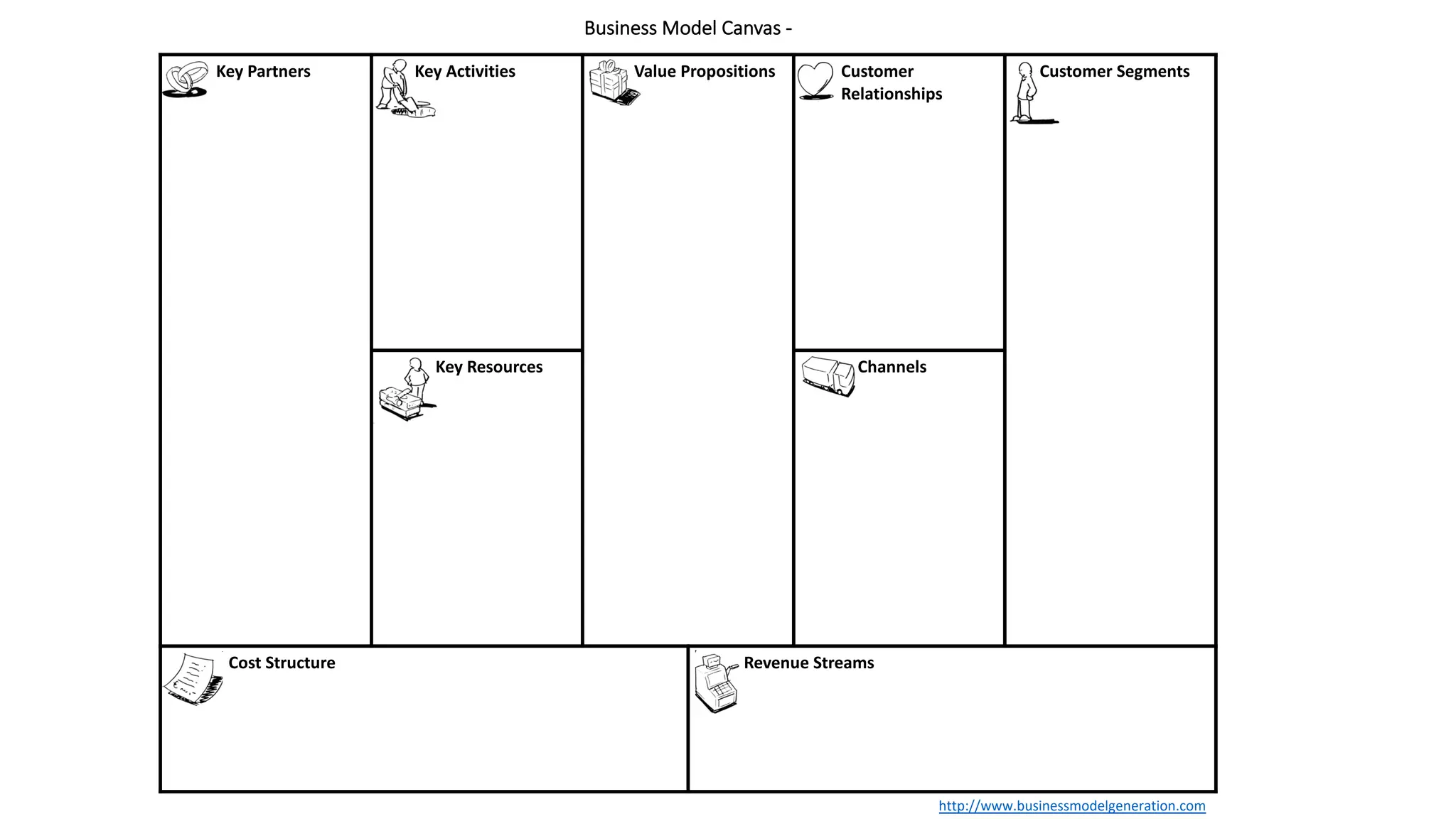
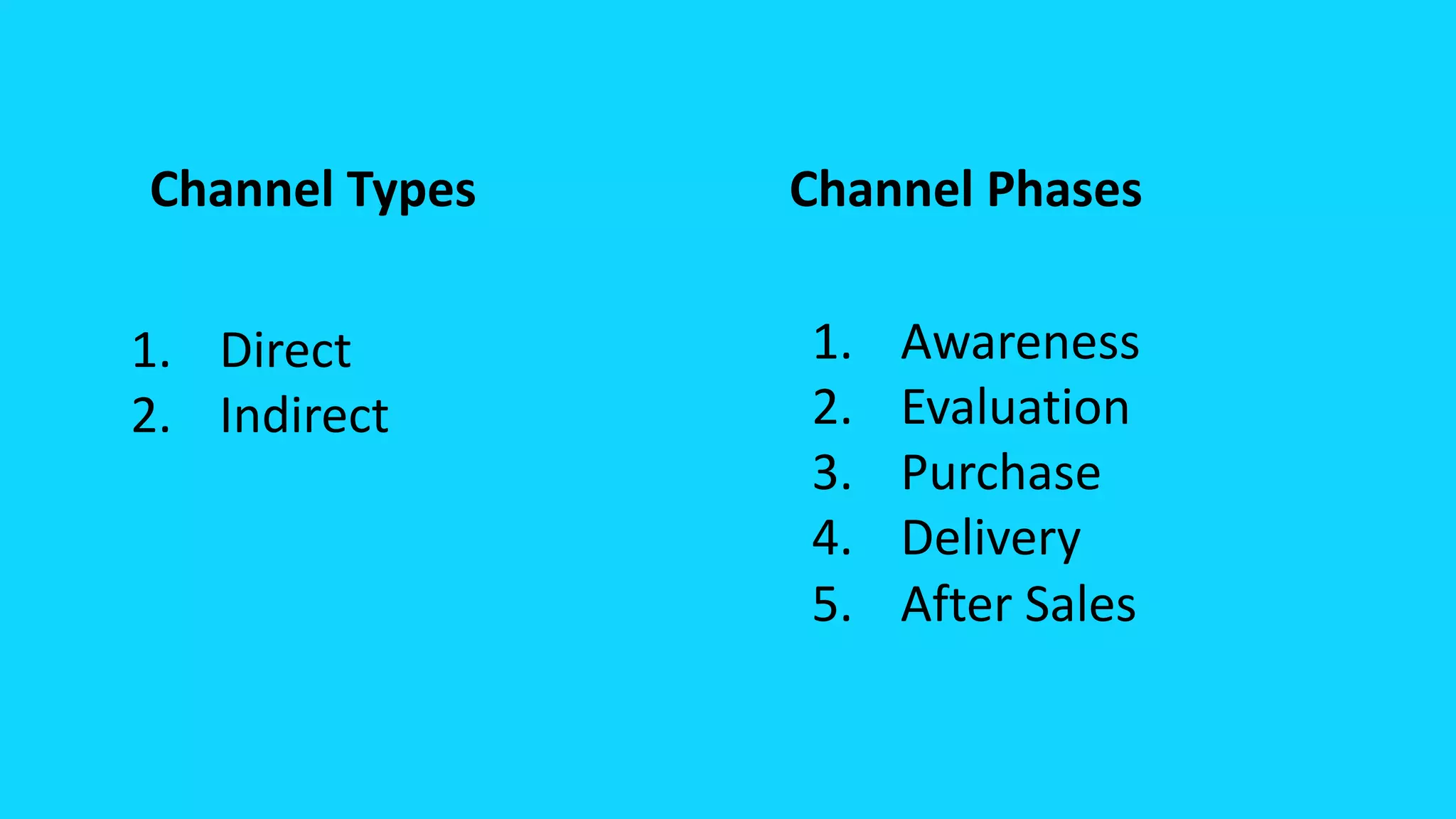
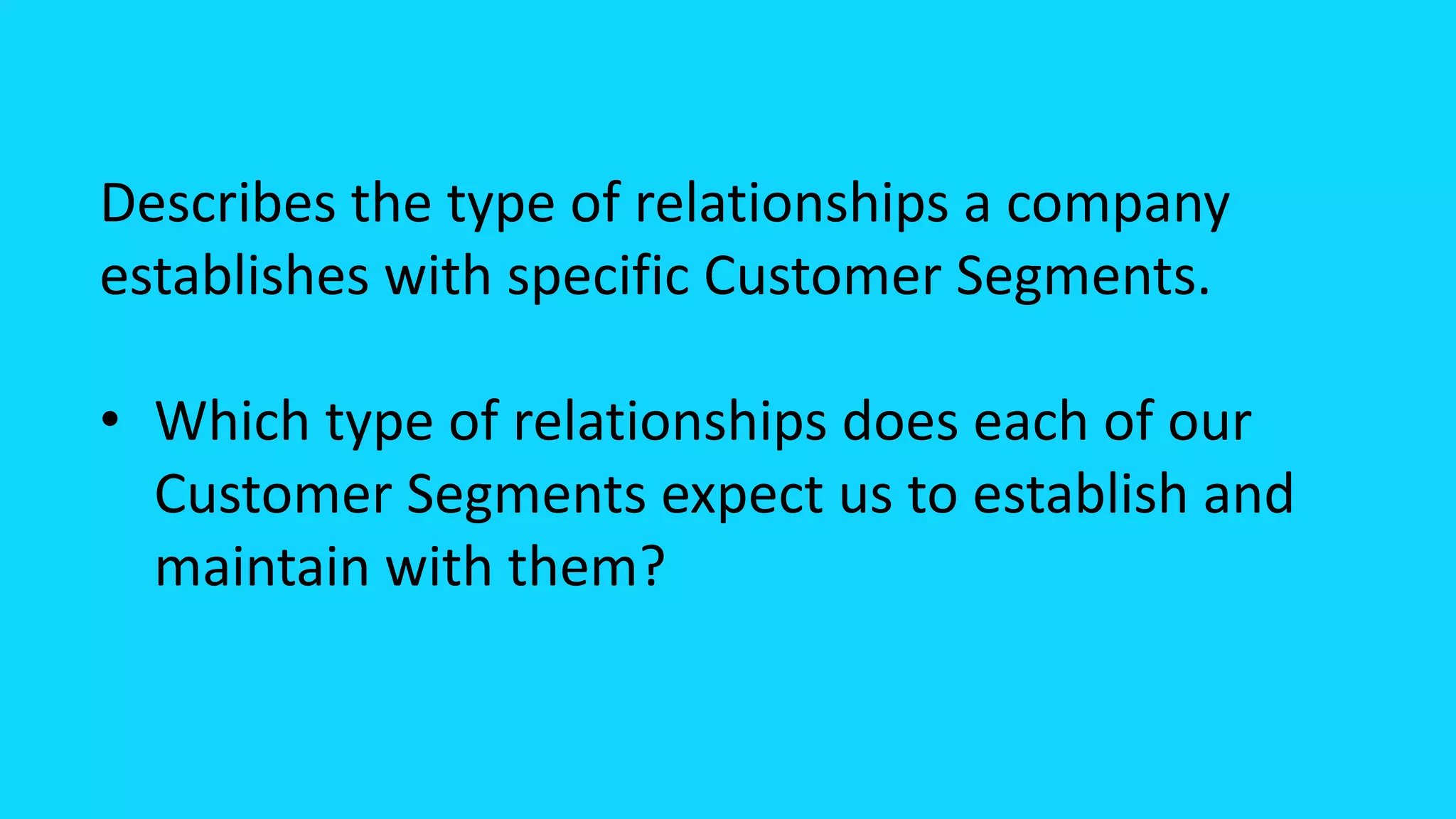
The document explains the business model canvas, a strategic tool for creating, delivering, and capturing value. It highlights key components such as customer segments, value propositions, channels, and revenue streams, emphasizing the importance of testing assumptions and iterating on business models. The canvas is favored over traditional business plans for its simplicity and adaptability in strategic planning and customer understanding.