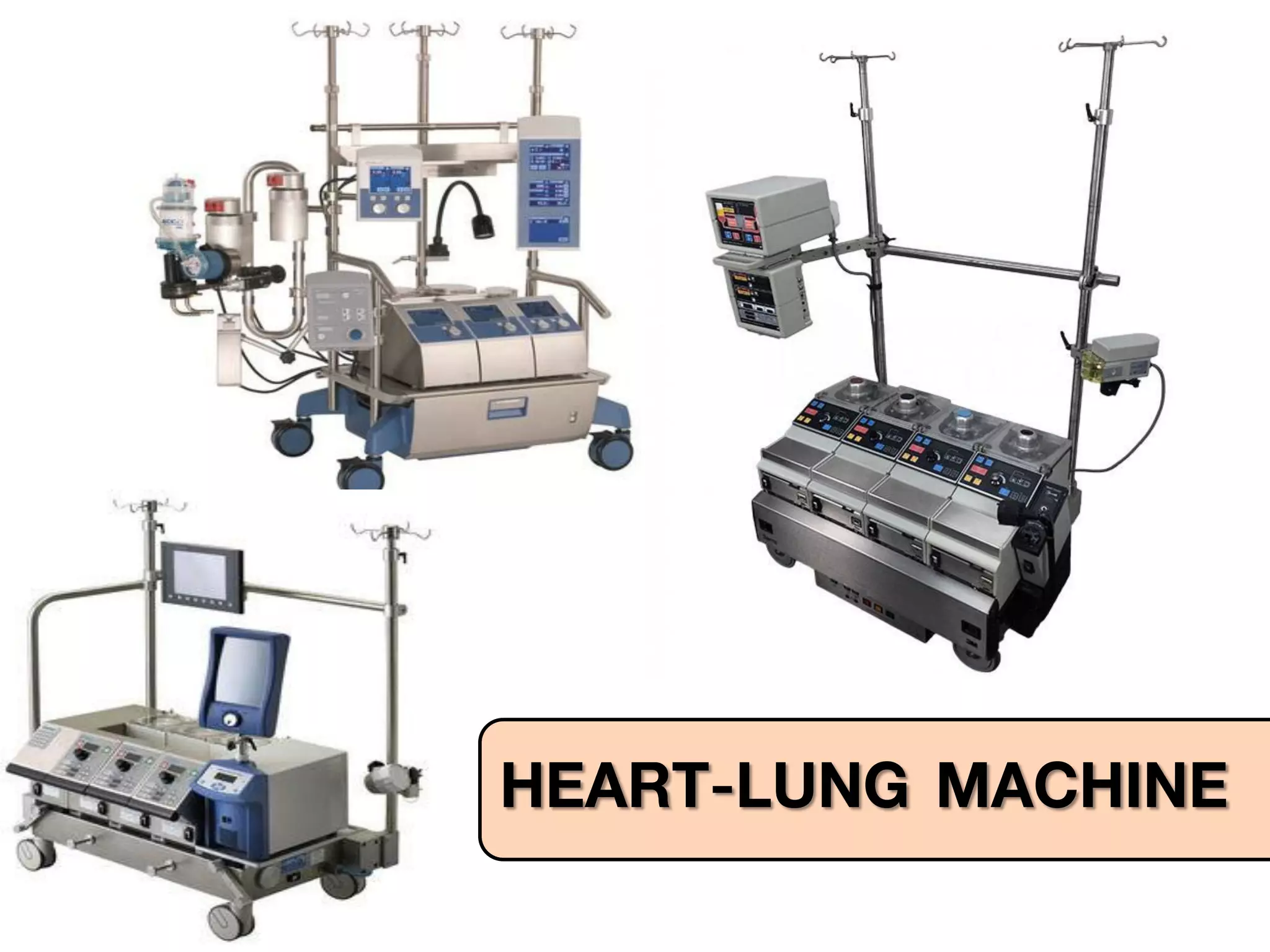
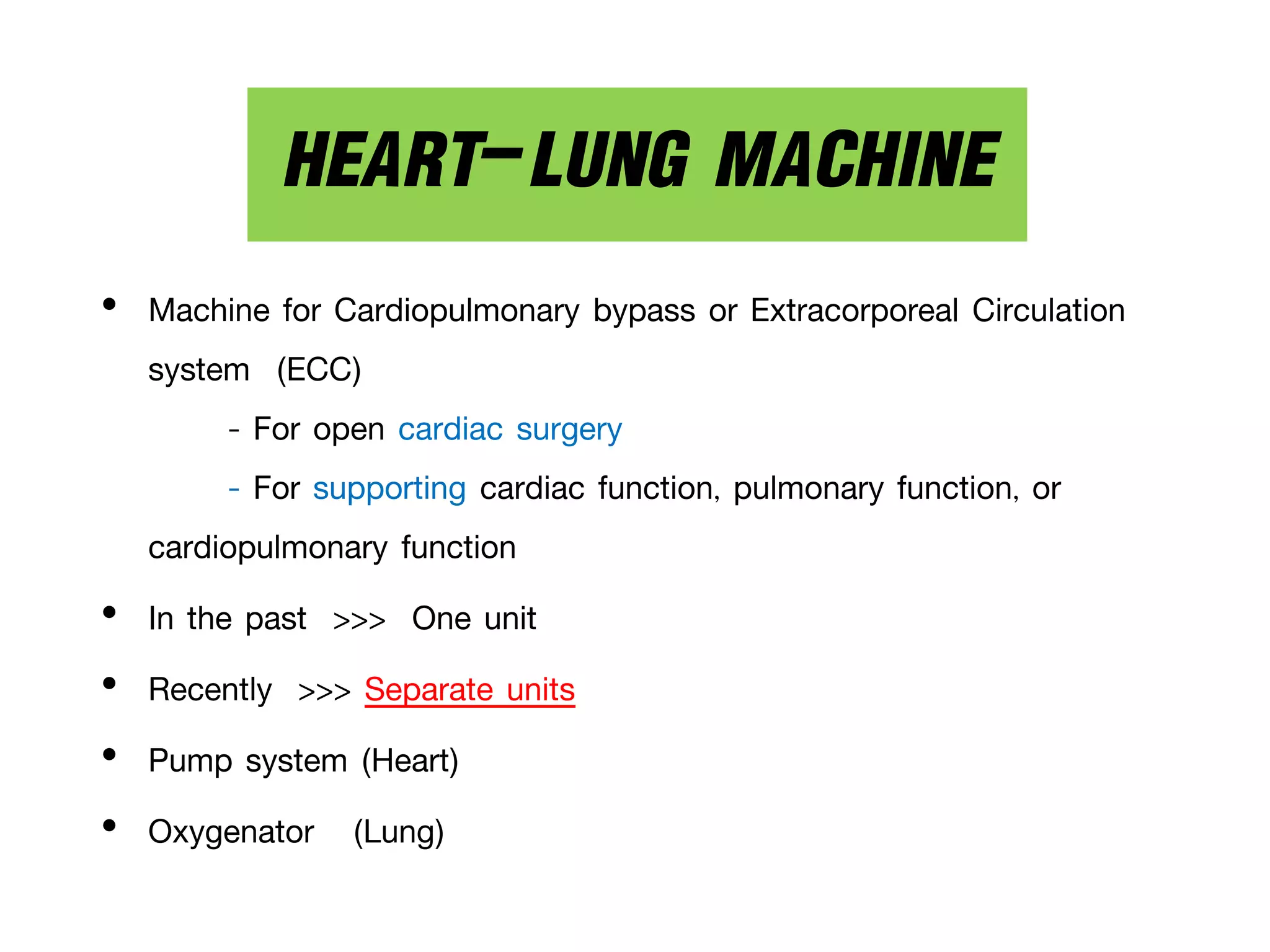
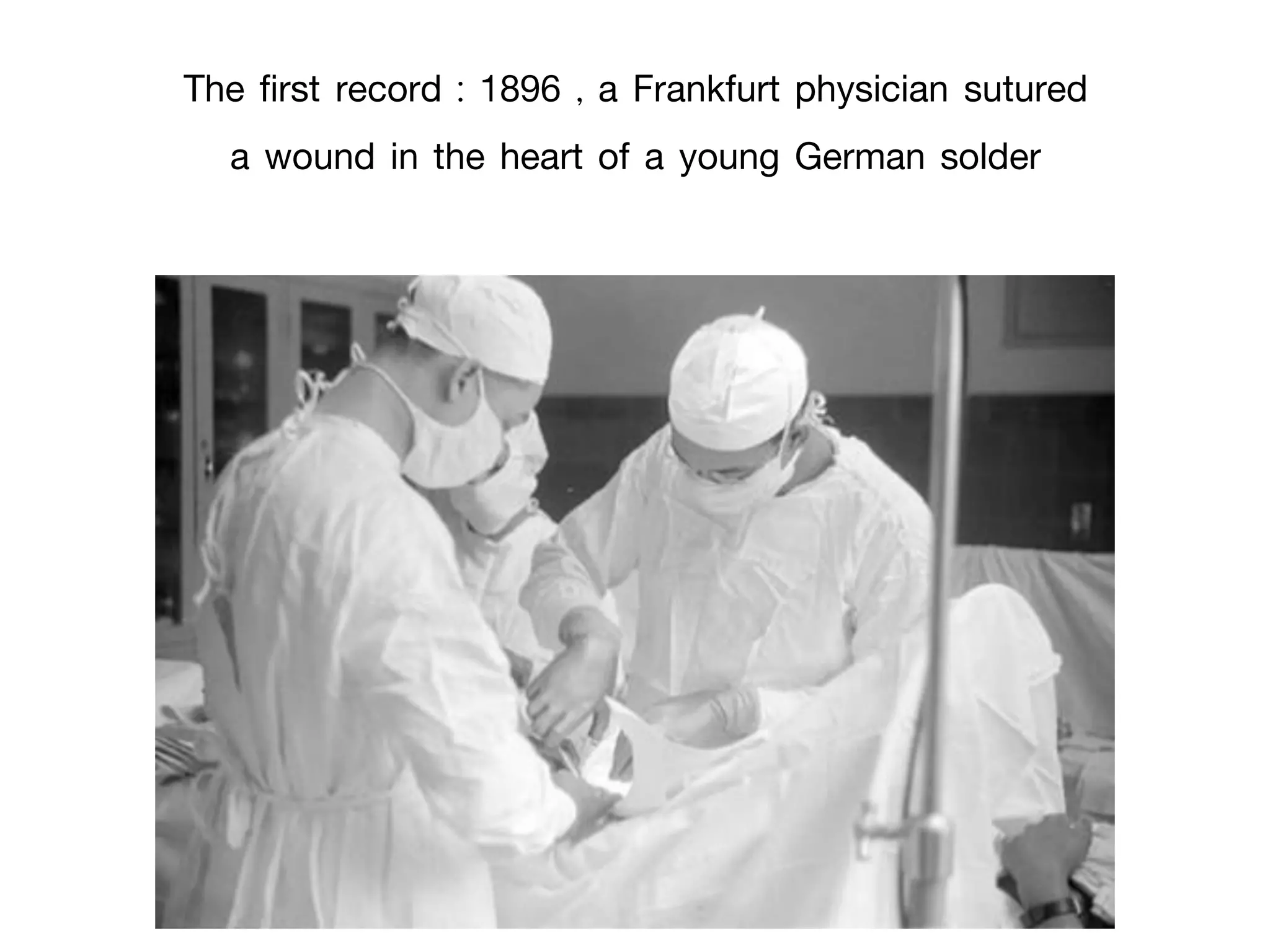
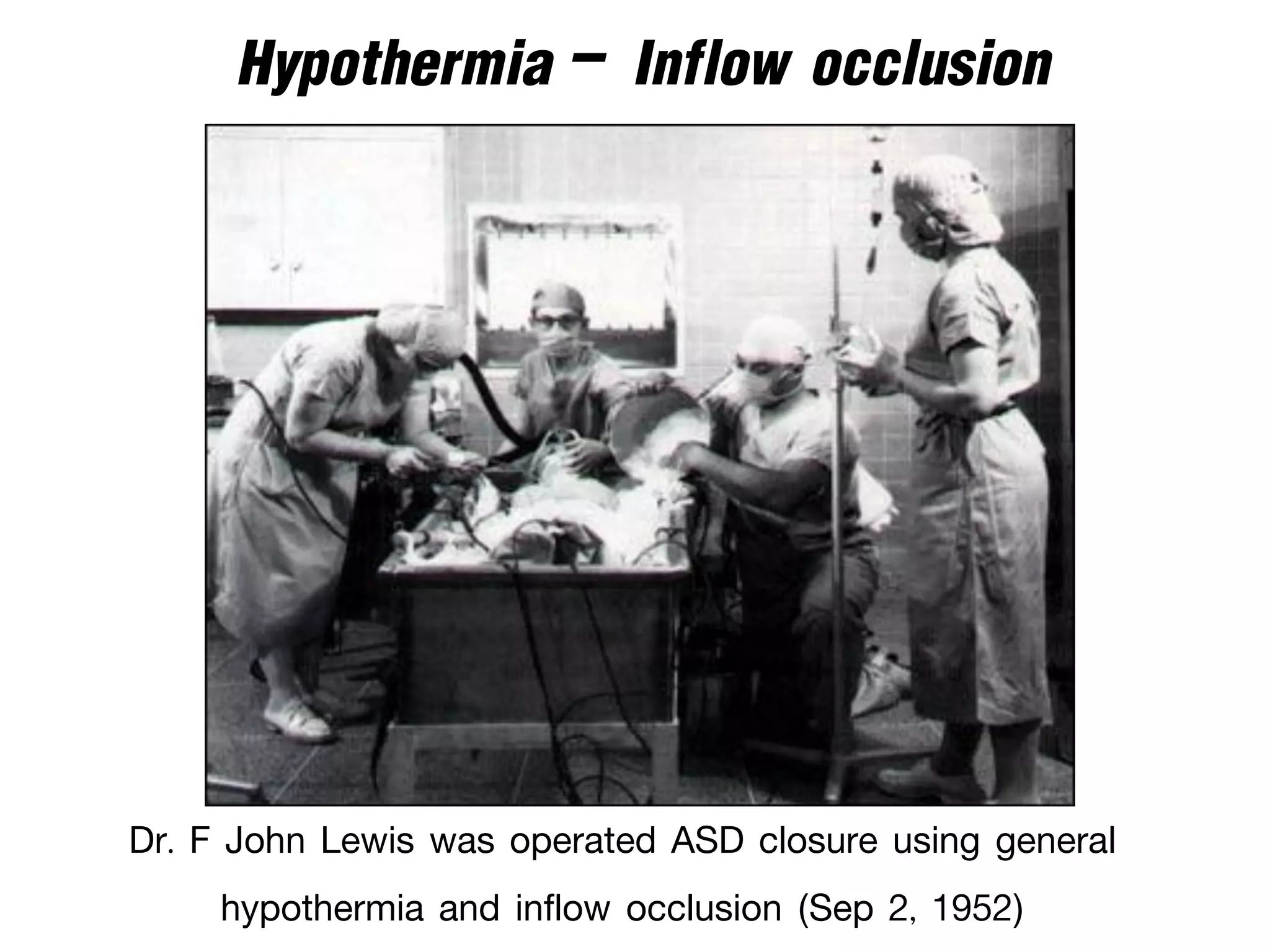
