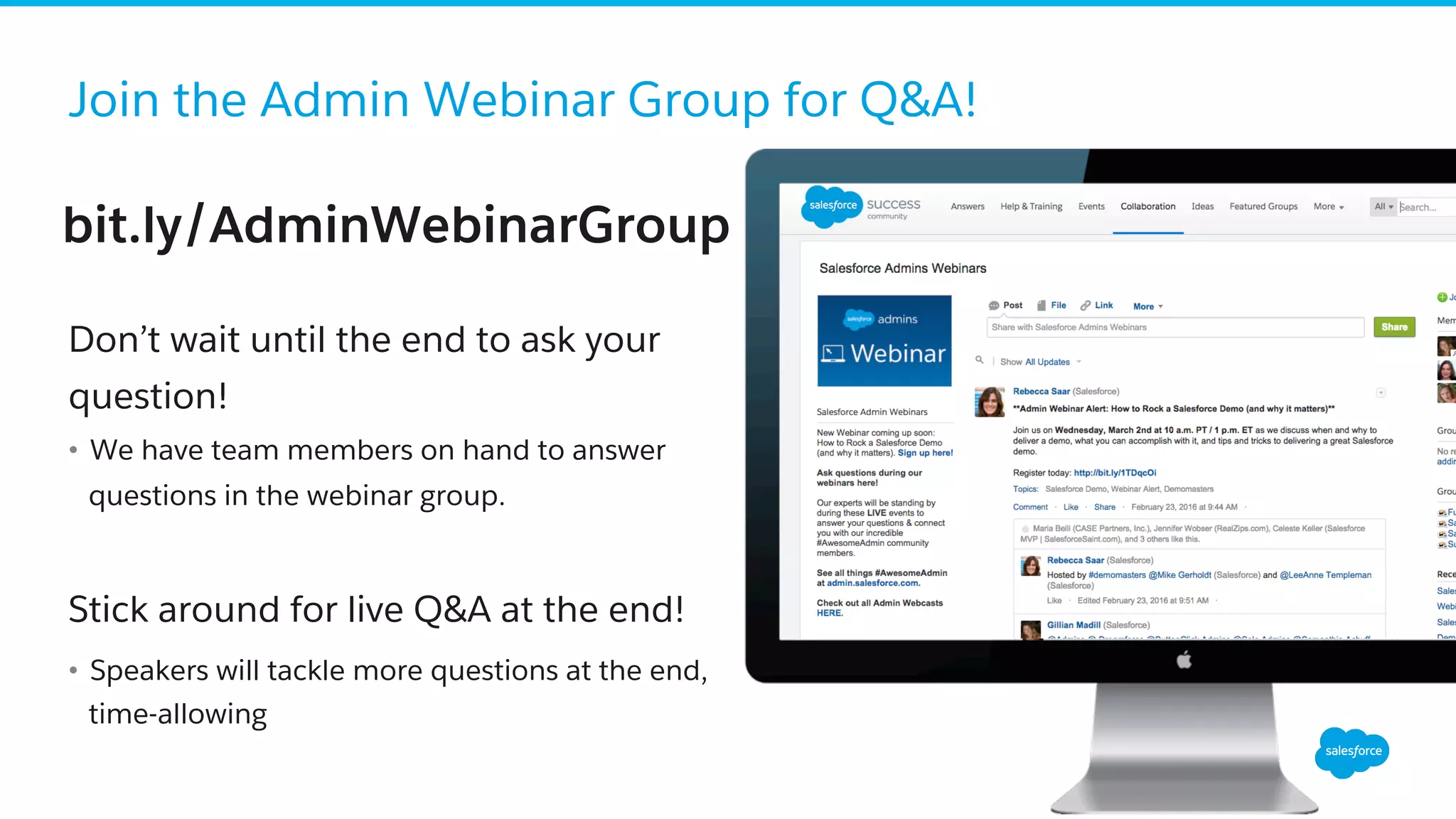
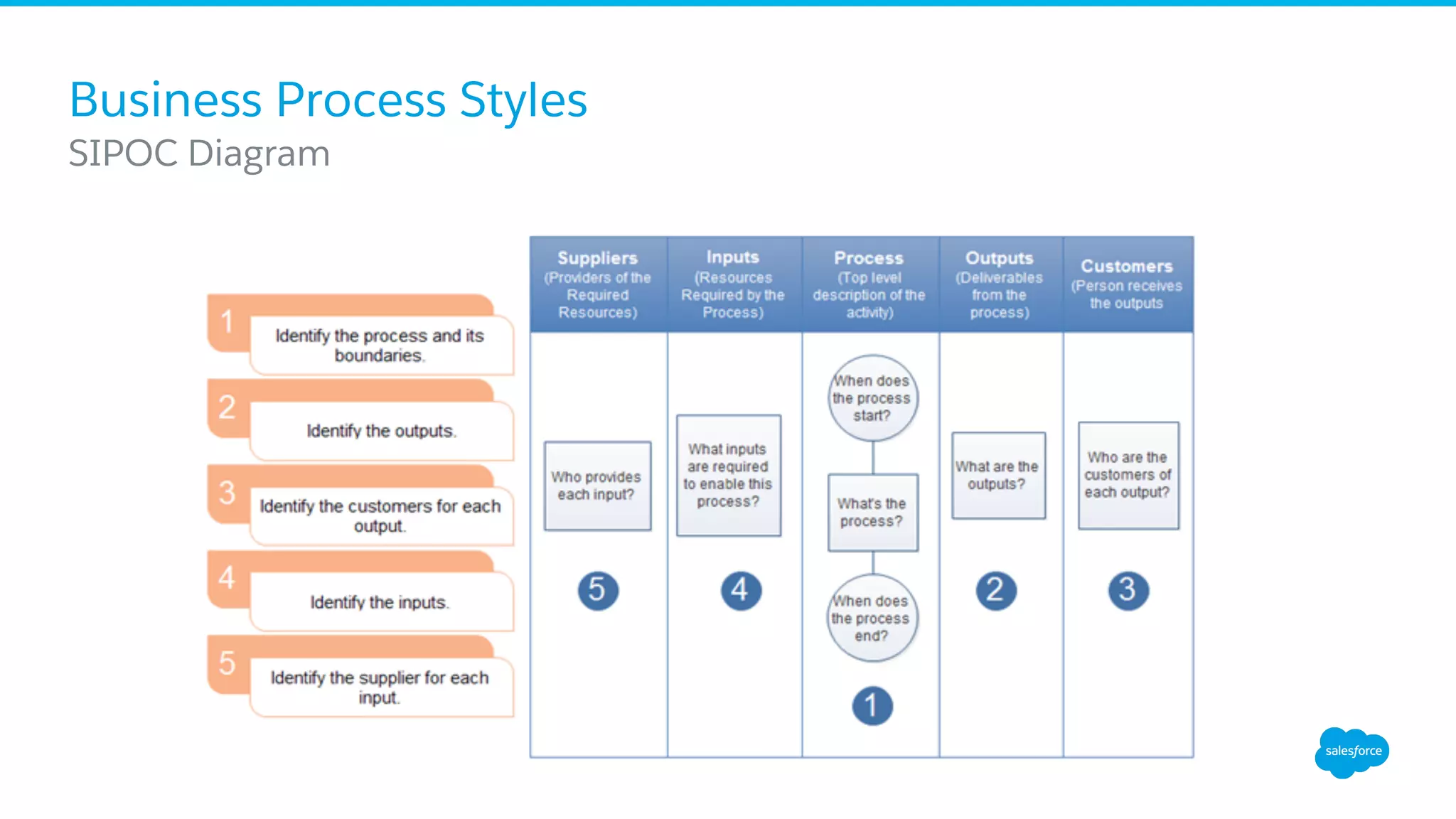
