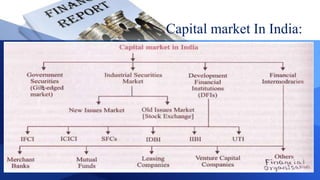
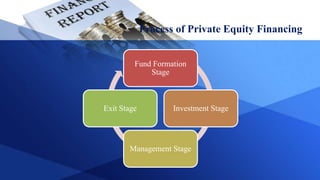
The document provides information on various aspects of the Indian capital market, including definitions of key terms like capital market, primary market, secondary market, and sources of long-term financing. It also discusses various capital market instruments like shares, debentures, term loans, leasing, hire purchase, venture capital, and private equity - outlining their meaning, types, advantages and disadvantages. The primary and secondary segments of the Indian capital market are described along with new issue market and stock market.