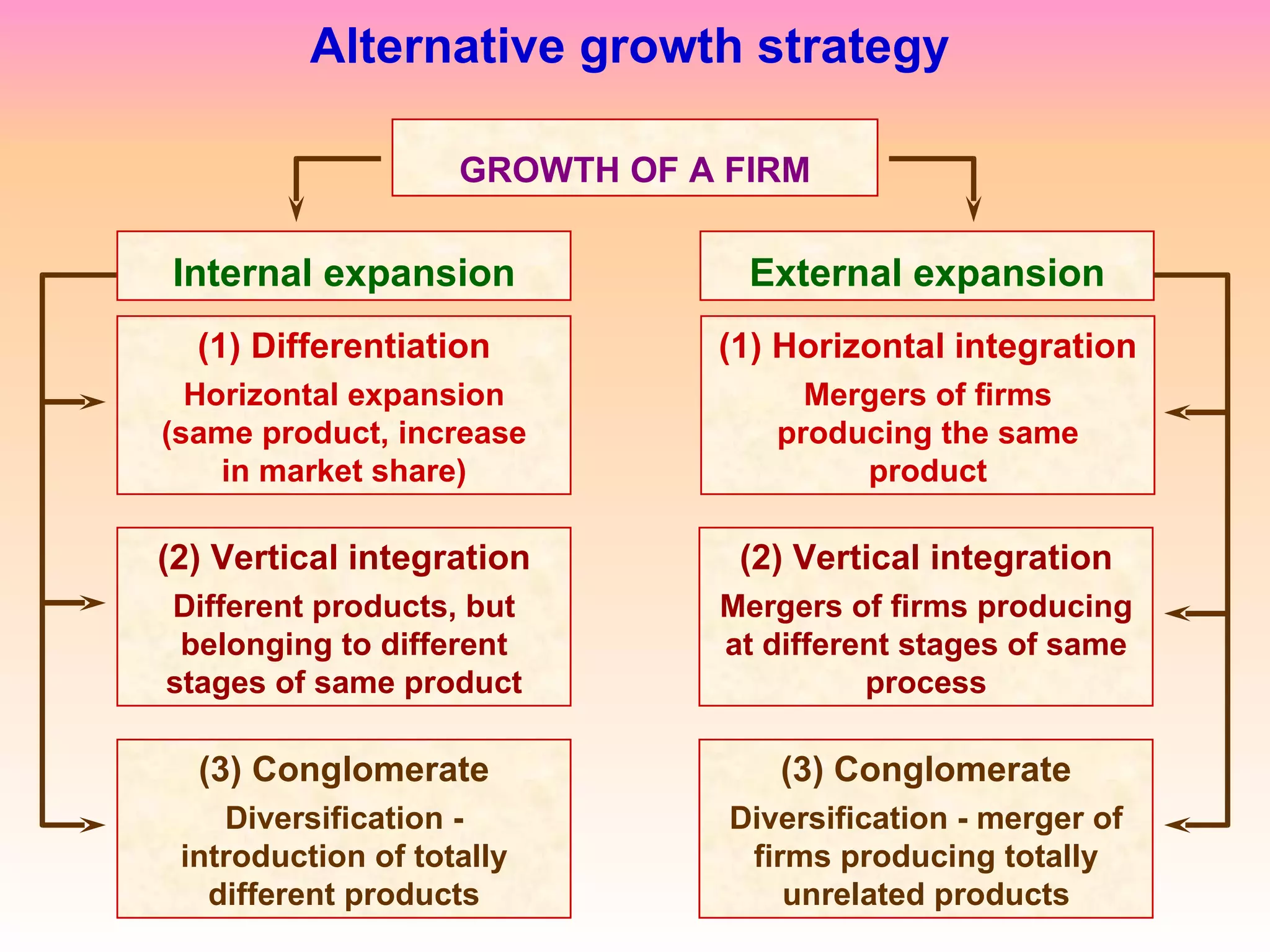
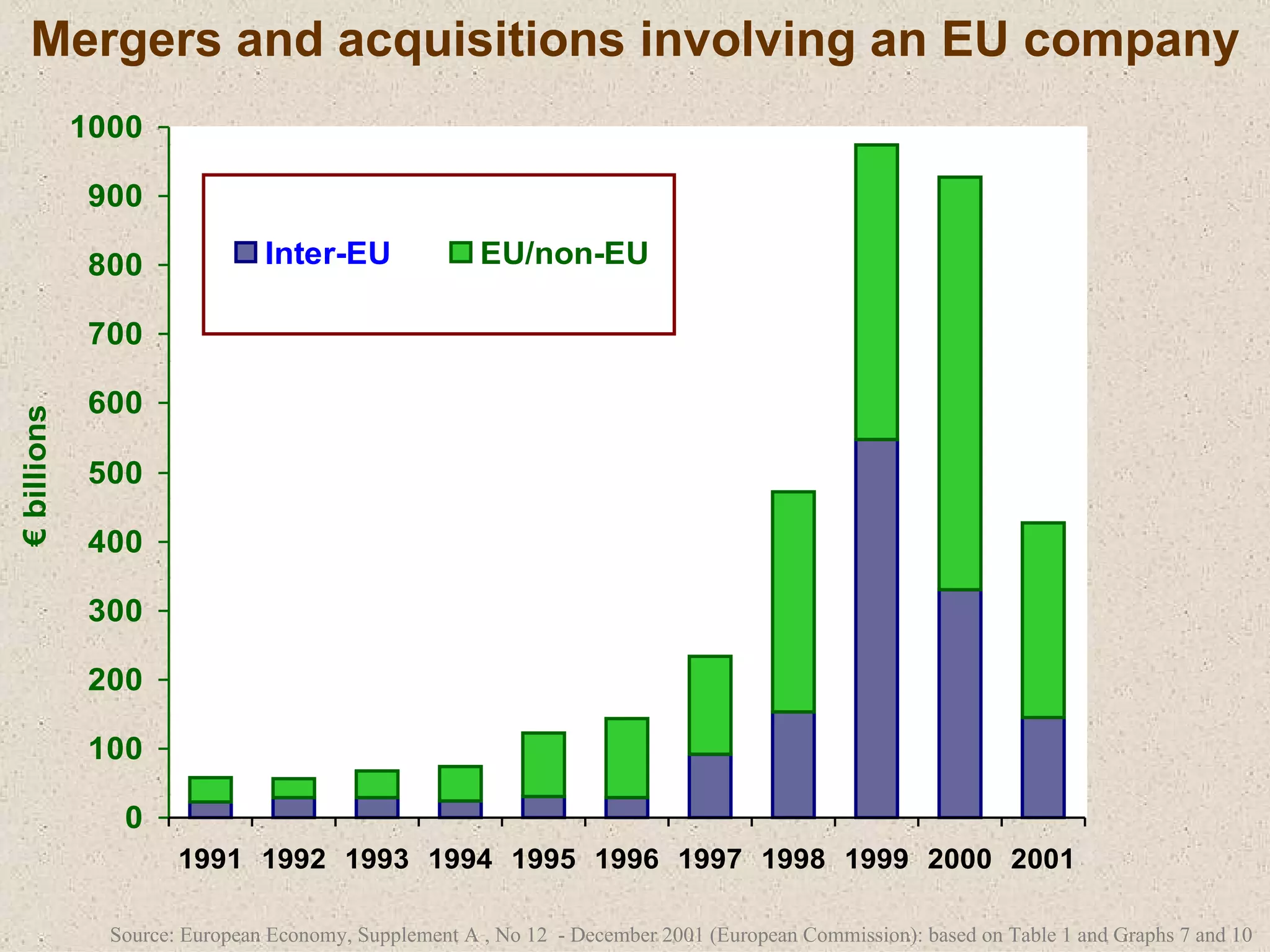
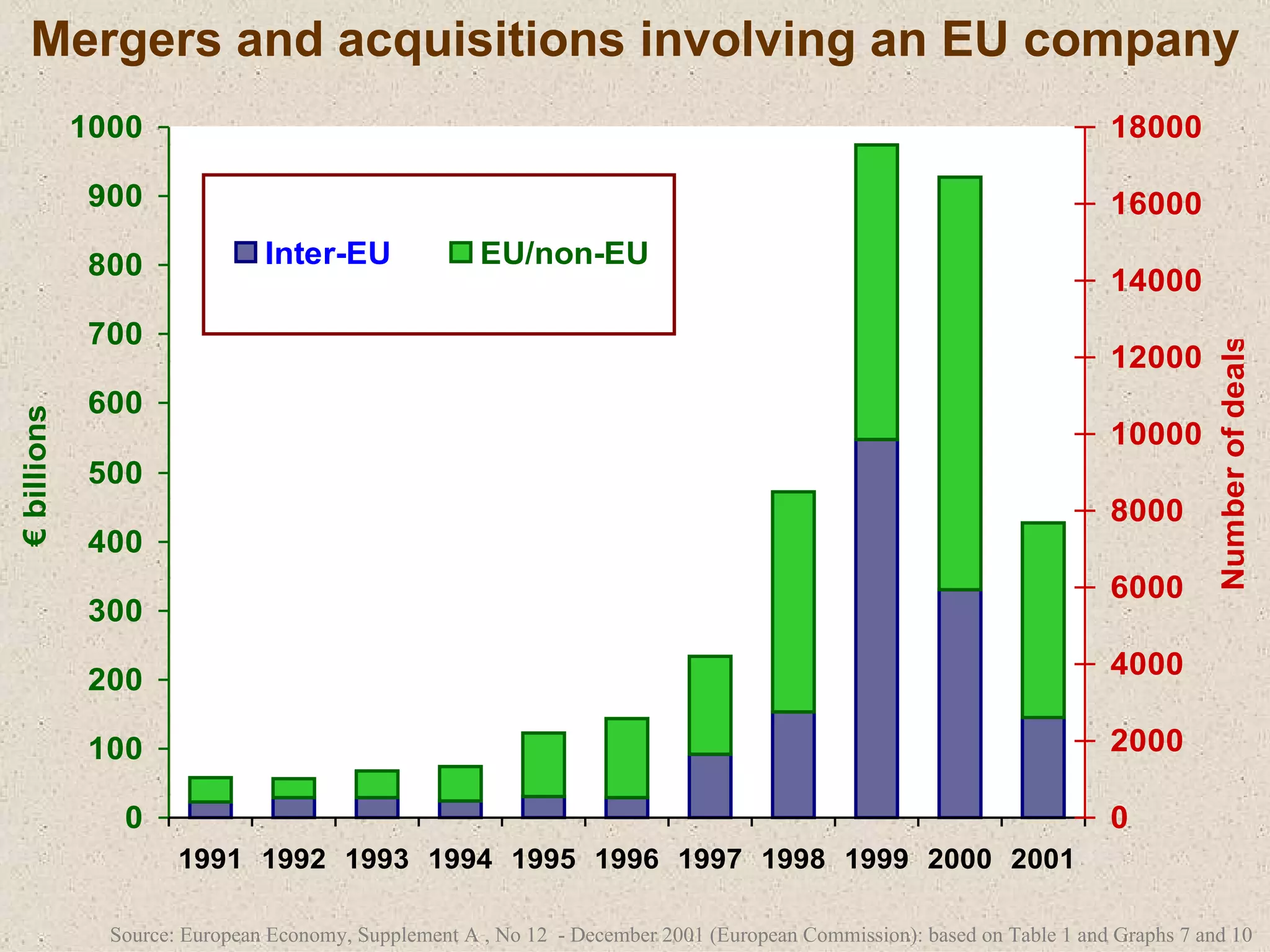
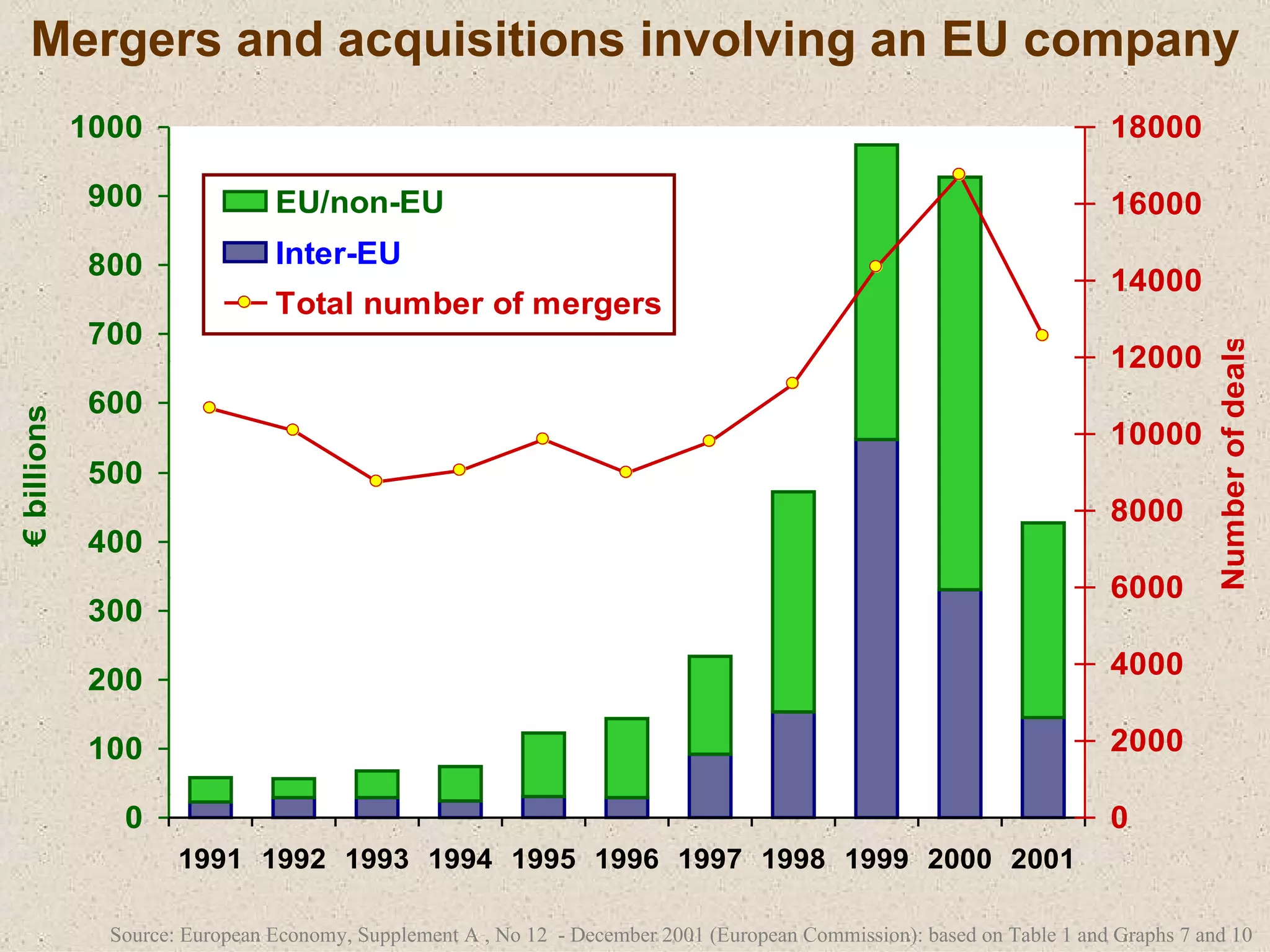