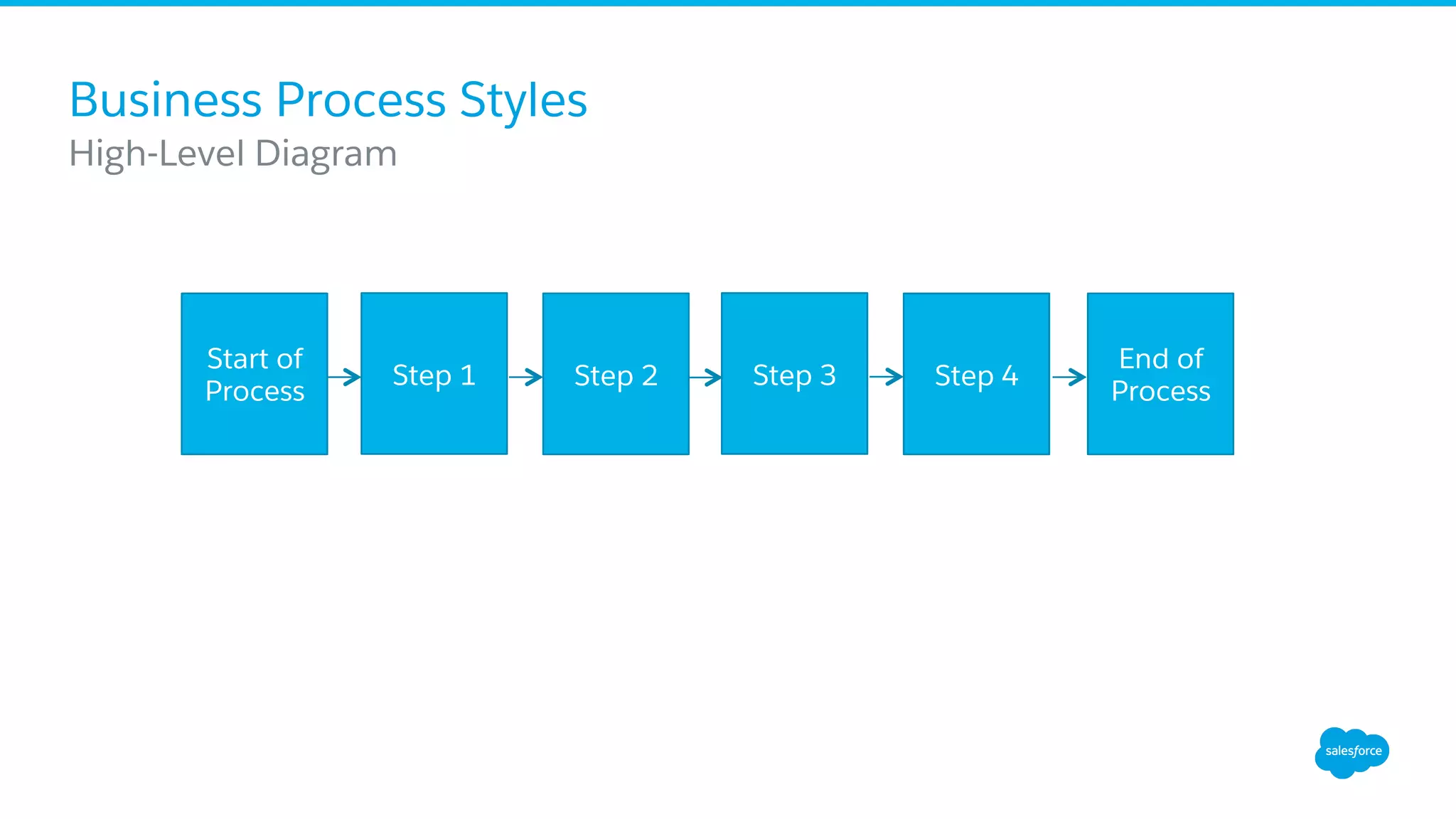
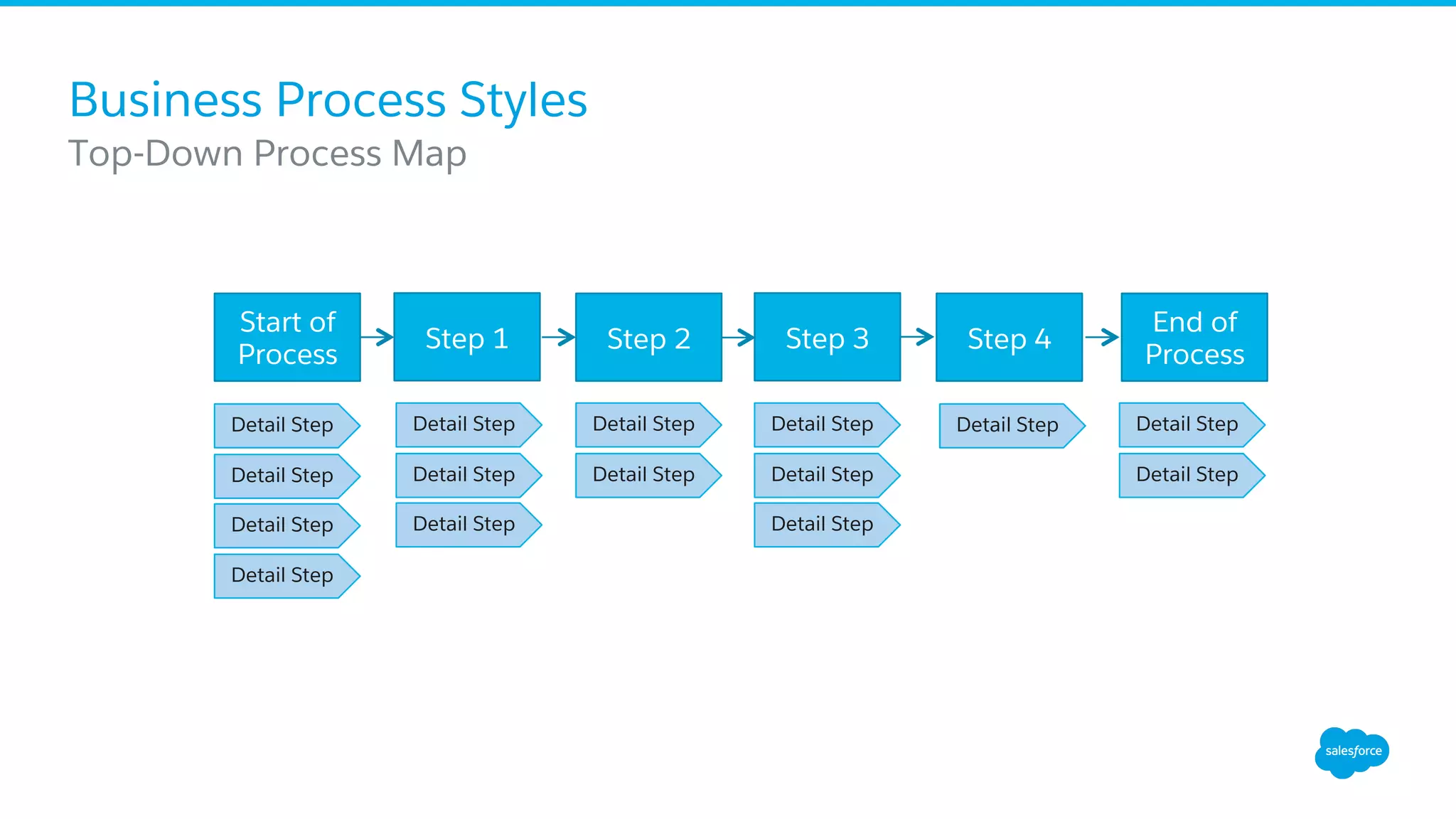
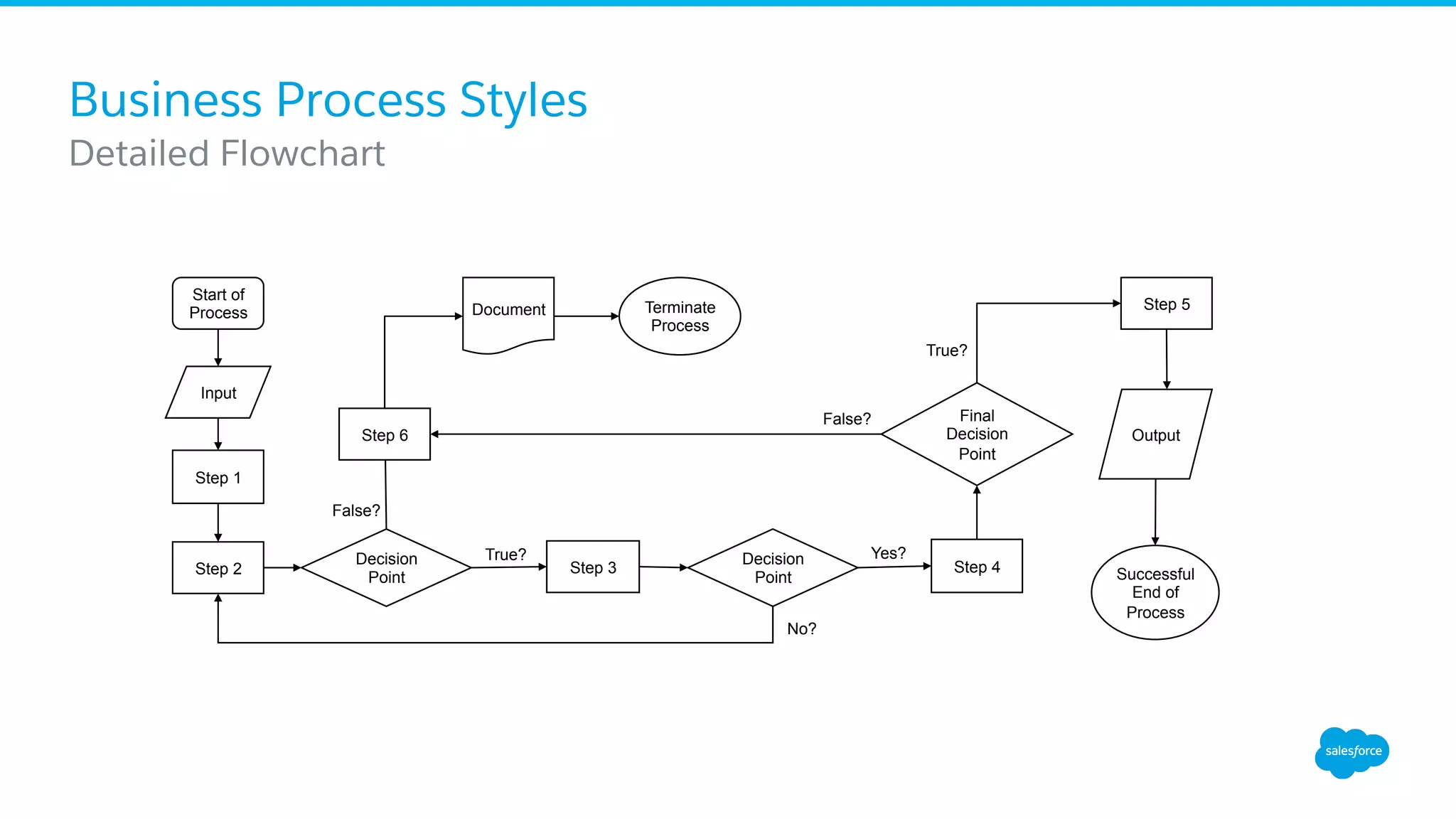
