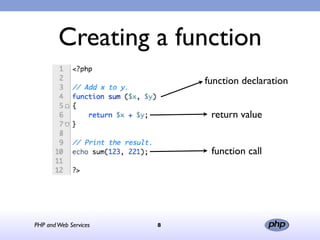
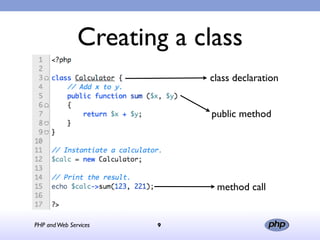
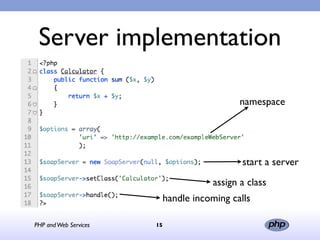
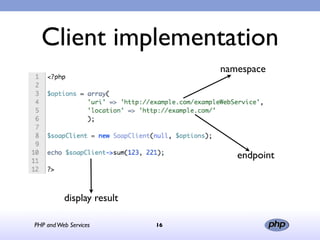
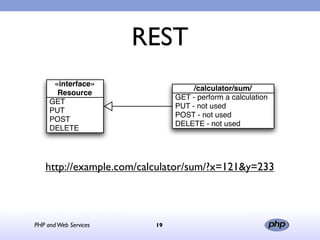
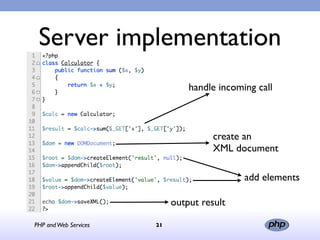
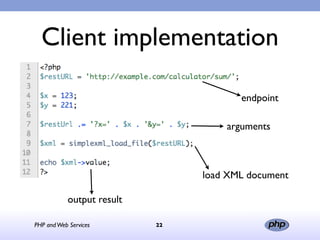
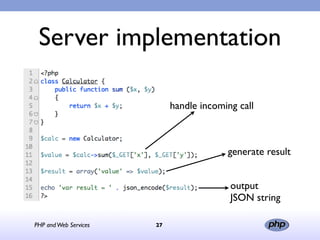
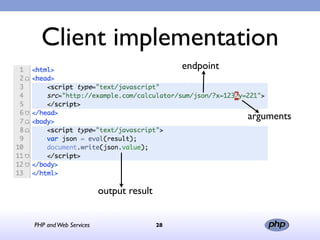
This document discusses PHP and various web service standards. It provides an overview of PHP, describing it as an open source scripting language used to build various web applications and sites. It also summarizes different web service standards like SOAP, REST, and JSON that can be used with PHP. The document concludes that while there are many standards, PHP can handle the underlying implementation and that REST requires more coding than SOAP, but JSON may be better for client-side applications.