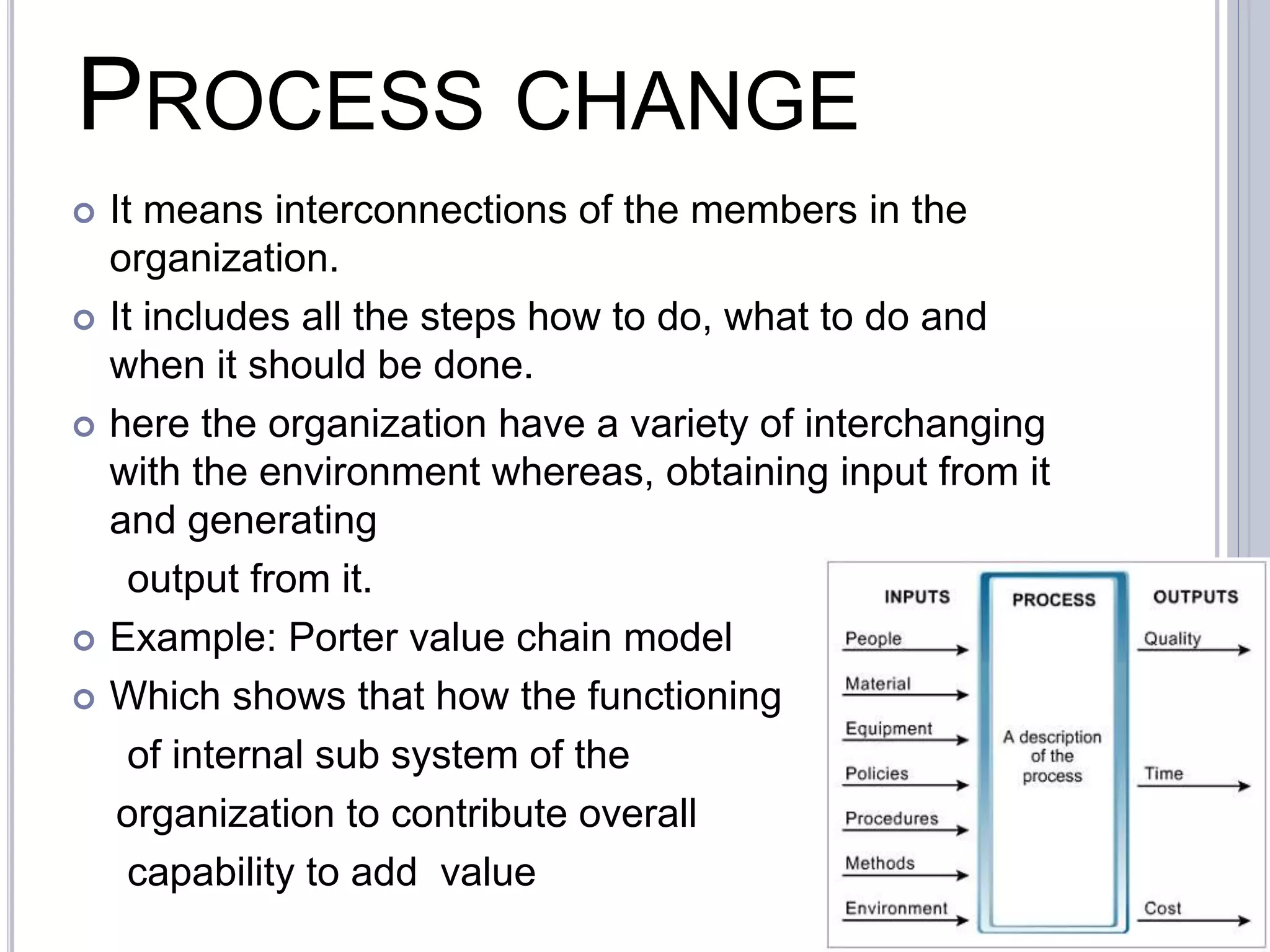
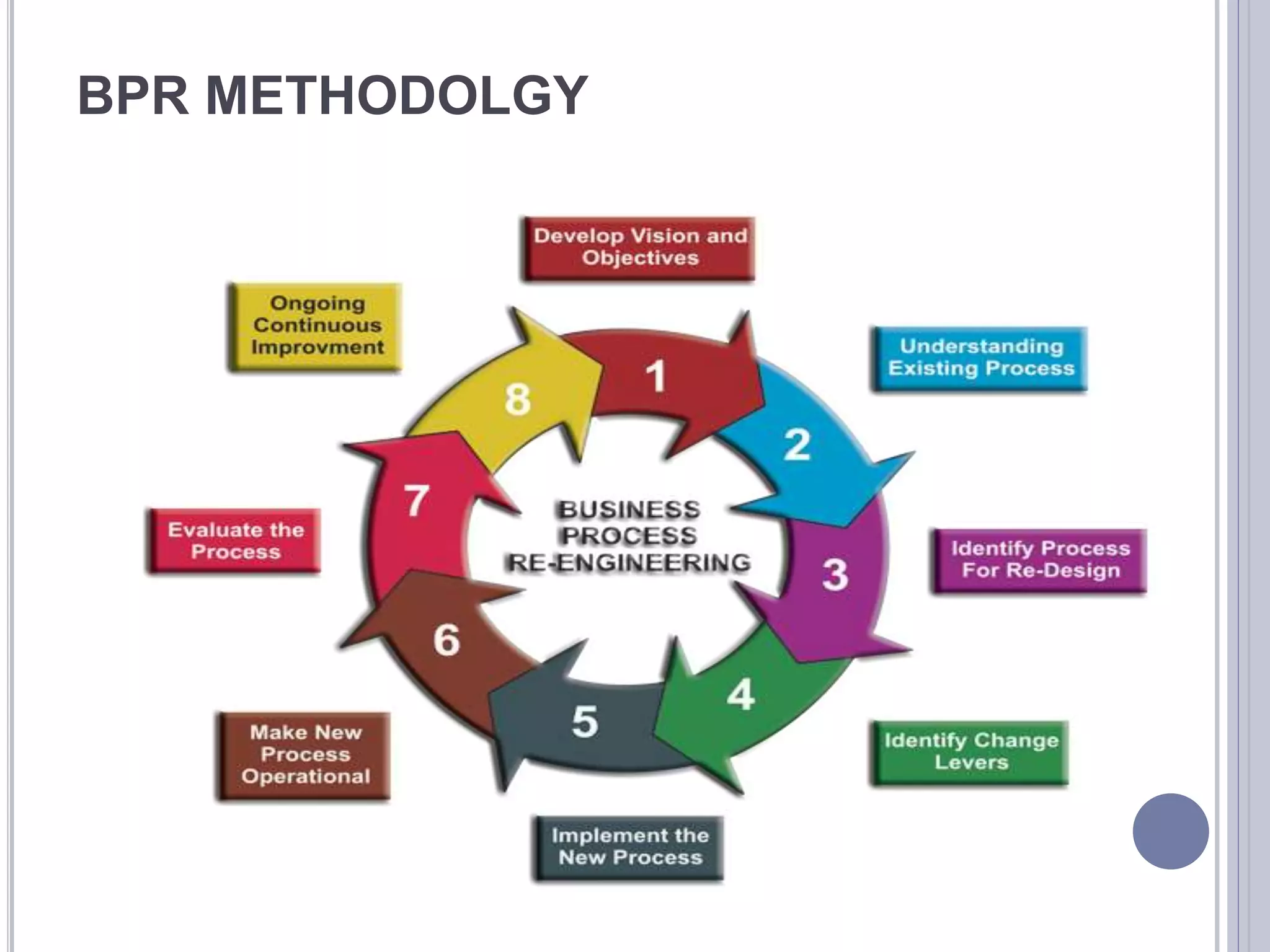
Business process change involves fundamentally rethinking and redesigning workflows to achieve dramatic improvements in performance. It consists of five stages: 1) Alignment with external environment and internal needs, 2) Definition by forming a business case and gap analysis, 3) Design using models like Popit, 4) Implementation through communication, training, and systems changes, and 5) Realization by assessing benefits. Business process reengineering specifically aims for radical redesign of processes to focus on customers and dramatically reduce costs and improve competition through strategic change management.