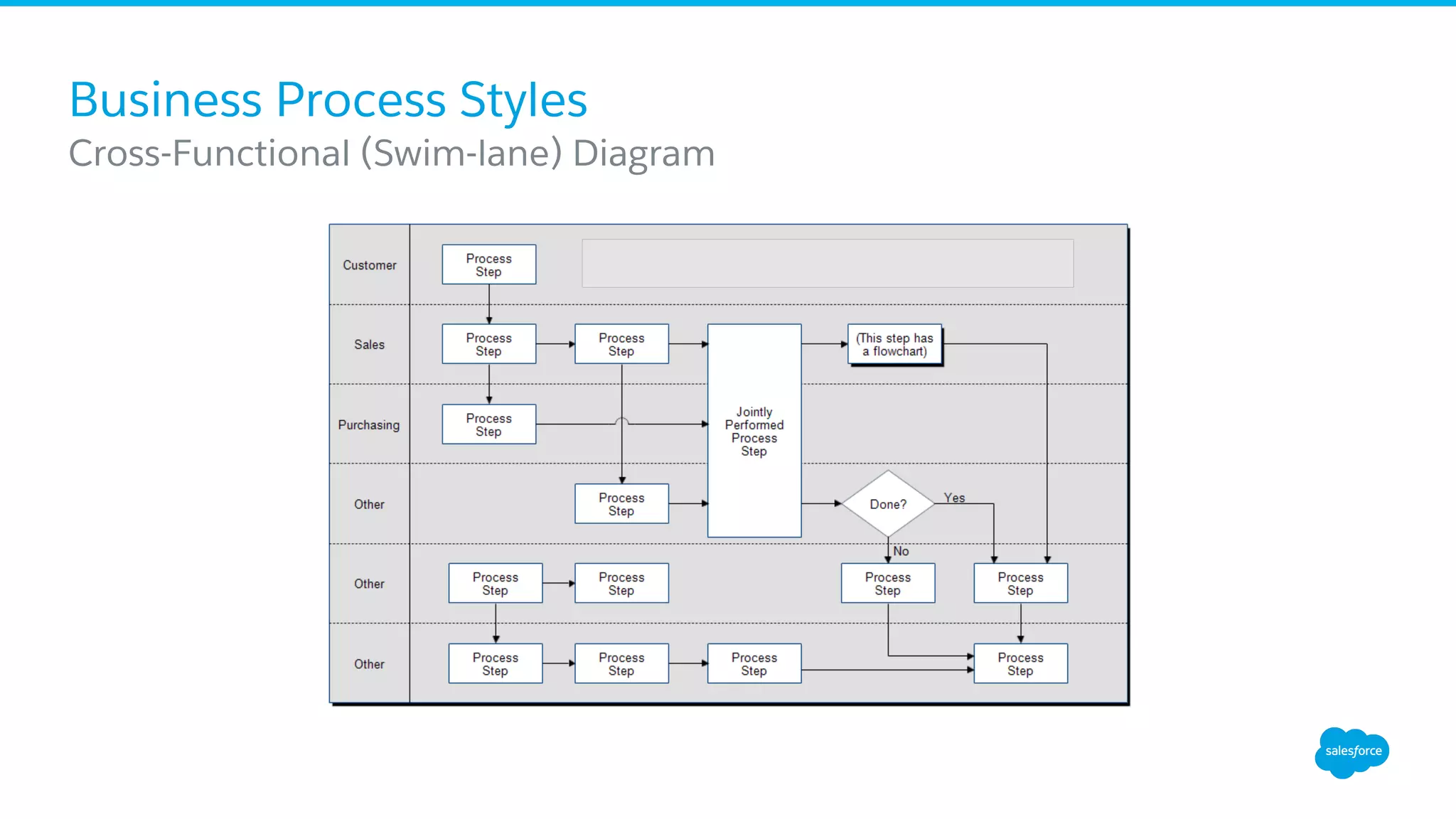
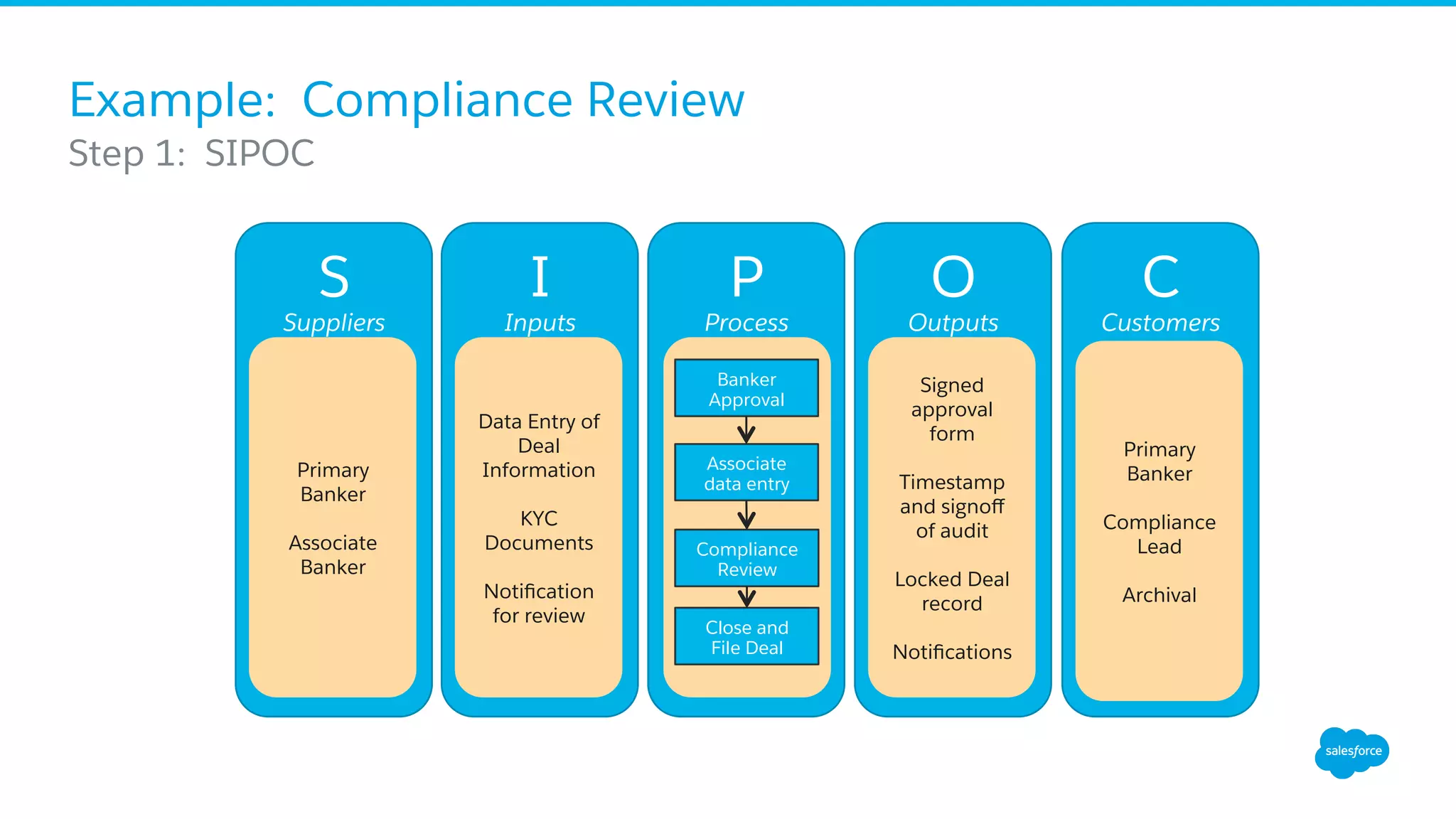