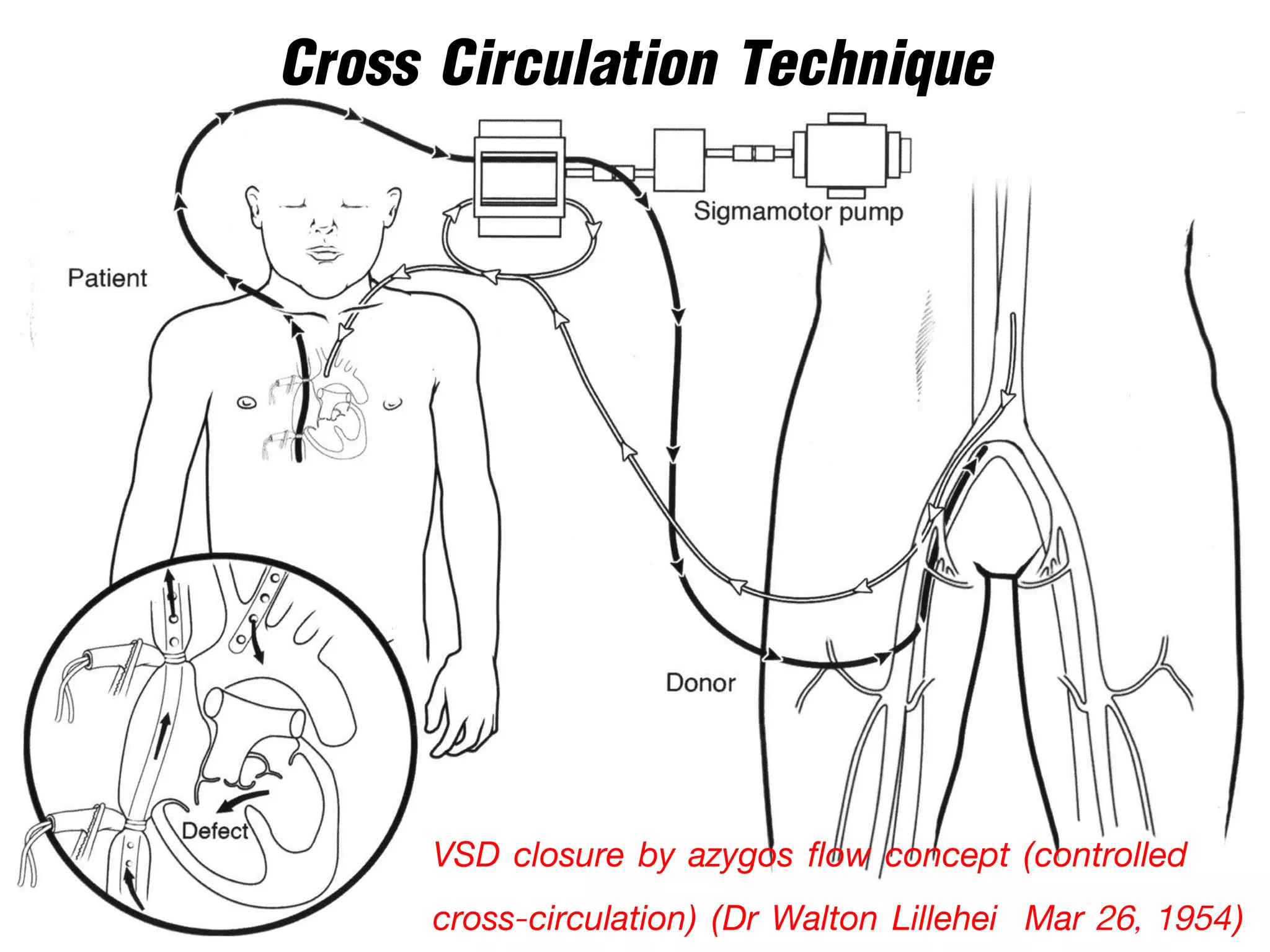
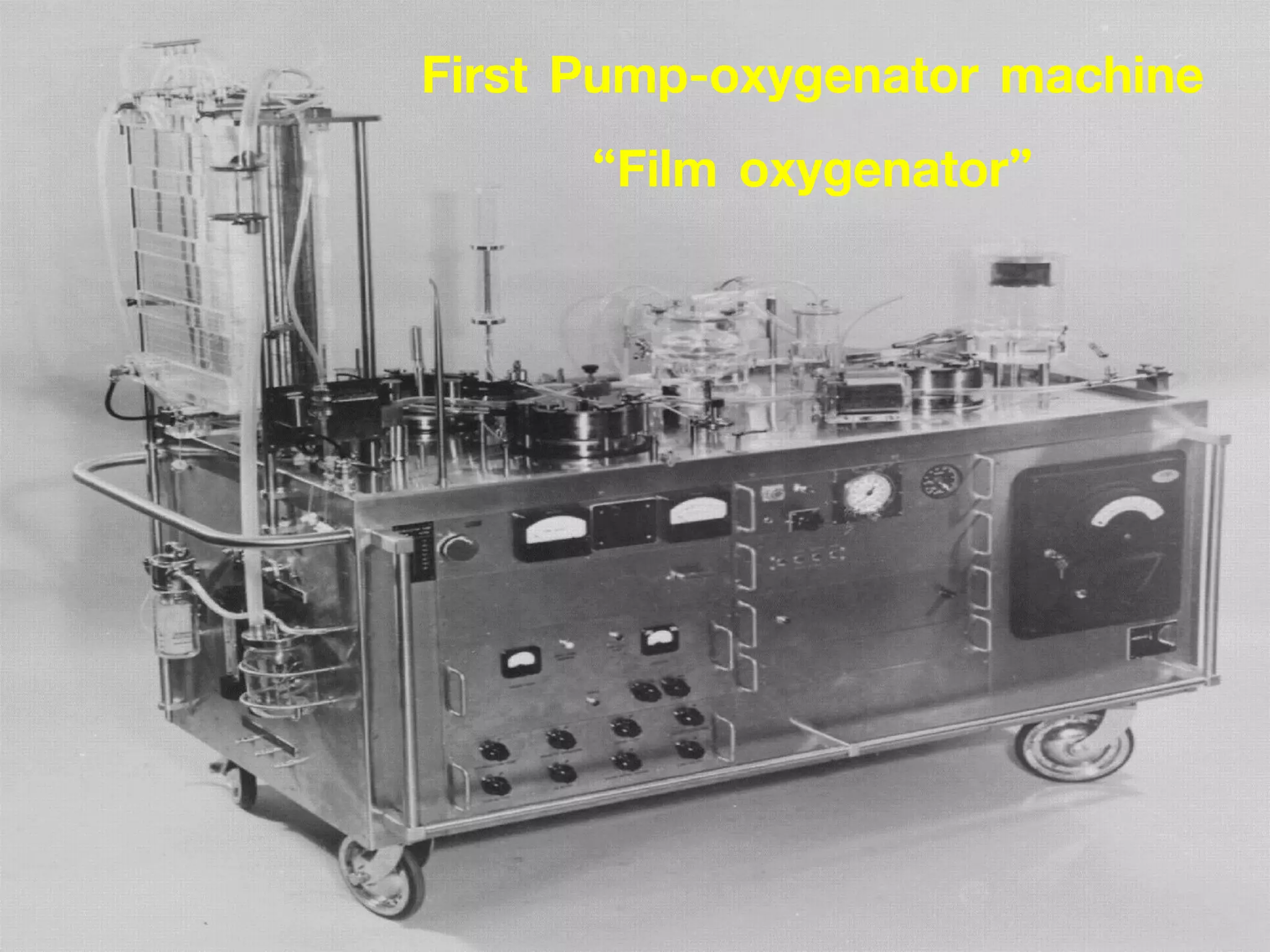
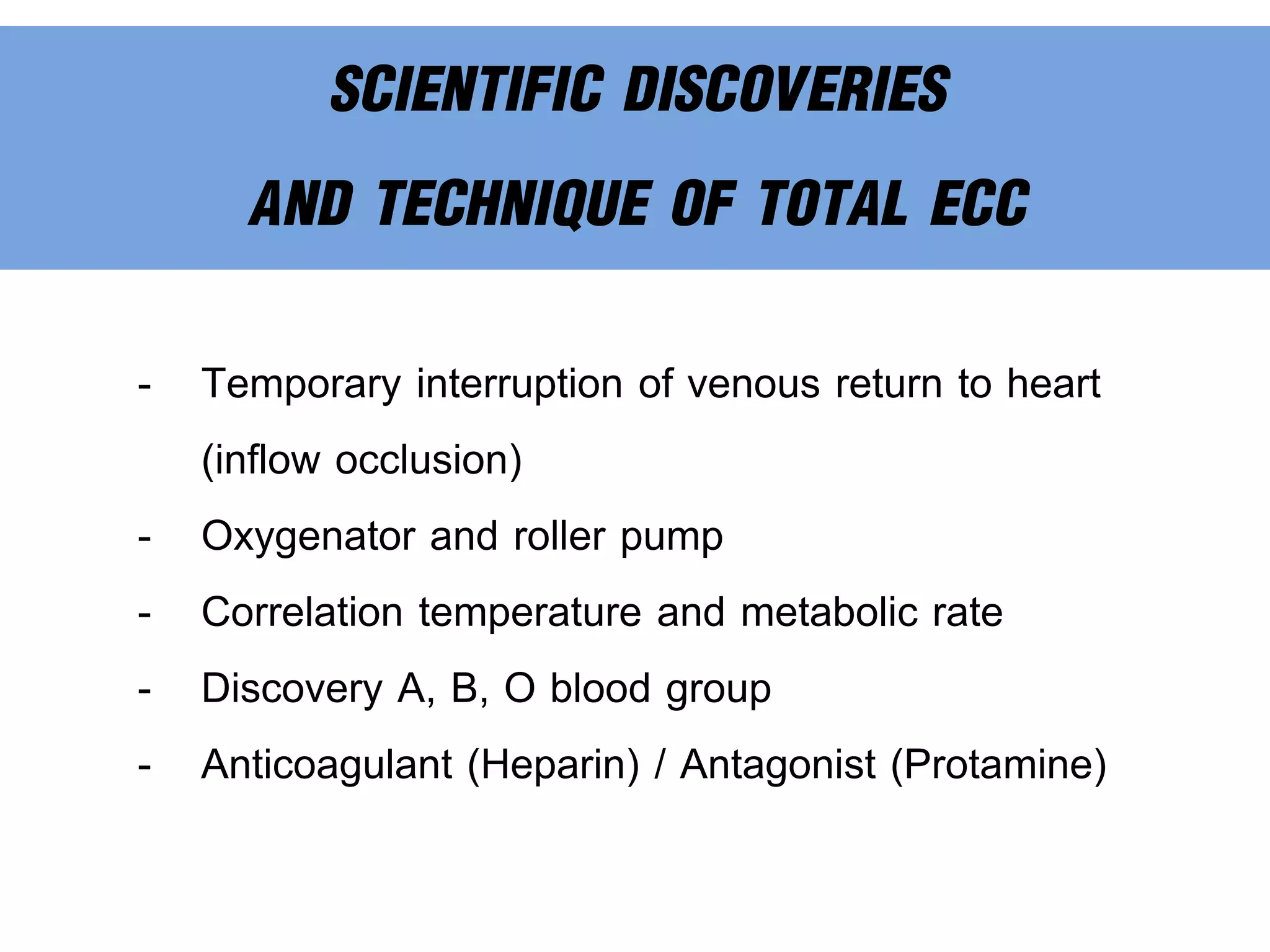
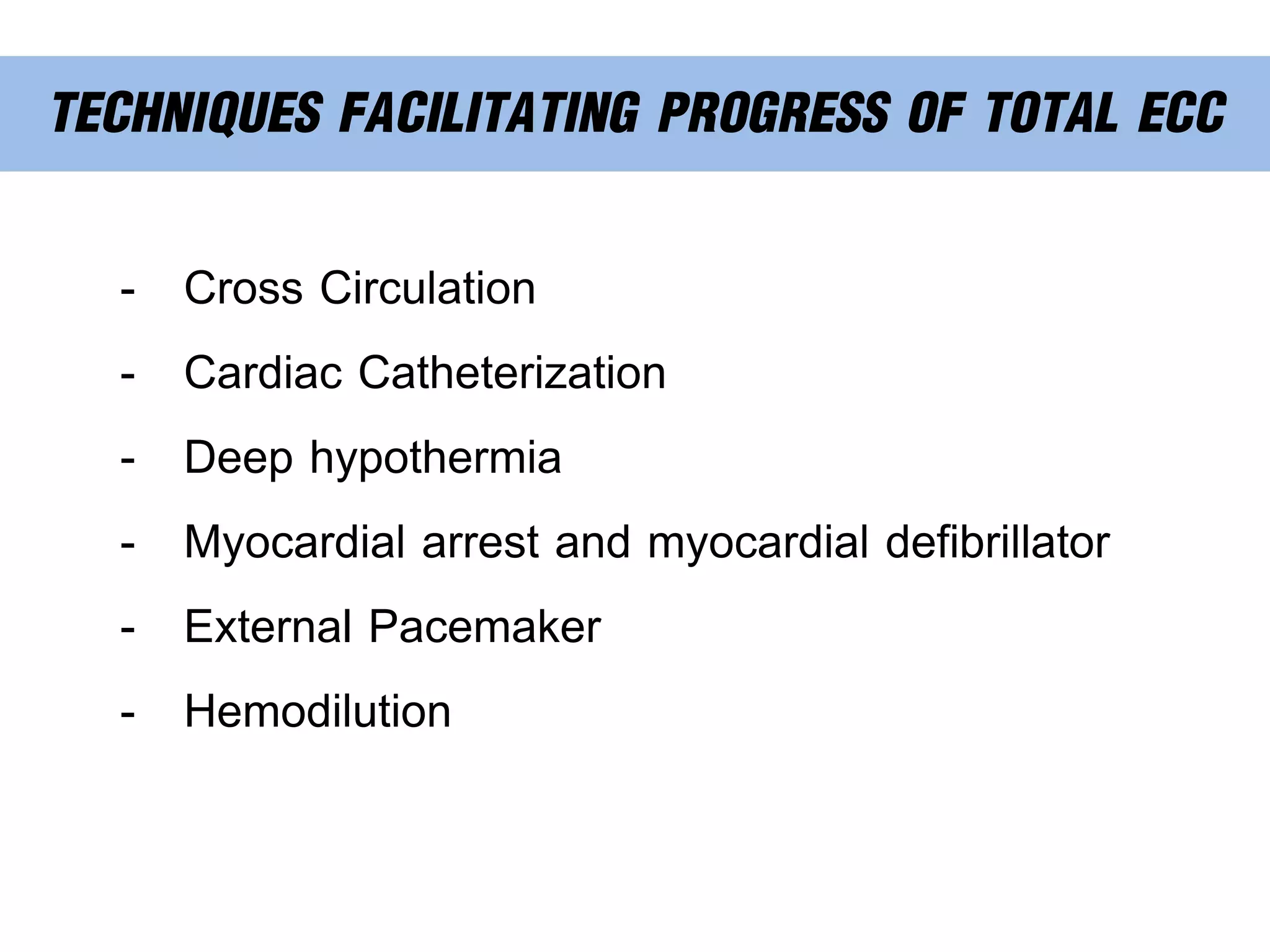
