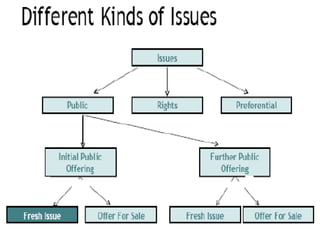
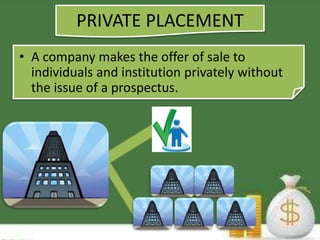
The primary market deals with the issuing of new securities by companies, governments, or public institutions to raise funds. This is typically done through an investment bank or syndicate of securities dealers through processes like initial public offerings (IPOs) of stock, follow-on public offerings (FPOs), private placements, rights issues, and bonus issues. The primary market creates long-term instruments through which corporate entities can borrow capital. It allows companies to attract new capital, transfer assets into financial assets, and invest money for short or long term goals.