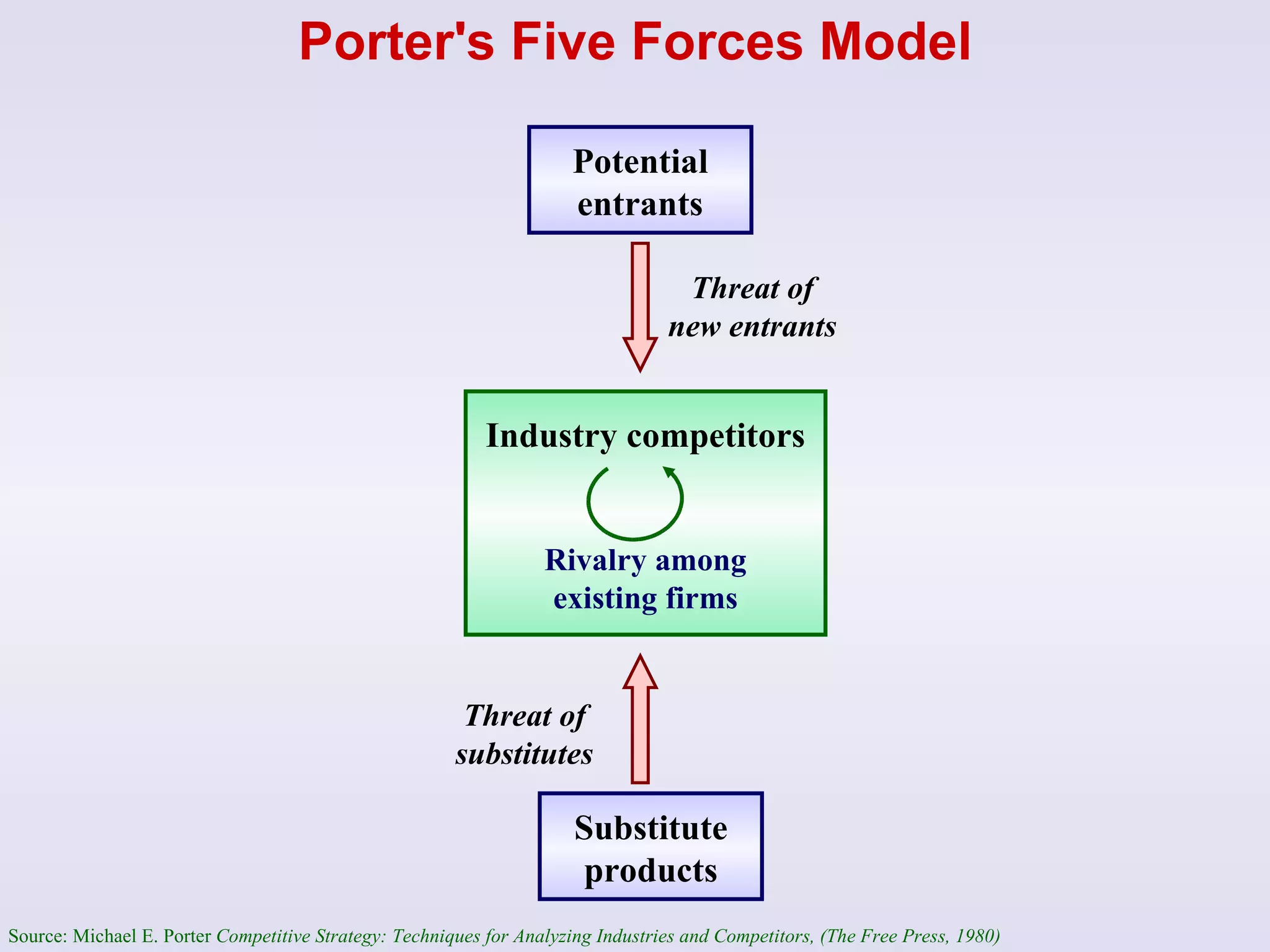
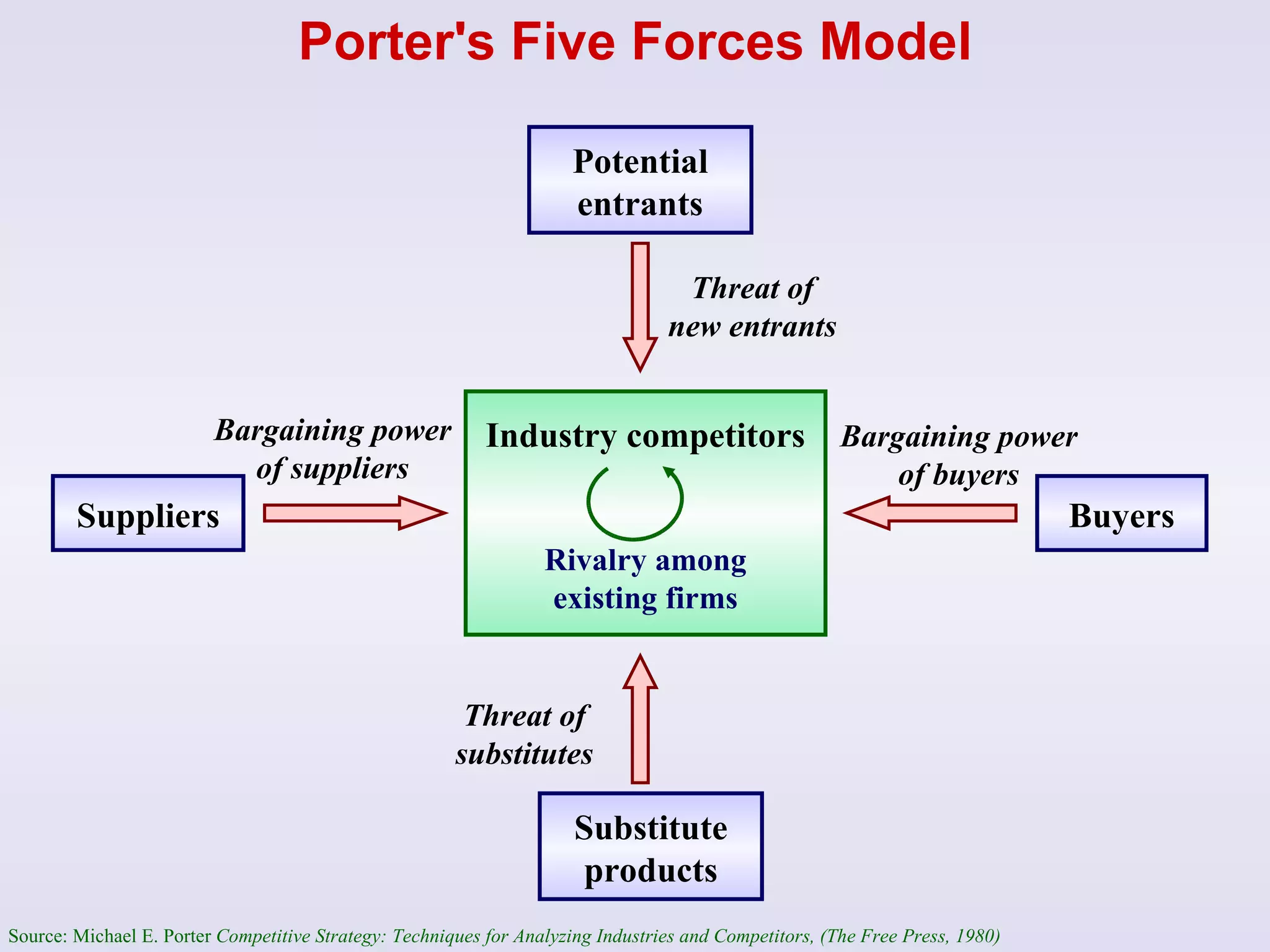
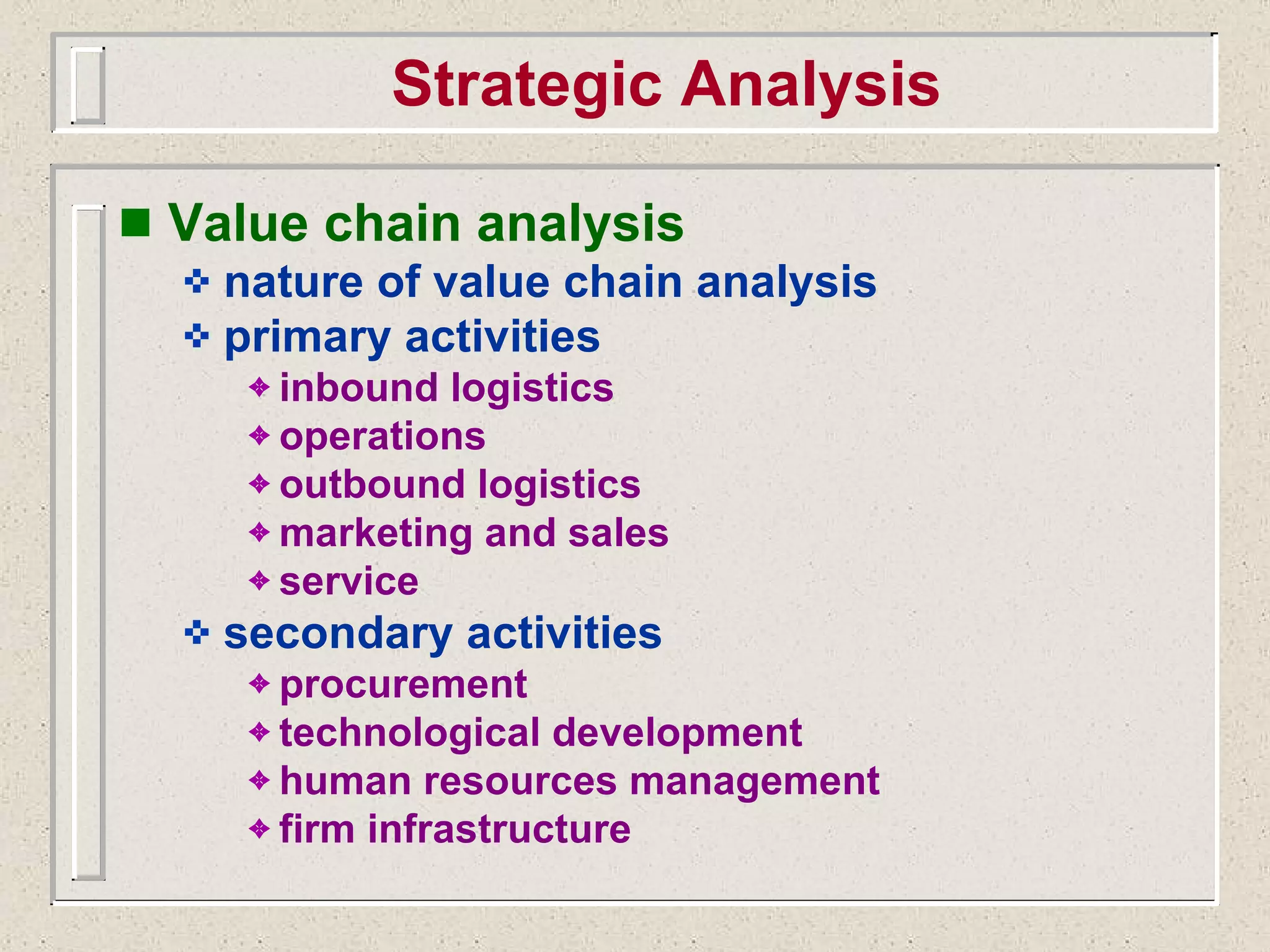
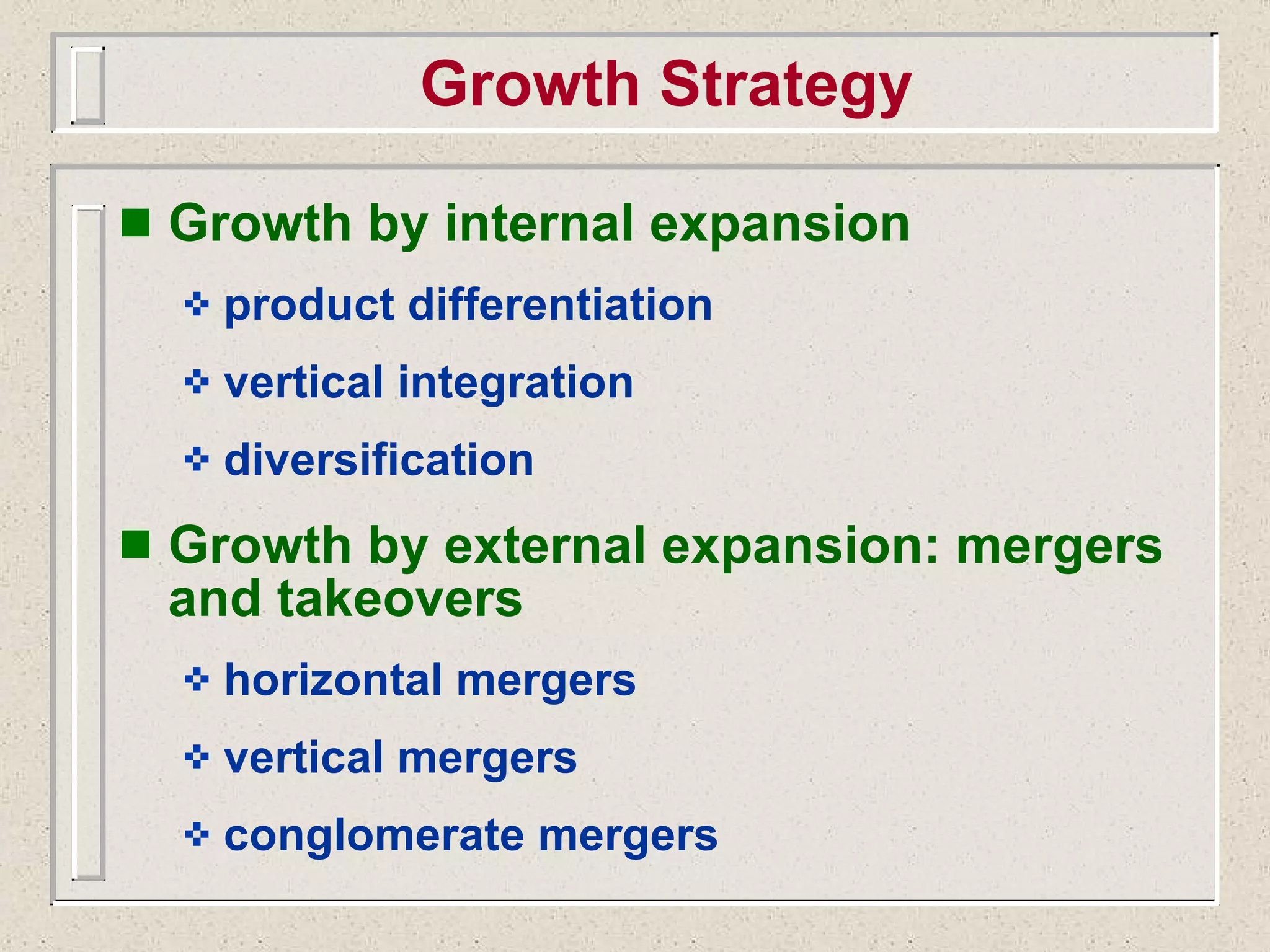
The document discusses strategic management and analysis tools such as Porter's Five Forces model and value chain analysis. It explains that Porter's Five Forces model analyzes the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and competitive rivalry. The value chain breaks down a firm's activities into primary and secondary categories. The document also covers strategic choices like cost leadership, differentiation, and focus strategies. It discusses growth strategies such as internal expansion, mergers and acquisitions, and the financing sources to support growth through internal or external means.