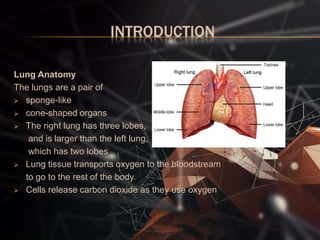
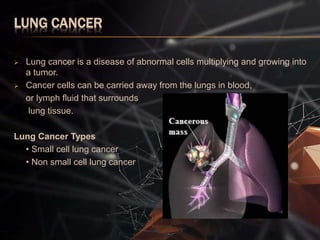
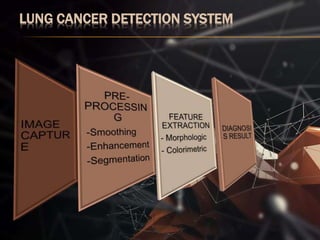
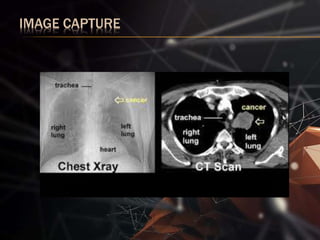
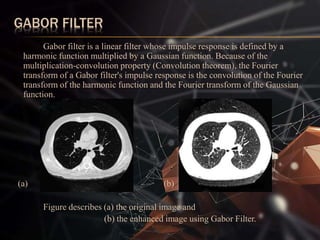
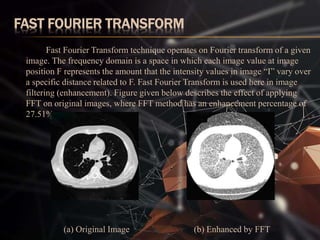
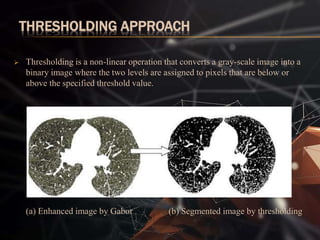
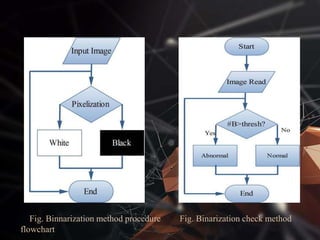
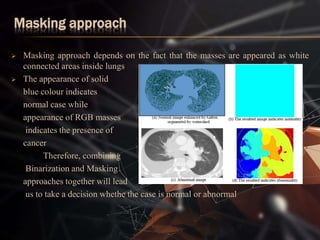
The document presents a lung cancer detection system using digital image processing techniques. It discusses lung anatomy and types of lung cancer. The system involves image capture, pre-processing using enhancement filters like Gabor and FFT, segmentation using thresholding and watershed approaches. Feature extraction is done using binarization and masking to detect cancer presence. The system helps in early detection of lung cancer to reduce mortality.