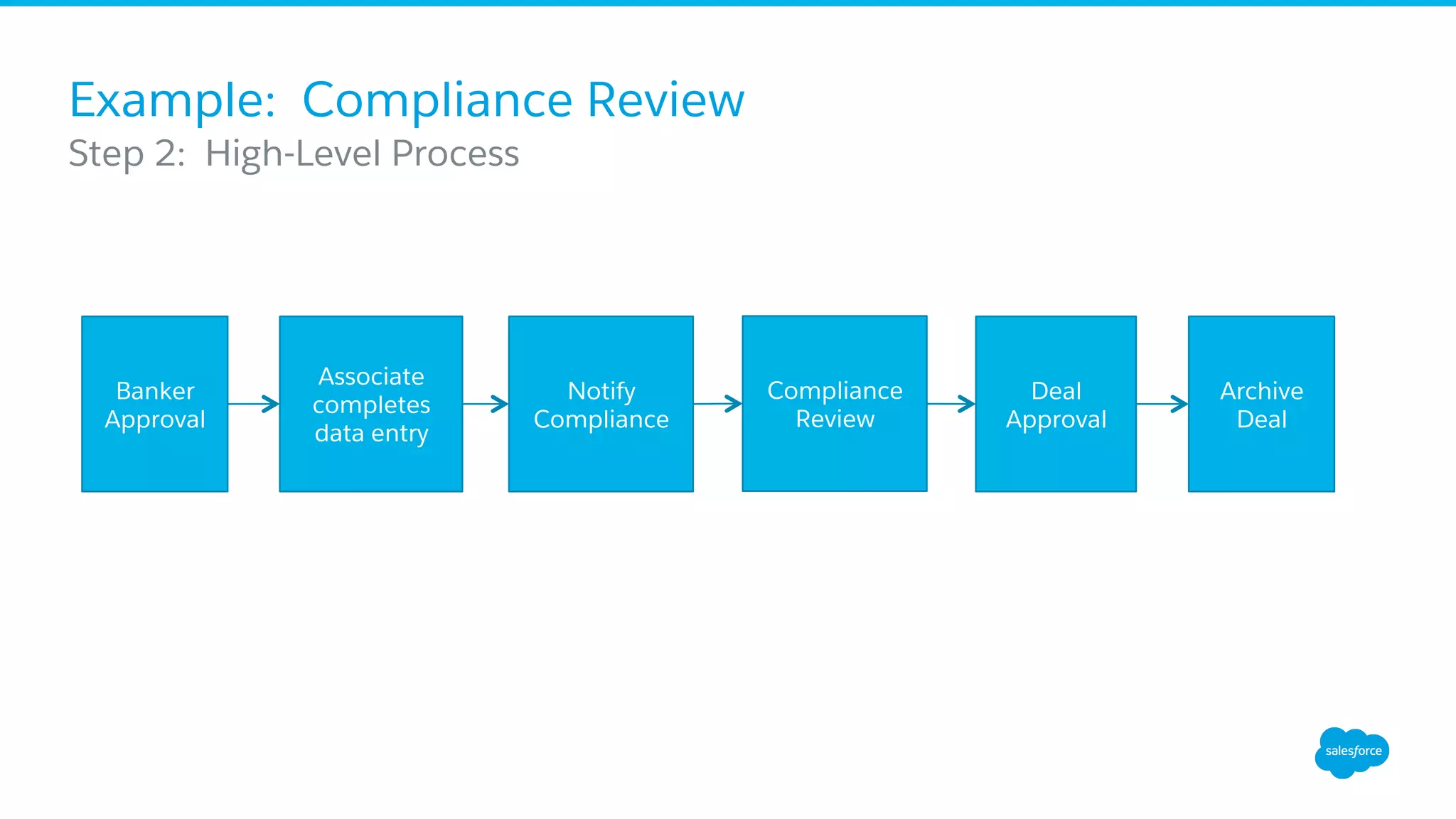
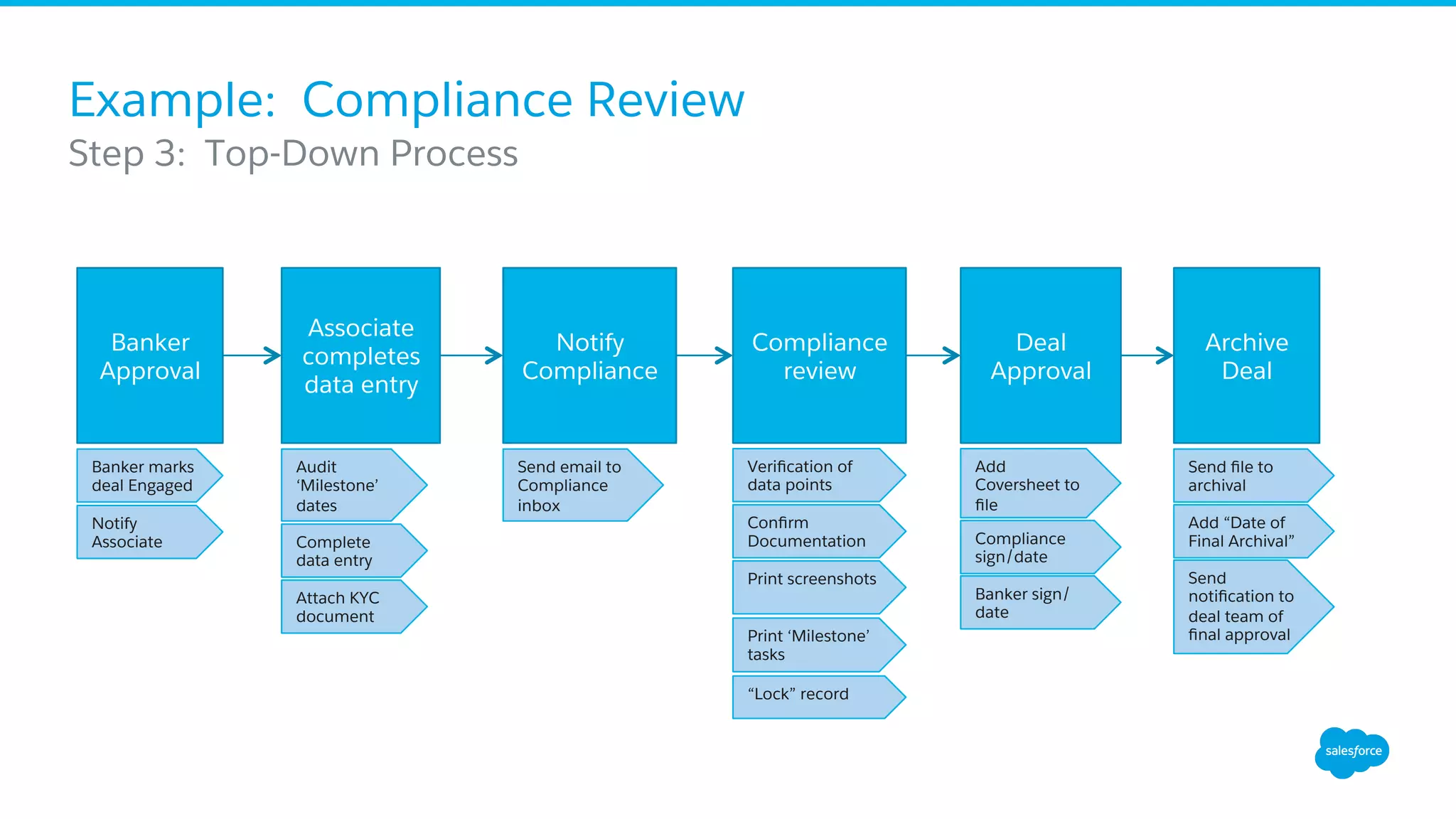
The document discusses business process mapping for Salesforce admins, emphasizing the importance of mapping processes to enhance efficiency and eliminate waste in operations. It outlines the steps for creating effective process maps and introduces lean methodology principles to improve development processes. The presentation also highlights the need for continuous improvement in Salesforce usage to drive business success.