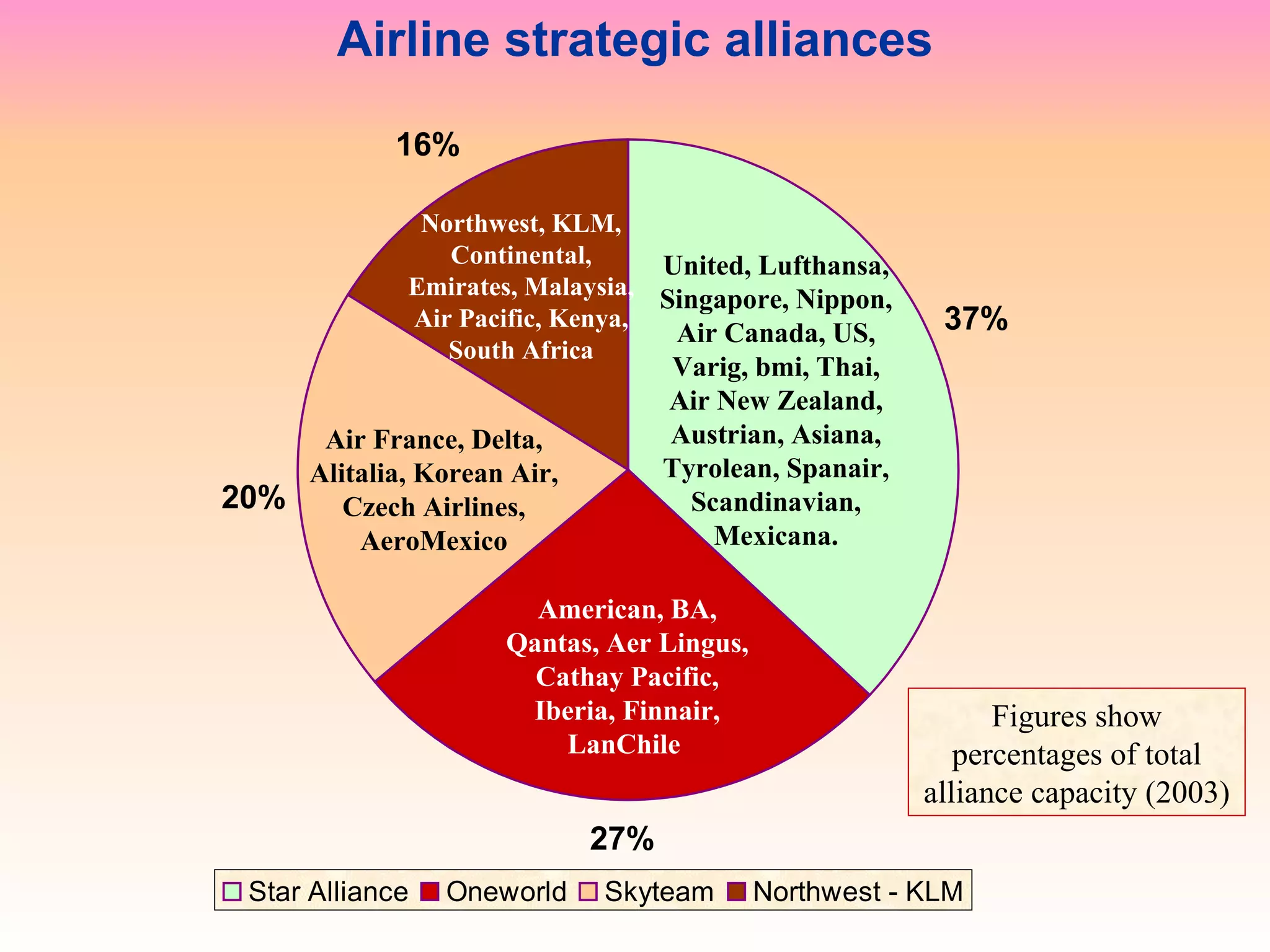
The document discusses various strategies that firms can pursue for growth, including internal expansion, external expansion through mergers and acquisitions, vertical and horizontal integration, diversification, and strategic alliances. It outlines the motivations, types, benefits, and challenges of each strategy. Constraints on growth include financial considerations, demand conditions, and managerial capabilities. Mergers and acquisitions can achieve economies of scale, increased market share, and stability, but also come with integration risks.