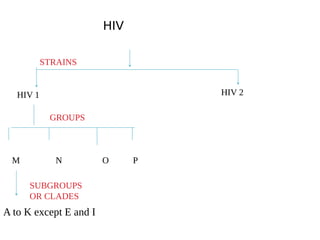
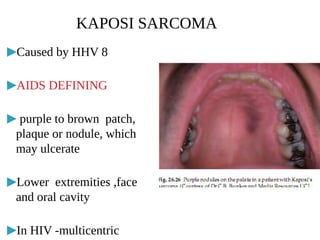
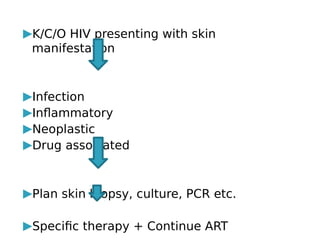
Cutaneous manifestations are common in HIV patients, occurring in over 90% of cases. They can represent the first signs of HIV infection and have prognostic significance. Skin conditions in HIV patients often present atypically with lesions in unusual sites, atypical morphology, being more extensive or not responding to conventional treatments. Common manifestations include generalized rashes, oral/genital ulcers, seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis, papulopruritic eruptions, eosinophilic folliculitis, granuloma annulare and various infections like herpes, molluscum, Kaposi sarcoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Dermatologists must have a high index of