1) The secondary market refers to the market where existing securities are traded, providing a platform for investors to buy and sell securities that are already listed on a stock exchange.
2) The primary difference between the primary and secondary market is that in the primary market, securities are first offered to the public for subscription to raise capital, while in the secondary market, already existing securities are traded.
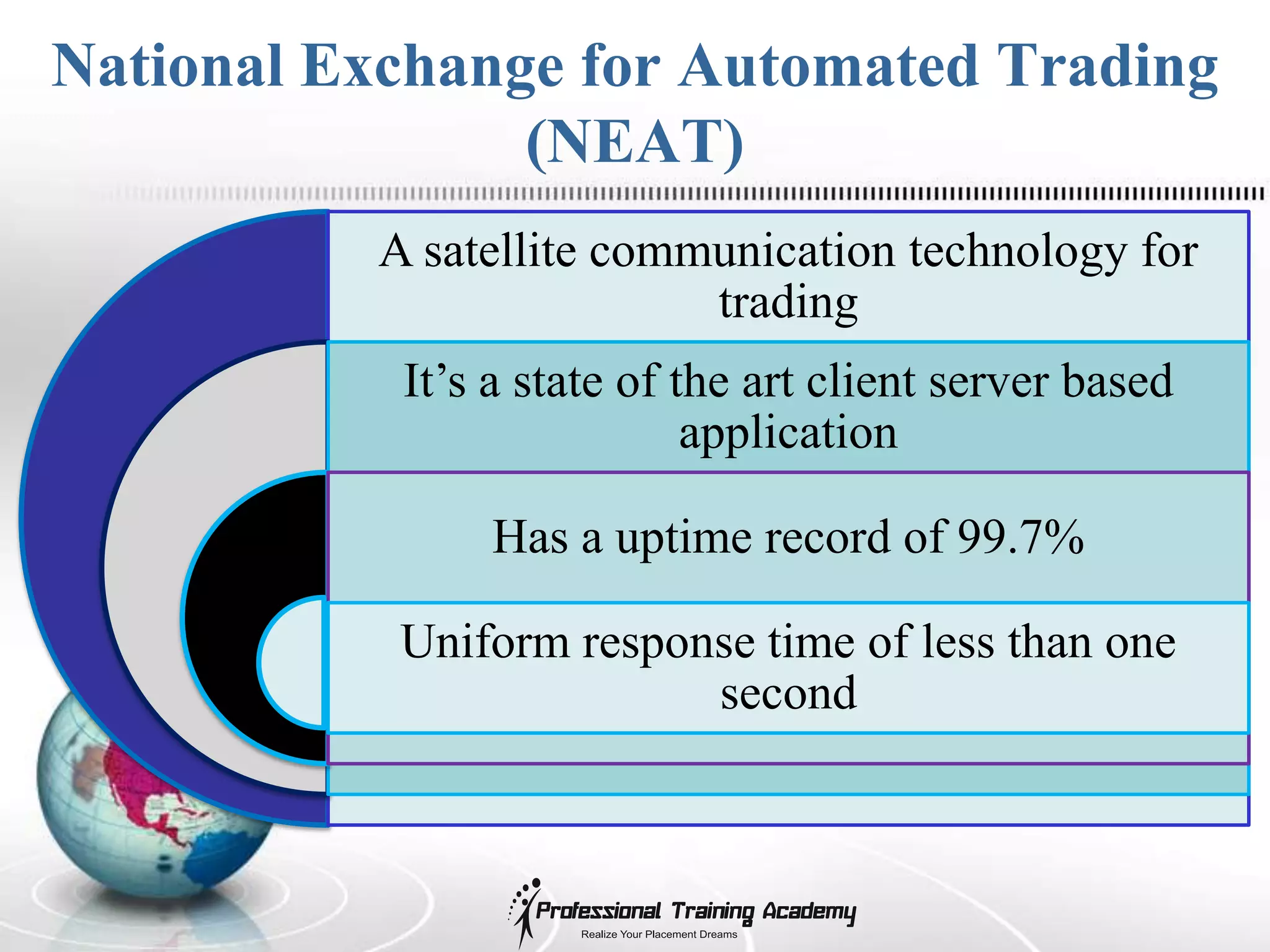
3) Stock exchanges like NSE provide a trading platform regulated by SEBI, where transactions in securities can be done electronically through systems like NEAT.