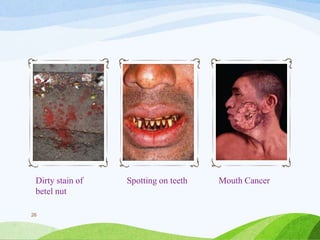
The document discusses areca nut (betel nut), its cultivation, uses, and associated health risks. It highlights the geographical origins, nutritional properties, and traditional significance in India, while also detailing its chemical constituents and associated toxicities, including cancer risks. Ultimately, it emphasizes the addictive nature of areca nut and the need for regulation due to its harmful effects on health.