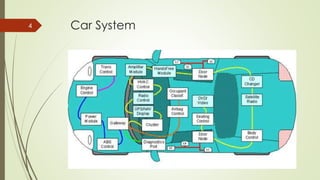
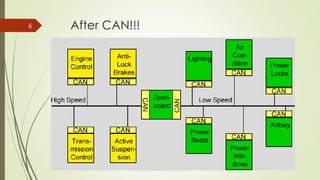
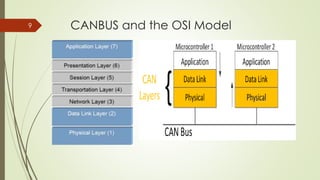
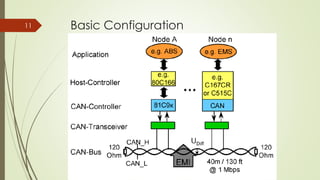
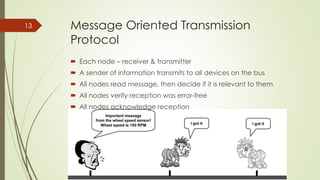
CAN (Controller Area Network) is a bus standard introduced in 1986 that defines protocols for microcontrollers and devices to communicate in applications without a host computer. It allows various electronic control units and devices to communicate with each other via a bus line. CAN was developed for use in automotive applications but is now also used in other fields like aerospace, maritime, and industrial automation. It provides robust messaging with efficient use of bandwidth and error detection.


![BUS topology
What is a Network Topology
It is the arrangement of various elements [Links, Nodes,
Etc.] for a Network [a telecommunication n/w] to
exchange Data
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/canbusm-141231030354-conversion-gate01/85/Can-bus-m-n-r-3-320.jpg)