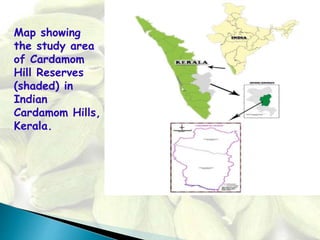
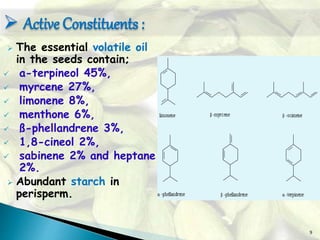
The document provides information about cardamom, including its definition, morphology, history, chemical constituents, common usable parts, traditional uses, extraction process, therapeutic uses, dosage, side effects, and contraindications. Cardamom is the world's third most expensive spice and originated in Guatemala. It grows well in areas with high rainfall and its seeds contain volatile oils including a-terpineol and limonene. Traditional uses of cardamom include use in cooking, baking, and as a breath freshener. Its extraction process involves grinding seeds and steeping them in water. Therapeutic uses include treating indigestion, infections, and inflammation. Proper dosage depends on factors like age, but side effects may