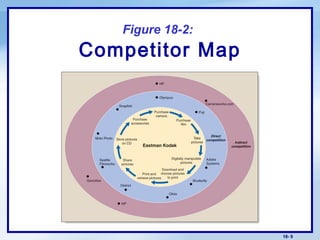
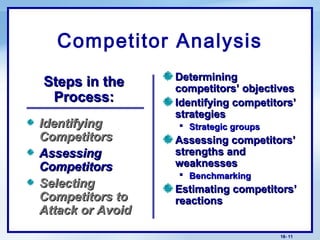
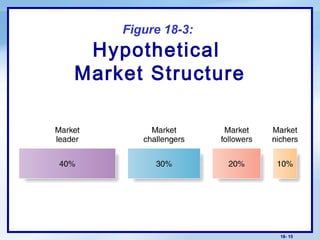
This document discusses competitor analysis and competitive strategies. It defines key terms like competitive advantage and outlines the process for analyzing competitors, including identifying them, assessing their strategies and strengths/weaknesses, and selecting which to attack or avoid. It also covers Porter's basic winning strategies of cost leadership, differentiation, and focus. Finally, it discusses different competitive positions like market leader, challenger, follower, and nicher. The overall purpose is to help understand competitors and develop effective competitive strategies.