This document provides an overview of using the libGDX framework to implement a simple 2D game in Java. It discusses topics such as setting up the starter class, loading assets like images and audio, rendering with an orthographic camera, sprite batch for drawing textures, handling input, collision detection using rectangles, and more. The goal is to demonstrate the basic building blocks for creating a 2D game with libGDX.

![Starter
Class:
Desktop
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LwjglApplicationConfiguration config = new
LwjglApplicationConfiguration();
config.title = "Gorba's Revenge";
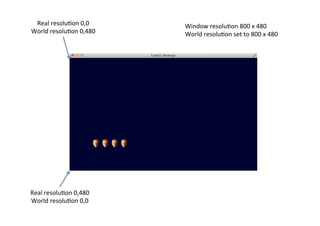
config.width = 800;
config.height = 480;
new LwjglApplication(new MyGame(), config);
}
}
// In Android, the resolution is set by operating system!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-simple-libgdx-game-140907062816-phpapp01/85/Implementing-a-Simple-Game-using-libGDX-2-320.jpg)










![Clear
Screen
@Override
public void render() {
// Direct OpenGL call
// float red [0,1]
// green
// blue
// alpha
// https://www.opengl.org/sdk/docs/man/html/glClearColor.xhtml
Gdx.gl.glClearColor(0, 0, 0.2f, 1);
// Clear the screen with the color chosen
// http://www.opengl.org/sdk/docs/man/html/glClear.xhtml
Gdx.gl.glClear(GL20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// SpriteBatch is ready for commands
batch.begin();
// Draw a texture to x = 100, y = 100
batch.draw(gorbaImage, 100, 100);
batch.draw(gorbaImage, 140, 100);
batch.draw(gorbaImage, 180, 100);
batch.draw(gorbaImage, 220, 100);
// No commands anymore, proceed to process the batch of commands
// received
batch.end();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-simple-libgdx-game-140907062816-phpapp01/85/Implementing-a-Simple-Game-using-libGDX-14-320.jpg)
![Gdx.input
• Ge]ng
input
from
user
is
very
easy
• Touch
– Gdx.input.isTouched()
– Gdx.input.getX()
– Gdx.input.getY()
• Accelerometer
– Gdx.input.getAccelerometerX()
– Gdx.input.getAccelerometerY()
– Gdx.input.getAccelerometerZ()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/03-simple-libgdx-game-140907062816-phpapp01/85/Implementing-a-Simple-Game-using-libGDX-15-320.jpg)