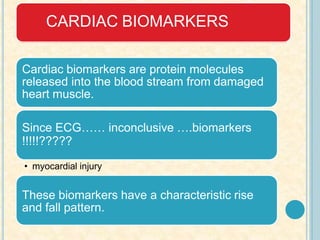
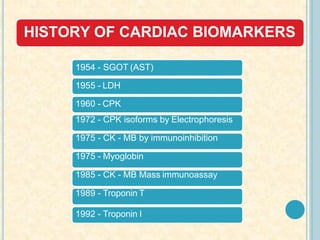
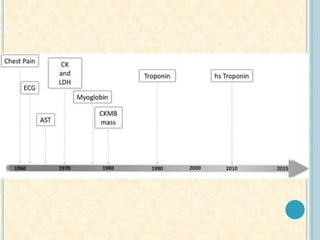
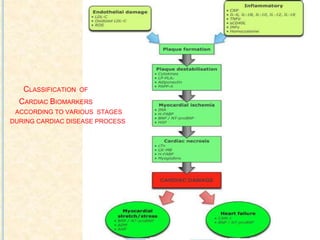
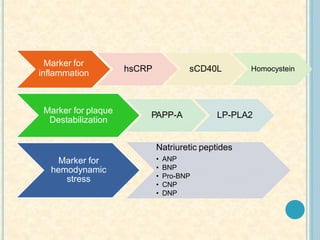
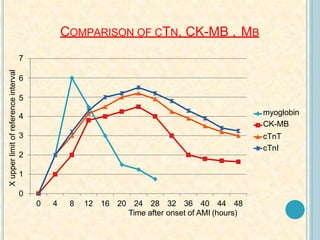
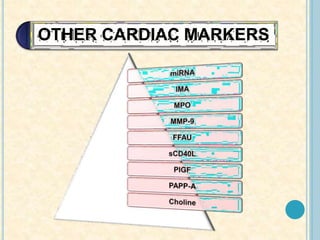
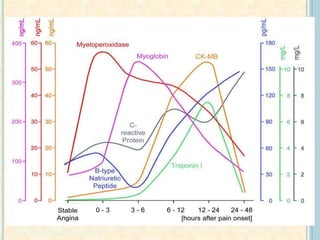
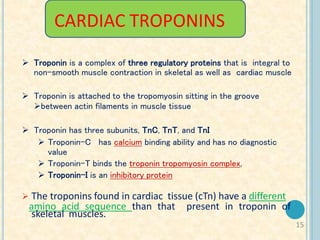
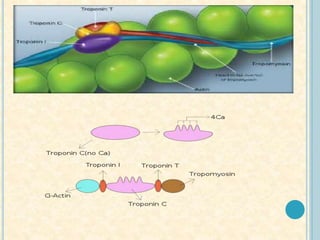
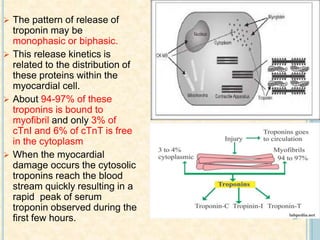
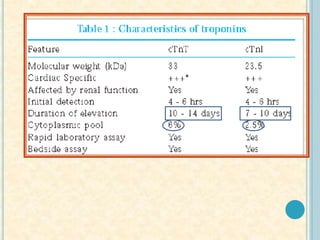
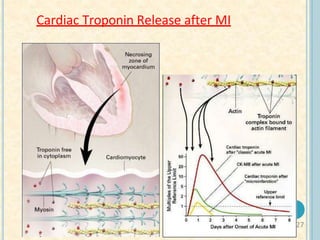
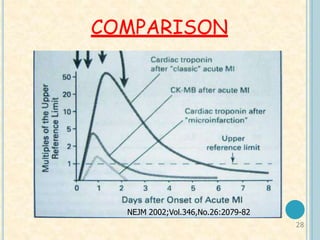
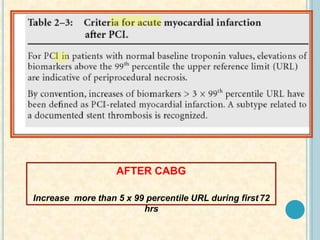
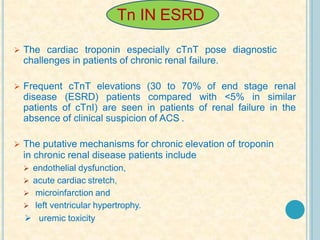
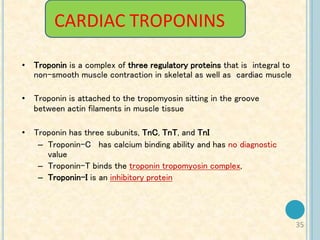
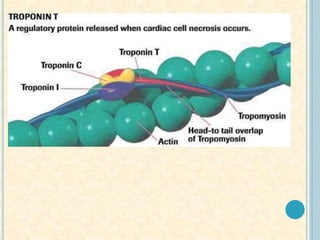
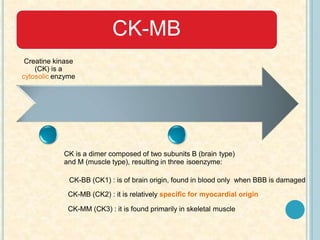
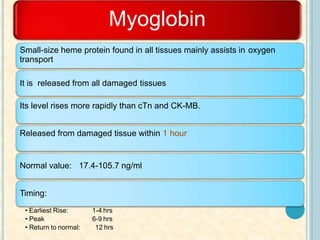
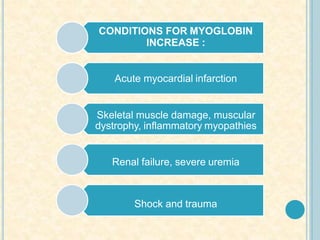
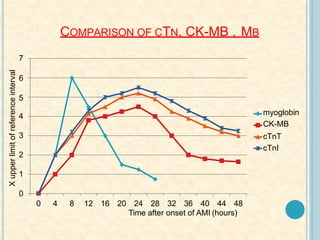
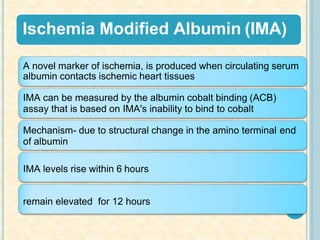
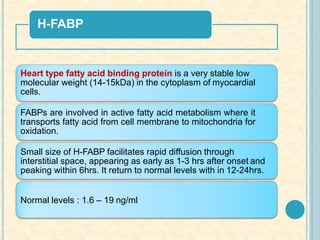
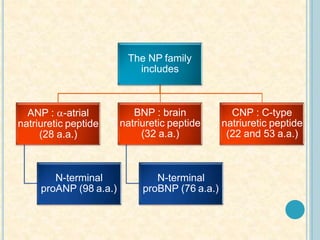
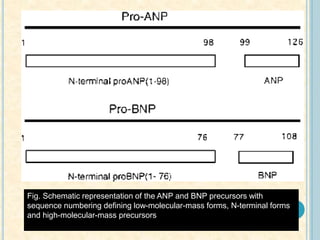
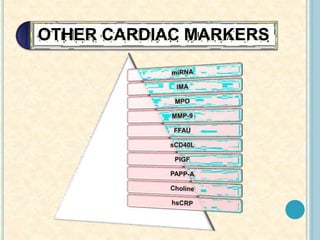
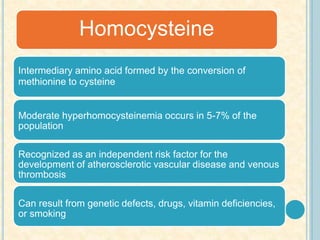