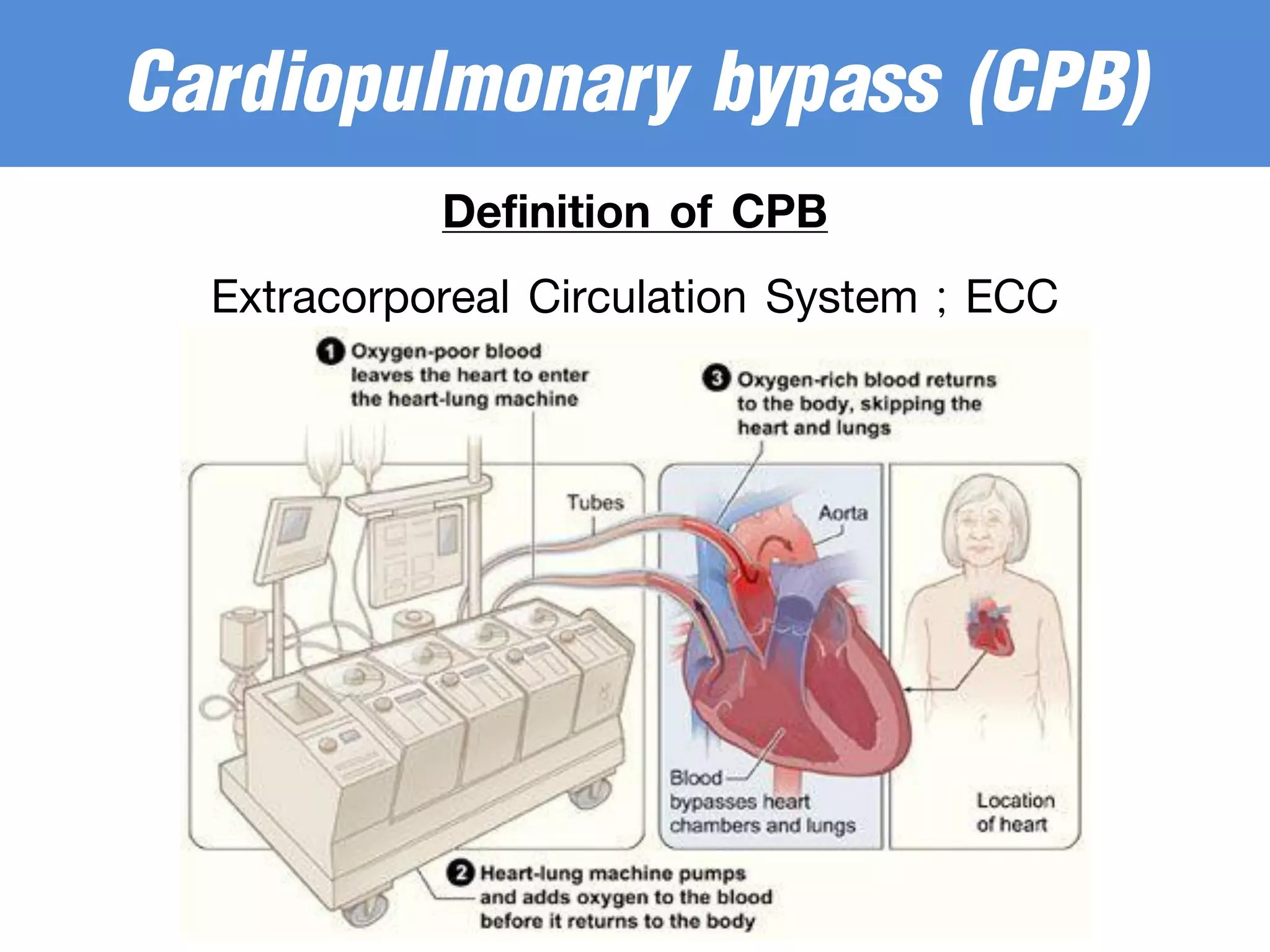
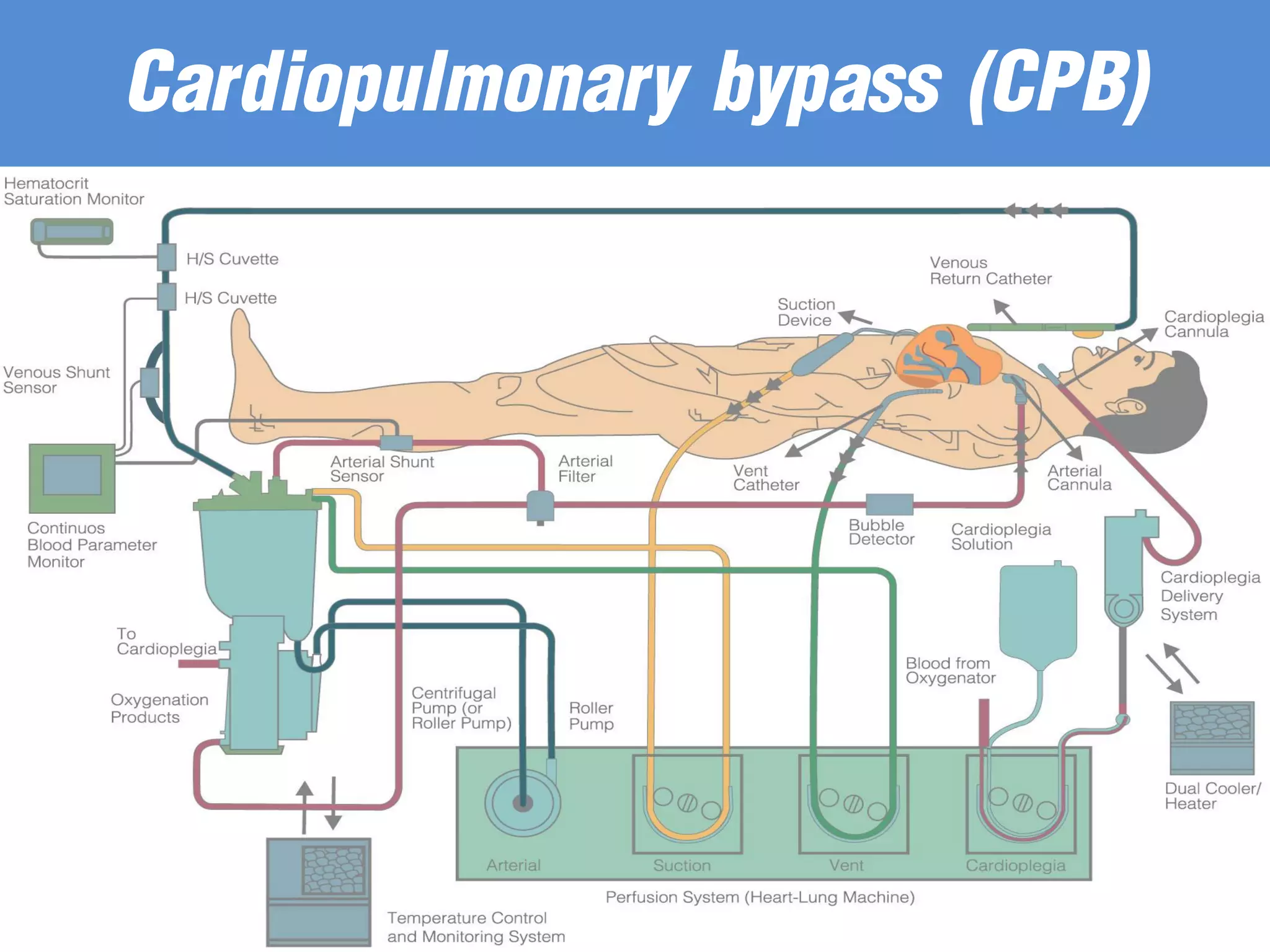
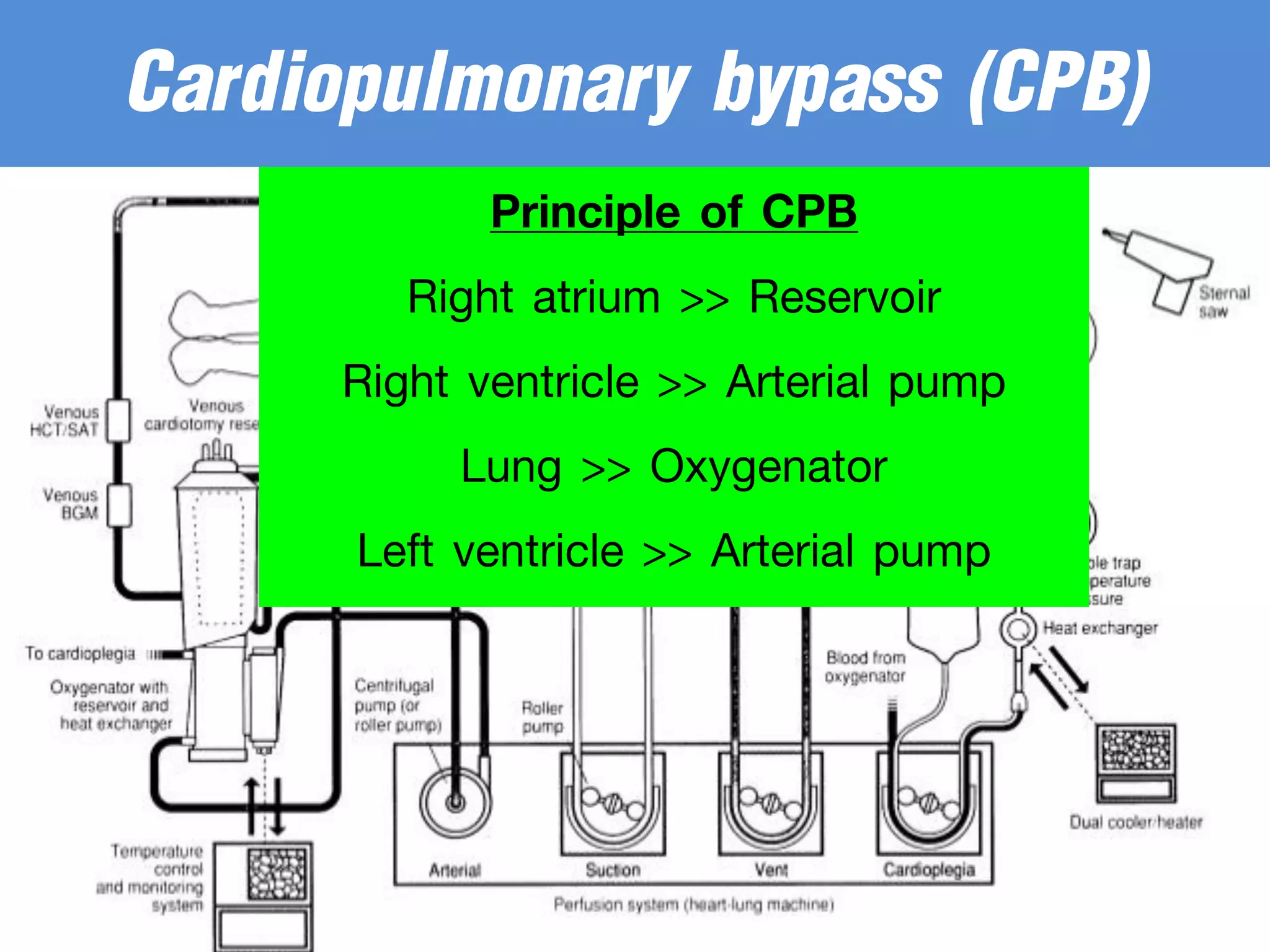
