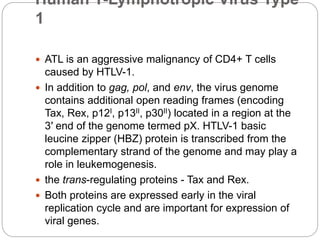
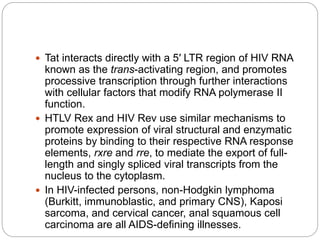
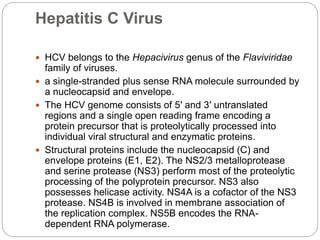
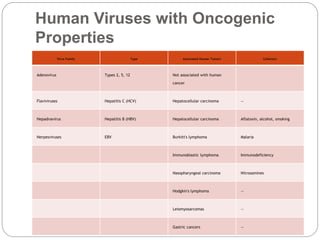
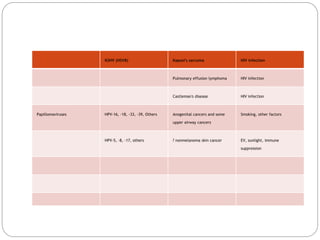
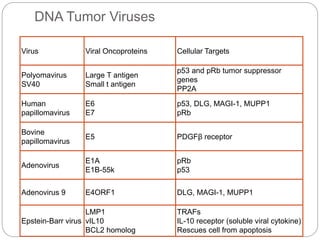
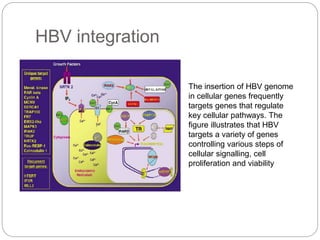
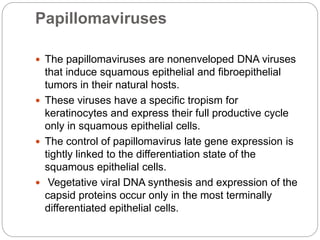
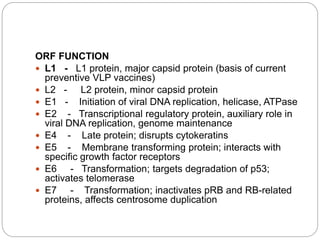
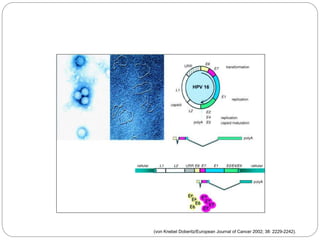
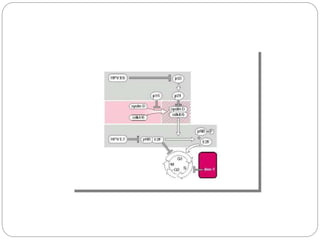
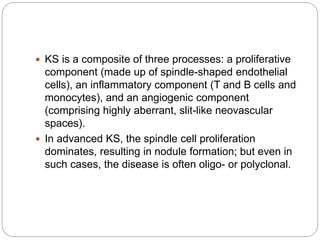
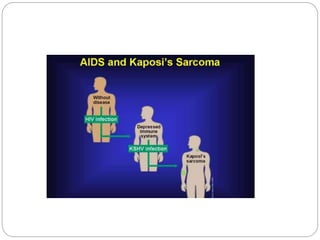
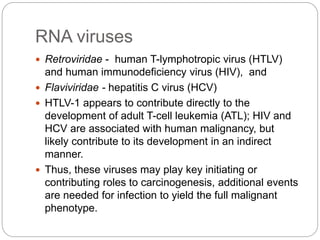
This document discusses viruses that can cause cancer in humans. It describes how certain DNA viruses, like HPV and HBV, integrate into the host cell's genome and influence cell cycle progression by encoding proteins that alter normal cell cycle control genes. This leads to cellular transformation and the potential for tumor development. It provides details on specific human cancer-causing viruses, their viral oncoproteins that subvert the cell cycle, and the cellular targets and cancers they are associated with, such as HPV's role in cervical cancer through the actions of the E6 and E7 proteins.






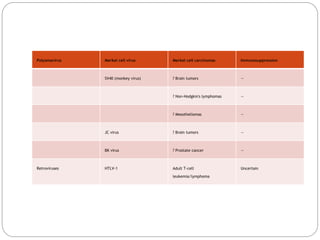


























![Mechanisms by which oncogenic retroviruses may
participate in the malignant transformation process are :-
Slowly transforming viruses (e.g., avian leukosis virus, an
Alpharetrovirus) alter cellular gene expression by random
integration of a provirus within or adjacent to cellular
protooncogenes (insertional mutagenesis). Direct physical
disruption of a gene or effects of viral promoters and
enhancers on cellular gene expression can lead to a
malignant phenotype in infected cells.
Acutely transforming retroviruses (e.g., Rous sarcoma
virus [RSV], an Alpharetrovirus) have incorporated into
their genomes viral oncogenes derived from cellular
protooncogenes (protooncogene capture) and
subsequently transfer these altered or deregulated
oncogenes into newly infected cells, thus leading to
development of a malignant phenotype.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cancerandvirsues-171212163333/85/Cancer-and-virsues-50-320.jpg)