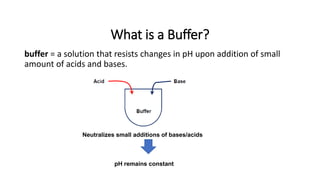
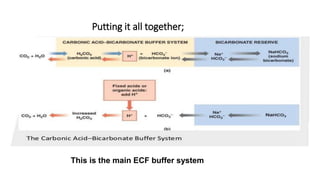
The document discusses acid-base balance and buffer systems in the body. It explains that the body has three main systems to defend against changes in hydrogen ion concentration: 1) body fluid buffers, 2) lungs, and 3) kidneys, with the kidneys being the most powerful. Buffers are solutions that resist pH changes upon addition of acids or bases and maintain pH. The main chemical buffers in the body are the bicarbonate, phosphate, and protein buffer systems. The bicarbonate buffer system acts the quickest and is the primary extracellular fluid buffer, functioning through the reaction of carbon dioxide, water, and bicarbonate ions.

![The Body’s Defense Against Changes in [H+]
Three main systems:
1.Body fluid buffers.
Works within seconds.
2.Lungs
Works within minutes.
3.Kidneys
Works within hours-days.
The most powerful of the three.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemistrylect-230305212326-54efbcf5/85/Chemistry-lect-3-pdf-2-320.jpg)

![Chemical Buffer Systems in the Body
There are 3 chemical buffers in the body;
1.The Bicarbonate buffer system.
2.The phosphate buffer system.
3.Proteins.
•They are the 1st line of defense against changes in pH i.e. [H+], act within seconds.
•Some are more powerful extracellularly and others are more powerful
intracellularly](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemistrylect-230305212326-54efbcf5/85/Chemistry-lect-3-pdf-5-320.jpg)






![Summary of Body’s Buffering Systems
Buffer systems do not work independently in body fluids but actually work together.
•A change in the balance in one buffer system, changes the balance of the other
systems.
•Buffers do not reverse the pH change, they only limit it.
•Buffers do not correct changes in [H+] or [HCO3-], they only limit the effect of
change on body pH until their concentration is properly adjusted by either the lungs
or the kidney.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemistrylect-230305212326-54efbcf5/85/Chemistry-lect-3-pdf-13-320.jpg)