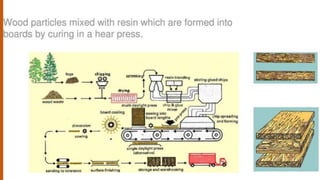
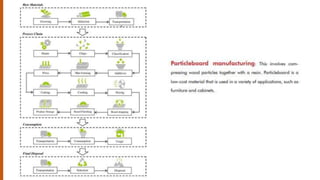
The document provides an extensive overview of various interior materials, focusing on types of wood, their properties, manufacturing processes, and applications. It discusses materials such as plywood, laminated wood, and particleboard, along with synthetic materials and glass, highlighting their advantages and uses in construction and design. The information is geared towards understanding material characteristics, manufacturing methods, and applications in interior design.