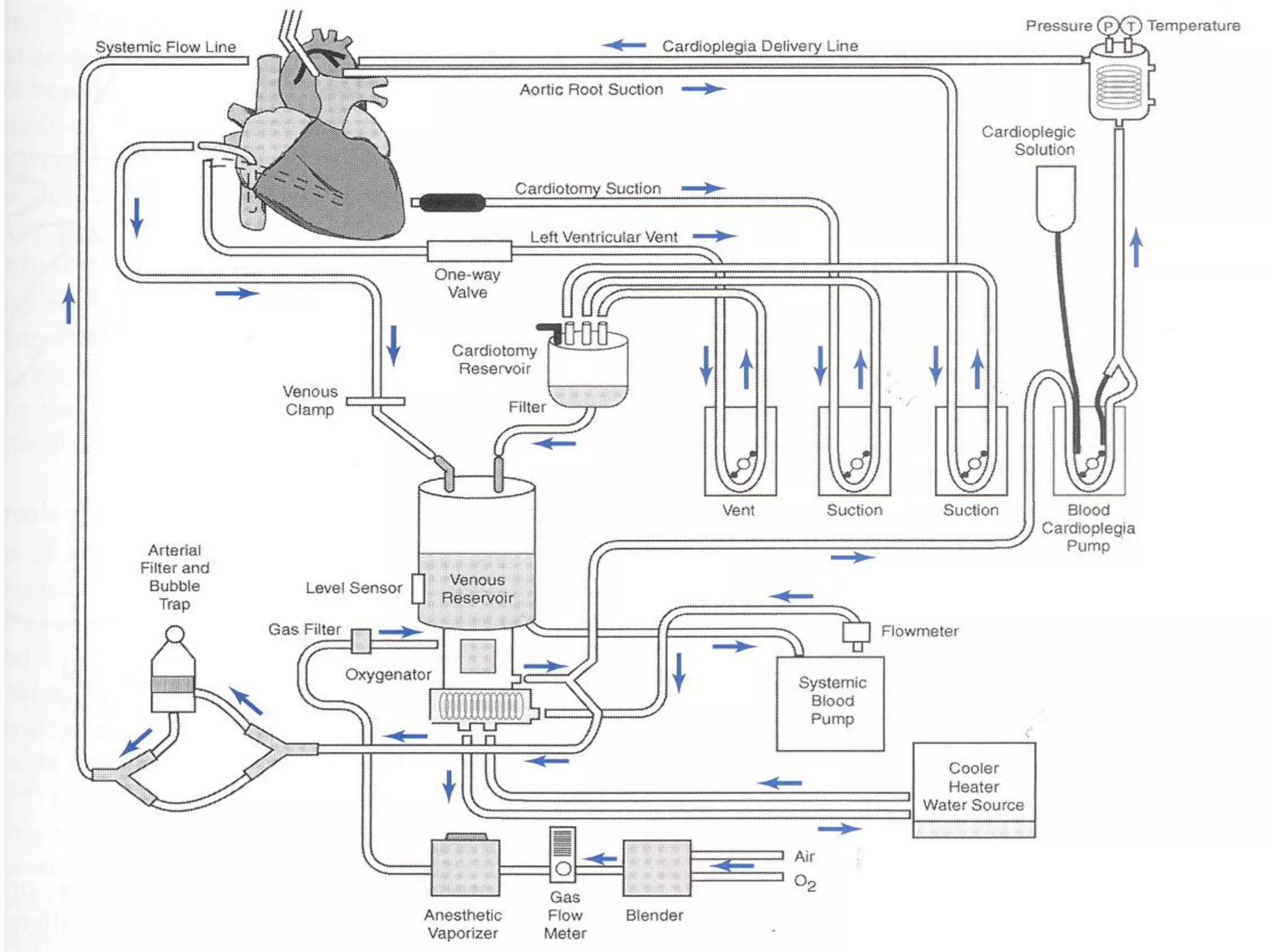
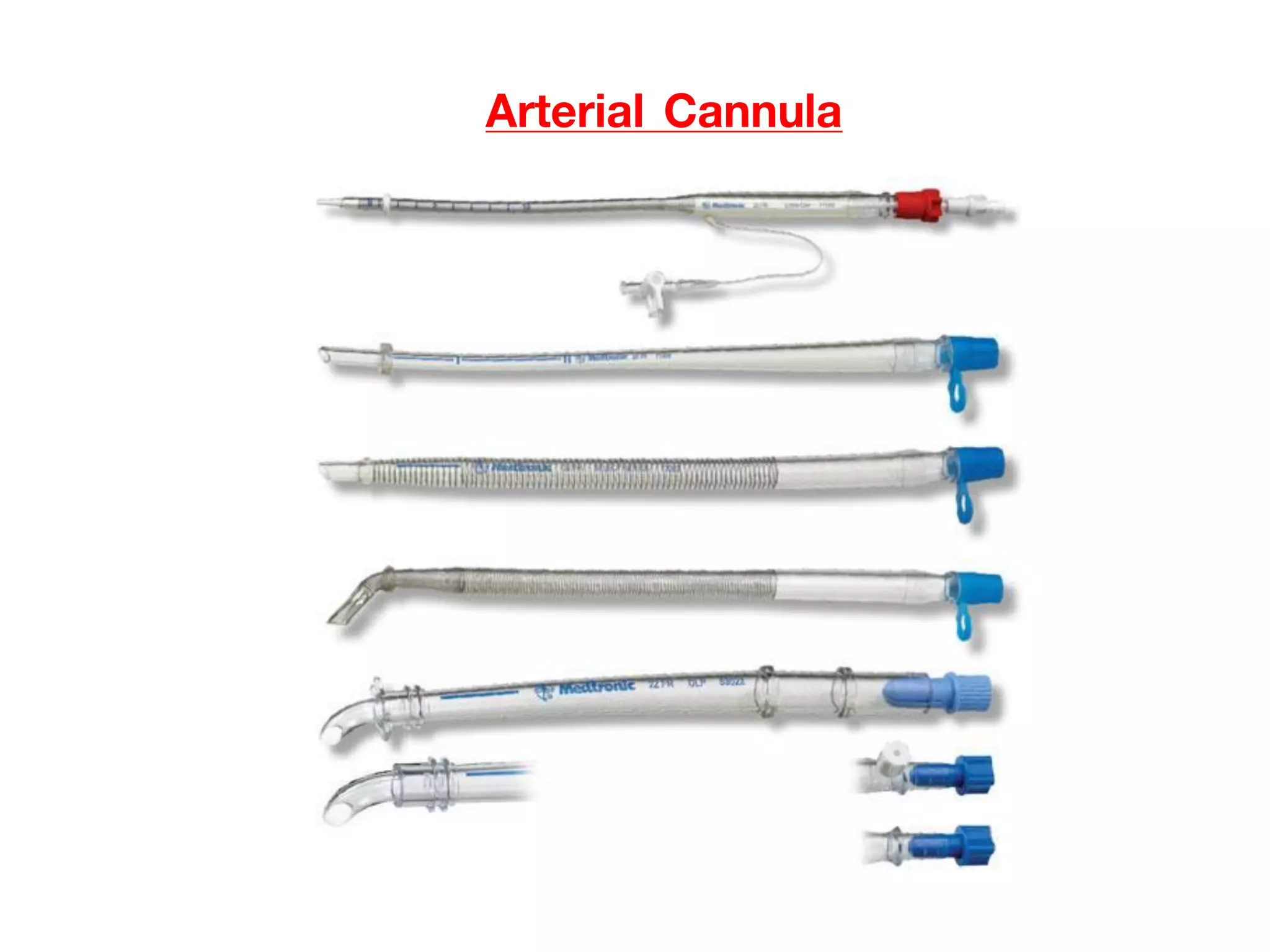
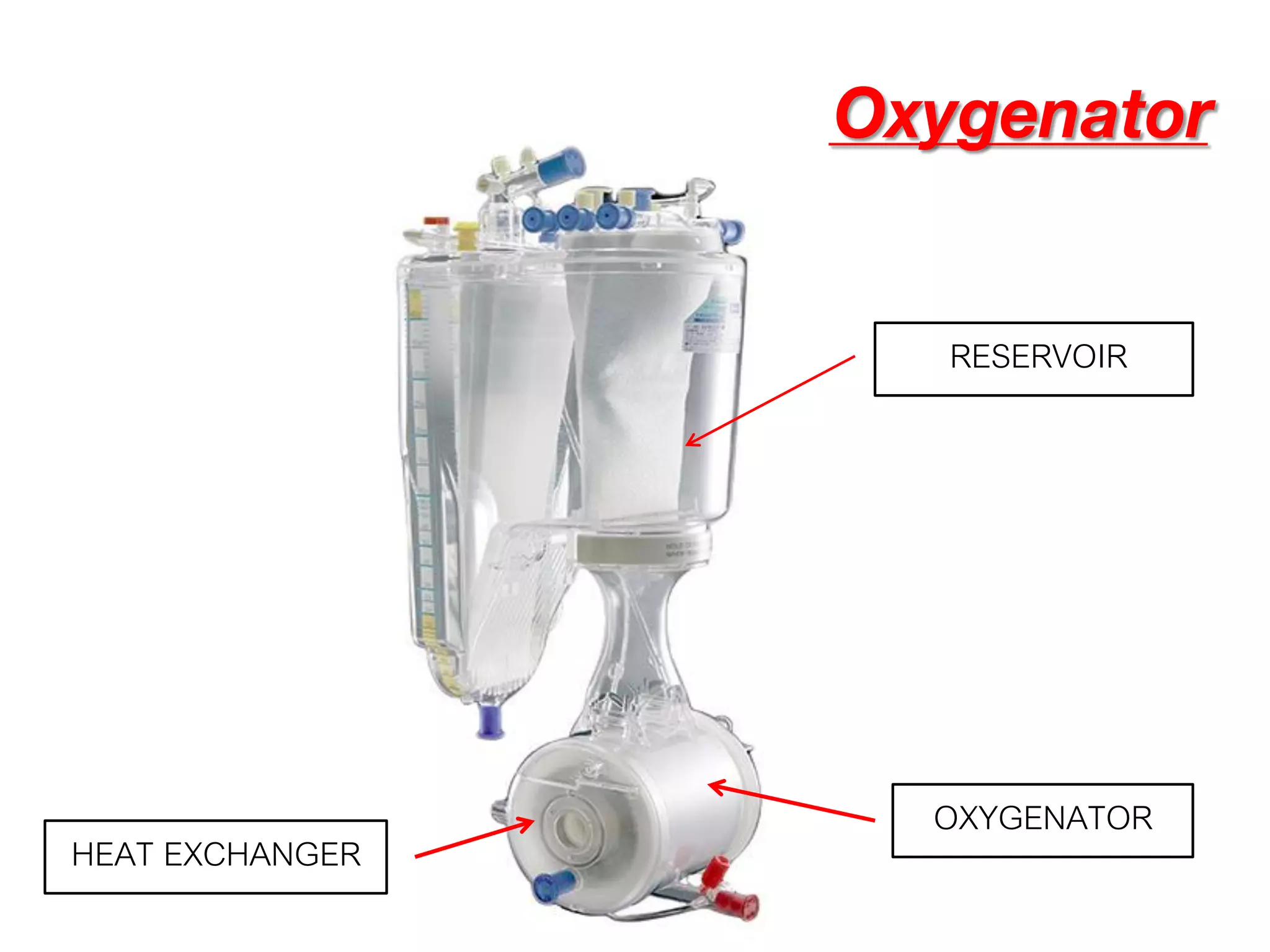
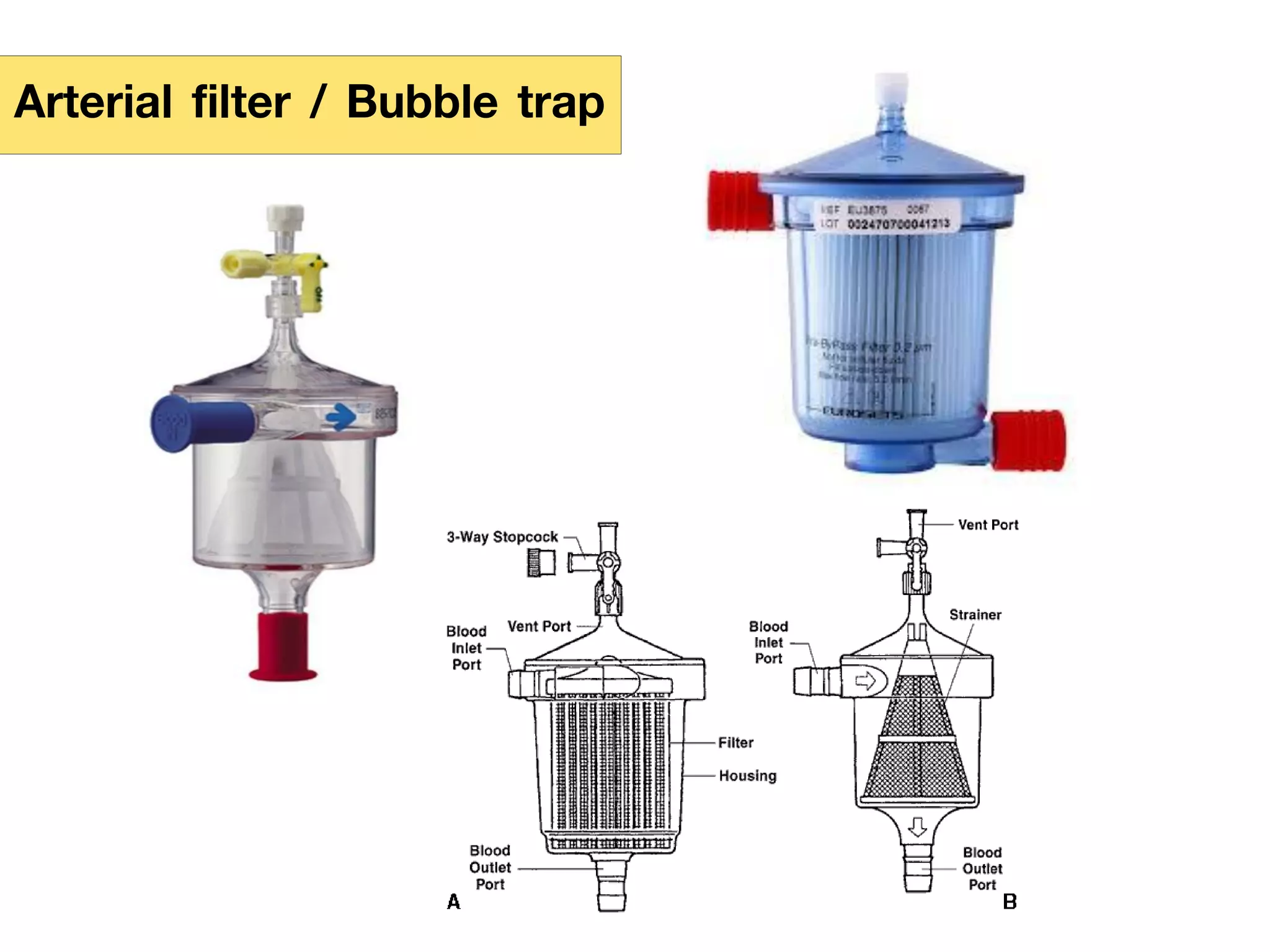
