The document provides information on three case studies of green buildings that received certifications from TERI-GRIHA or UGBC-LEED:
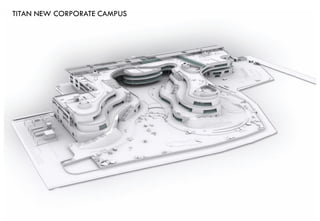
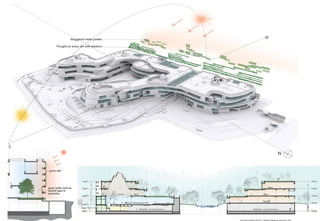
1) Titan New Corporate Campus in Bangalore received a 5 star rating from TERI-GRIHA for its sustainable design features like preserving existing trees, renewable energy systems, water management, and use of sustainable materials.
2) The expansion of The British School in New Delhi received a 5 star TERI-GRIHA rating for its passive design strategies like courtyards, efficient water and energy systems, and use of local materials.
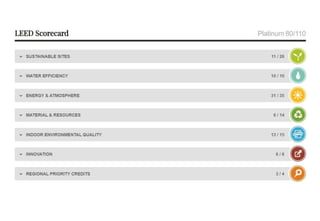
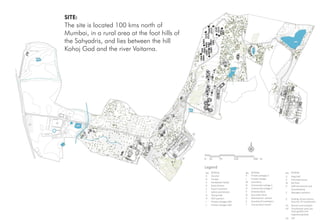
3) The Stony Brook Millstone Watershed Association environmental center in New Jersey achieved Platinum LEED certification for