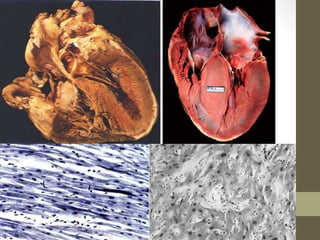
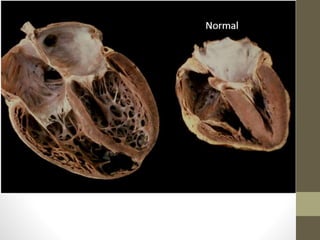
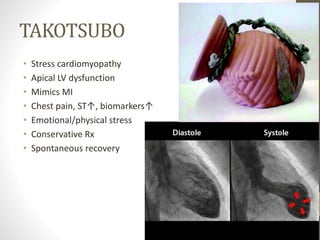
This document provides an overview of different types of cardiomyopathy including hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), restrictive cardiomyopathy (RCM), and arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (ARVD). It describes the pathology, diagnosis, and management of each type. HCM is characterized by unexplained left ventricular hypertrophy. DCM involves dilated chambers and systolic dysfunction. RCM causes increased myocardial stiffness. ARVD primarily affects the right ventricle with replacement by fibrofatty tissue. The document also briefly discusses left ventricular non-compaction and Takotsubo cardiomyopathy.