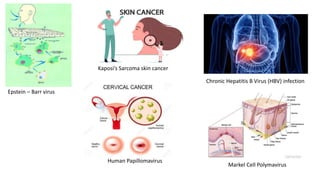
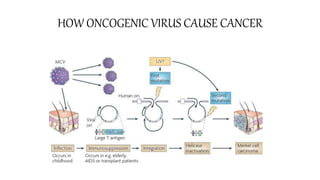
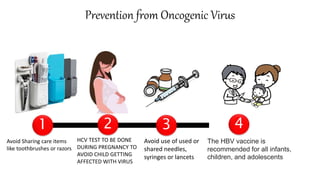
Oncoviruses are viruses that cause cancer. They originated from studies in the 1950s-60s of retroviruses that could transform cells. Now the term refers to any virus with a DNA or RNA genome that causes cancer. Approximately 17.8% of human cancers are caused by viral infections, with 11.9% caused by seven main viruses. These include Epstein-Barr virus, Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, hepatitis B and C viruses, human papillomavirus, and Merkel cell polyomavirus. Oncoviruses cause cancer through encoding transforming proteins that stimulate tumor formation and cell proliferation.