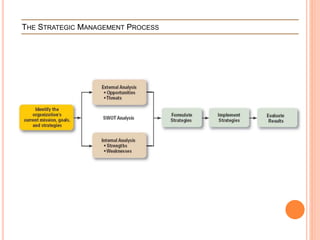
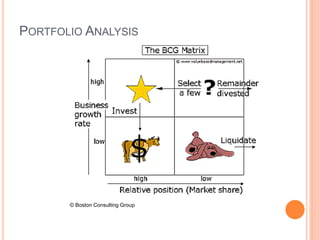
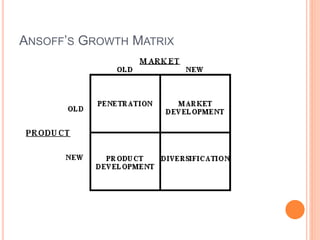
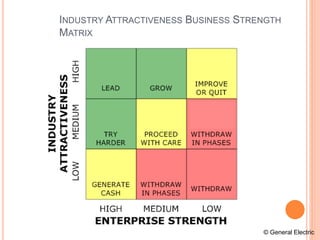
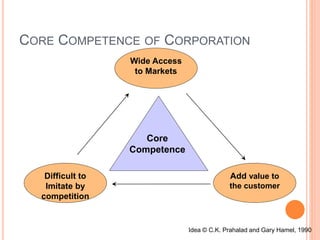
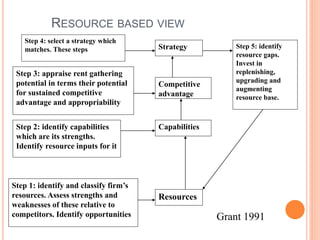
The strategic management process involves 6 steps: 1) defining the organization's mission and goals, 2) external analysis of opportunities and threats, 3) internal analysis of strengths and weaknesses, 4) formulating strategies to leverage strengths and address weaknesses, 5) implementing strategies, and 6) evaluating results and making adjustments. Key tools used include SWOT analysis, BCG matrix, Ansoff's growth matrix, Porter's five forces model, and identifying core competencies. The overall process allows organizations to systematically analyze their environment and capabilities to develop strategies that create a competitive advantage.