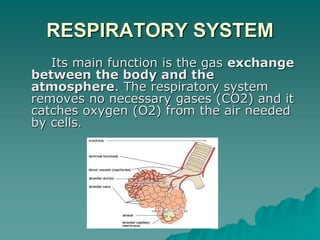
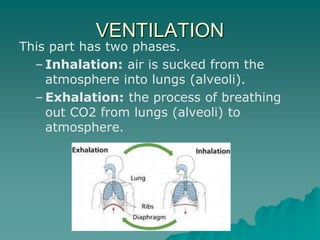
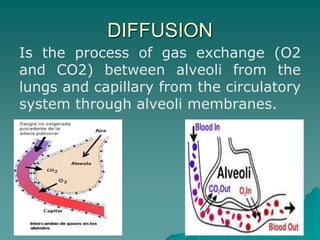
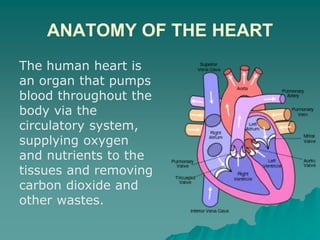
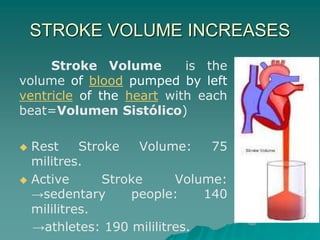
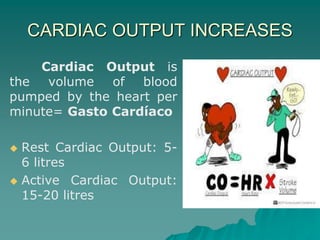
The document summarizes the cardiorespiratory system and its response to exercise in 3 parts. The respiratory system is responsible for gas exchange and increases ventilation during exercise. The cardiovascular system transports oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removes waste; it responds to exercise by increasing heart rate, stroke volume, and cardiac output to deliver more oxygen to active muscles. Regular exercise can increase lung capacity and lower resting heart rate over time.