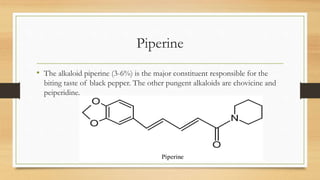
Black pepper is native to southern India and is now widely cultivated in tropical regions around the world. Karnataka is India's leading producer, accounting for approximately 50% of national production. Pepper plants are woody vines that produce clusters of small, green berries that turn red and then black or white upon ripening. There are over 100 varieties cultivated in India, with the most important including Tellicherry, Malabar, and Cheriakodi. Black pepper is used widely as a spice and preservative, and also has traditional medicinal uses. It is harvested when berries start to change color, then dried or processed into products like white, green, and powdered pepper. India is a major exporter, contributing over a third of spice