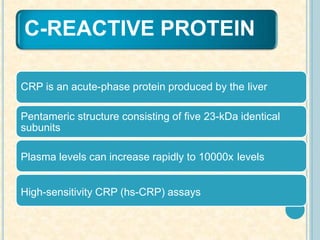
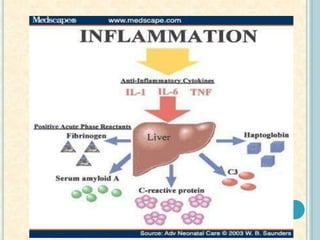
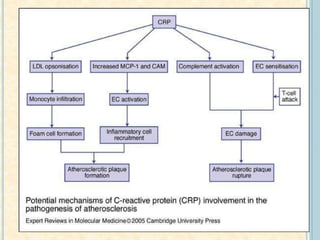
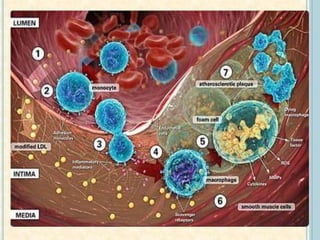
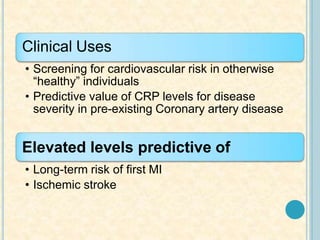
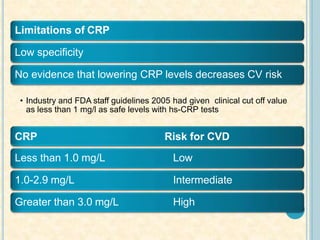
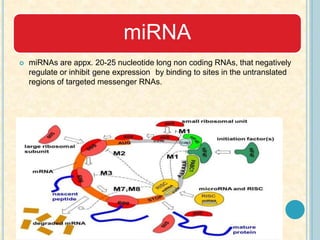
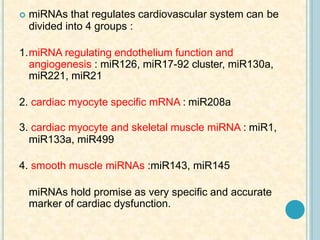
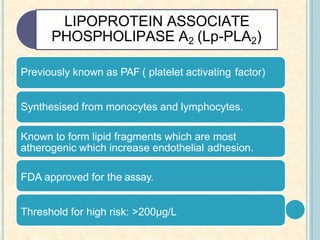
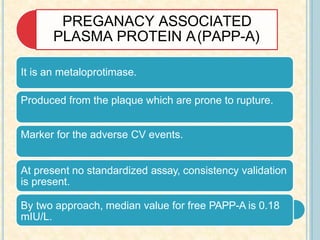
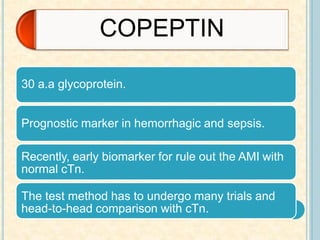
Cardiac biomarkers are proteins released from damaged heart muscle and can indicate myocardial injury. The ideal cardiac marker is highly specific to the heart, allows for easy diagnosis, and helps guide treatment. Historically, markers like CK, CK-MB, myoglobin were used but troponins are now preferred due to their high cardiac specificity and ability to detect even minor myocardial damage. Troponin I is 100% specific to the heart while troponin T can occasionally be elevated in other conditions. Both become elevated within 4-5 hours of injury and remain so for several days, making them useful for diagnosing older myocardial infarctions. Their levels also correlate with injury severity.