The document discusses building web services. It describes some challenges with implementing remote procedure calls (RPCs) and how using HTTP and XML-based standards like SOAP and REST can help address those challenges. It provides details on XML web services, including how they use SOAP, WSDL, and .NET and Java integration. It also covers REST/RESTful APIs and some of their constraints like being stateless and cacheable. The document is an introduction and overview of key concepts related to building and implementing web services.












![Server
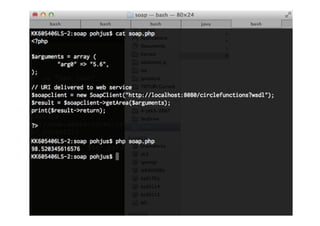
package hello;
import javax.xml.ws.Endpoint;
class Publish {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Endpoint.publish(
"http://localhost:8080/circlefunctions",
new CircleFunctions());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webservice-130909012242-/85/Building-Web-Services-15-320.jpg)








![.htaccess
# Let's use the mod_rewrite module
RewriteEngine On
# Set's the base URL for per-directory rewrites
RewriteBase /
# Defines a condition under which rewriting will
# take place
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
# Make the rule
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ /xampp/rest/index.php/$1 [L]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webservice-130909012242-/85/Building-Web-Services-27-320.jpg)

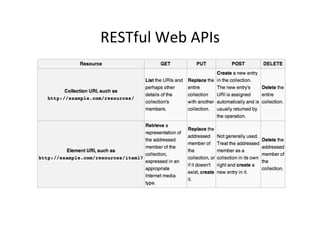
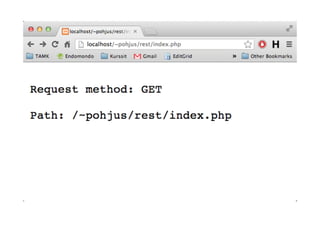
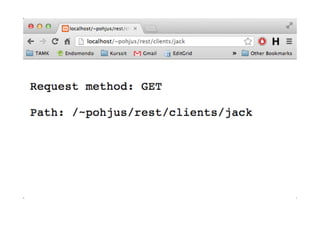
![Gekng
info
about
Request
and
Path
<?php
$requestMethod = $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'];
print("Request method: " . $requestMethod . "nn");
$urlPaths = $_SERVER['REQUEST_URI'] ;
print("Path: " . $urlPaths);
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webservice-130909012242-/85/Building-Web-Services-29-320.jpg)
![Modifica9on
<?php
$requestMethod = $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'];
$urlPaths = $_SERVER['REQUEST_URI'] ;
$paths = explode("/", $urlPaths);
$paths = array_splice($paths, 3);
print_r($paths);
?>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webservice-130909012242-/85/Building-Web-Services-32-320.jpg)