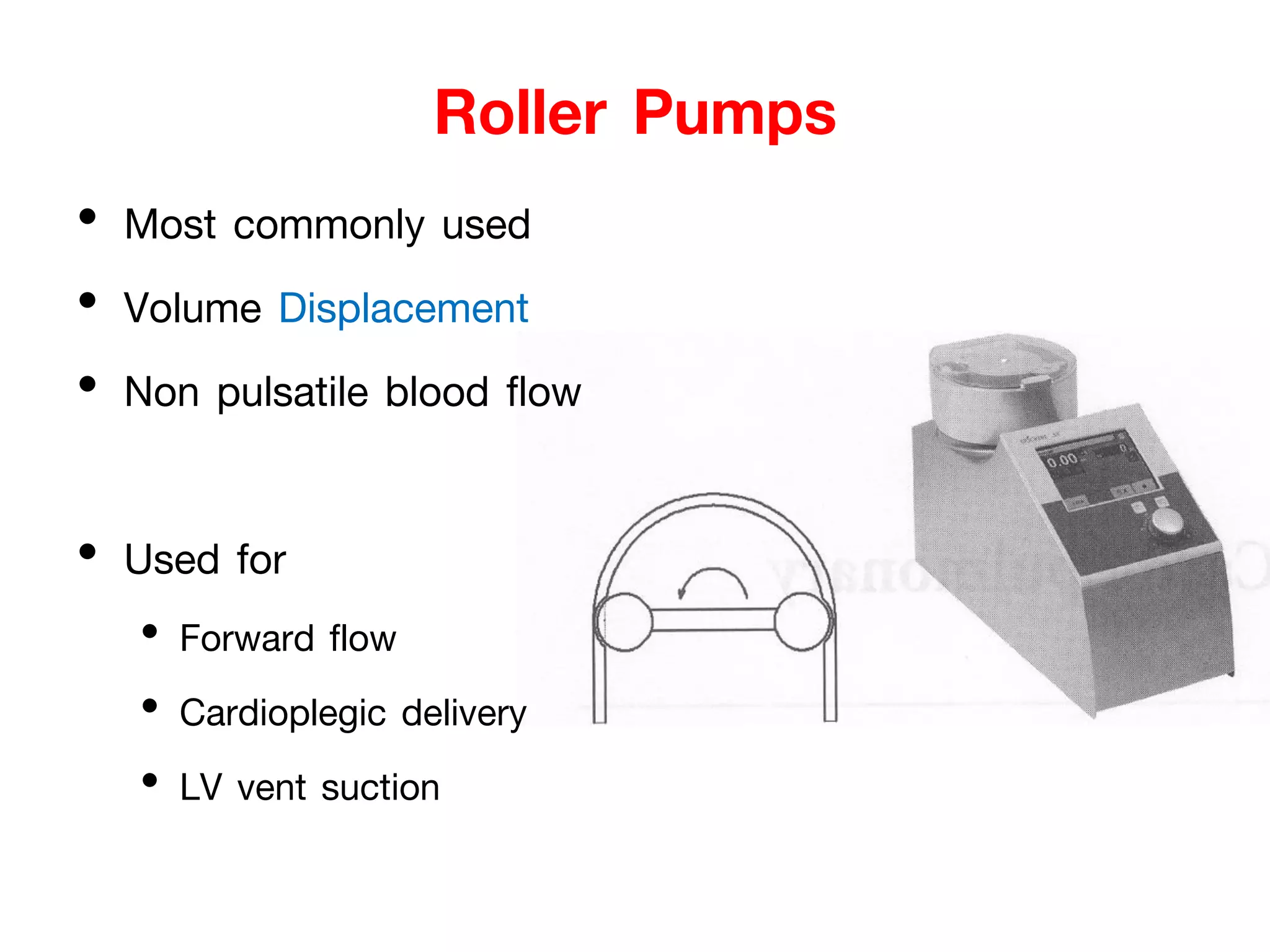
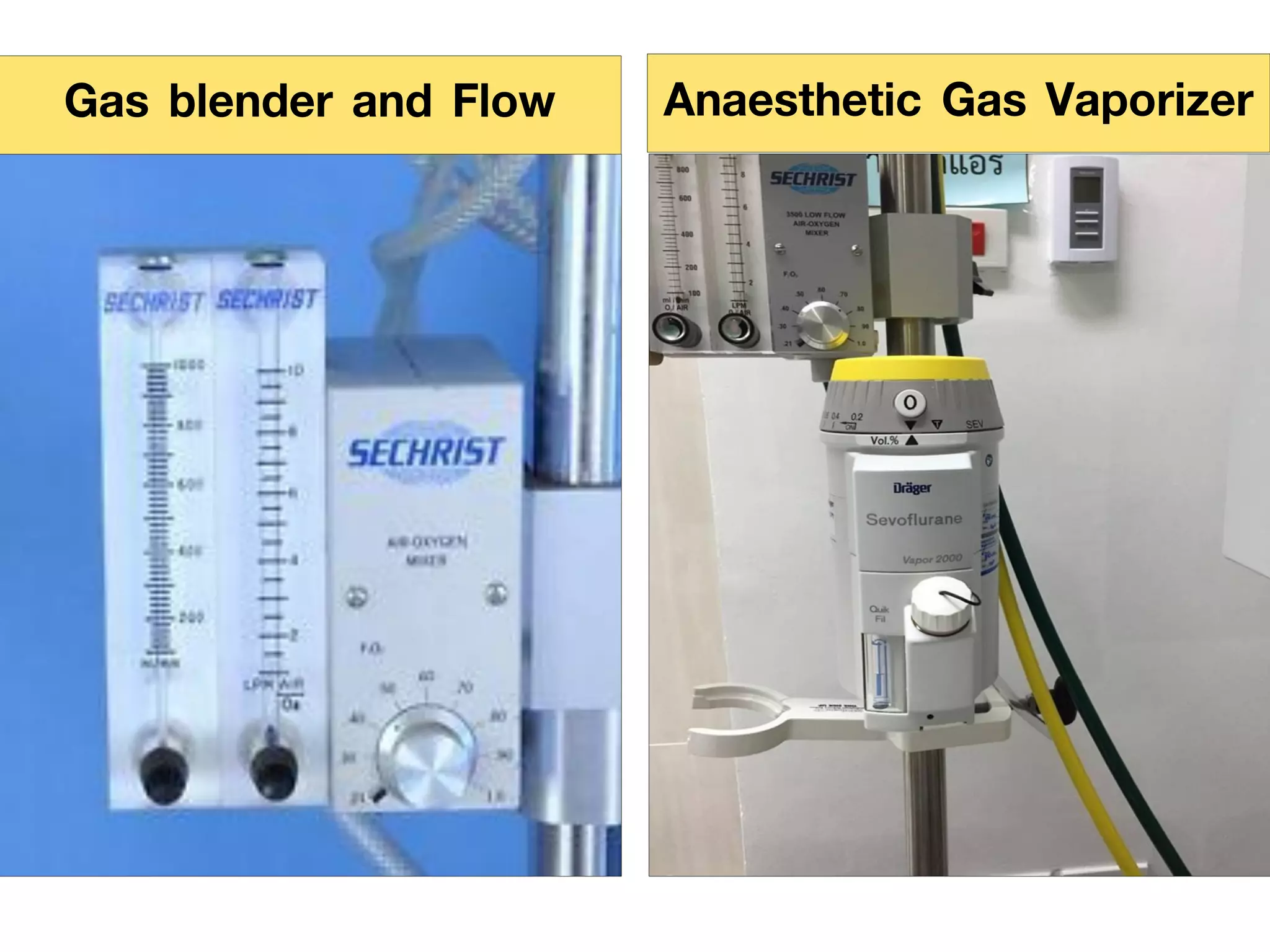
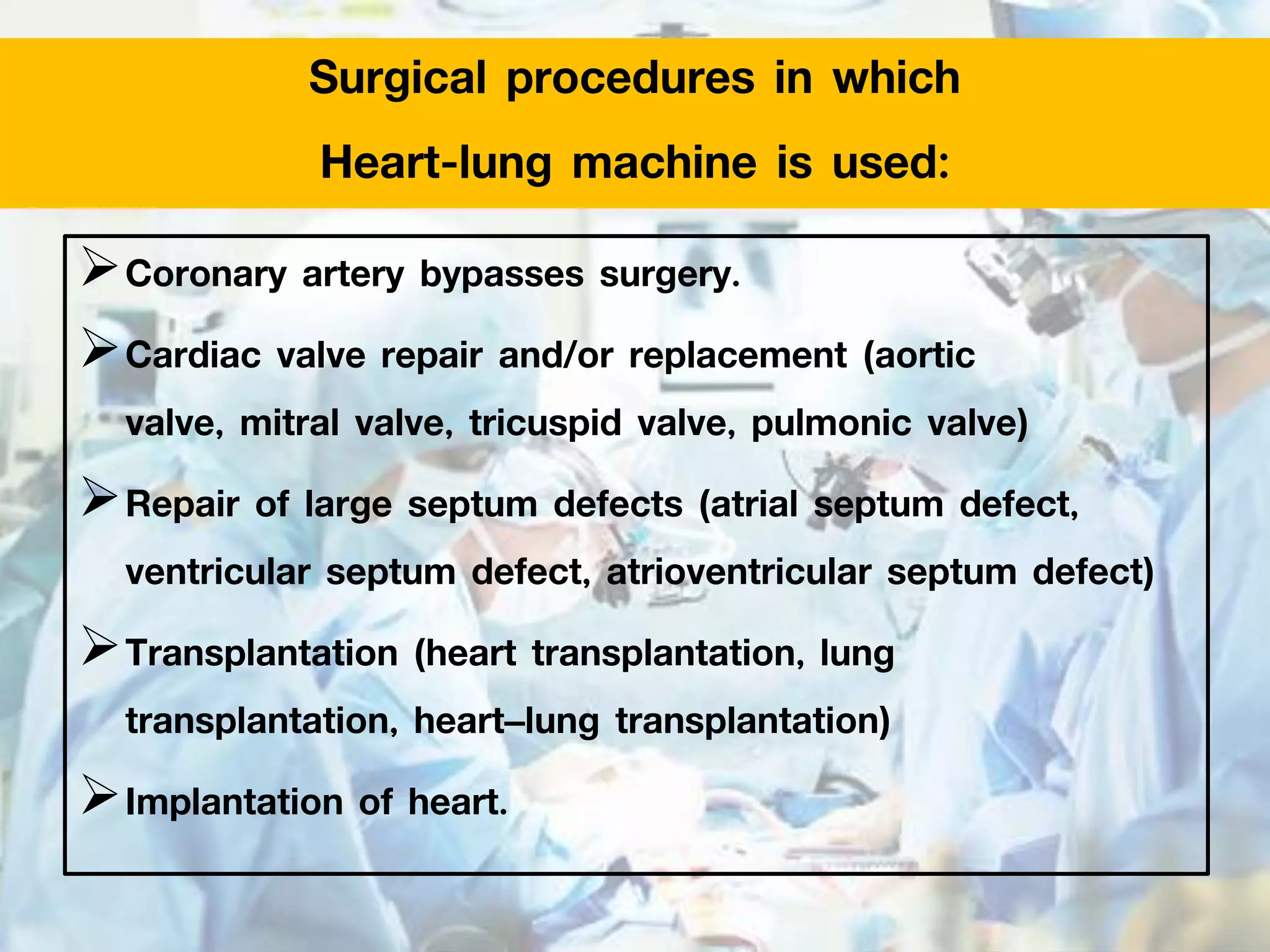
The document discusses the heart-lung machine, a vital component in cardiac surgery for cardiopulmonary bypass, which supports heart and lung function during procedures. It outlines its historical development, key components, such as oxygenators and pumps, and the objectives of using the machine, including maintaining blood flow and protecting the myocardium during surgery. Additionally, it addresses potential complications and the various surgical procedures where the heart-lung machine is utilized.