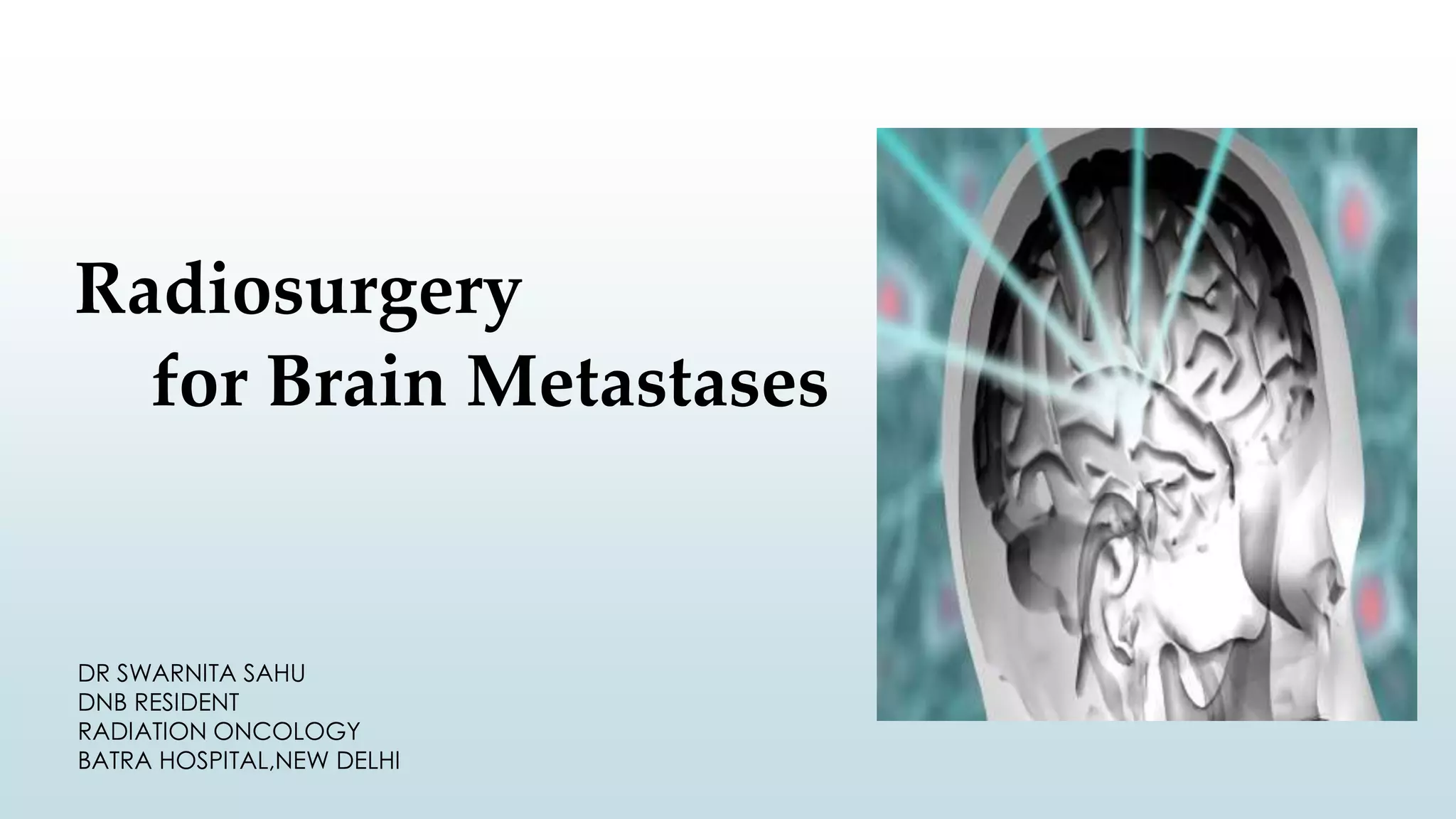
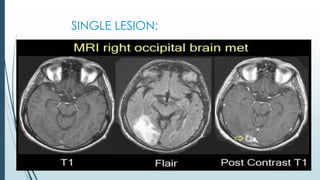
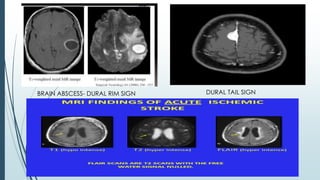
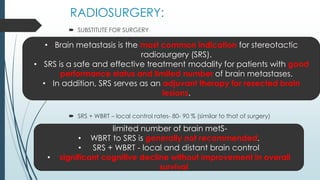
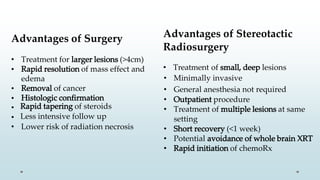
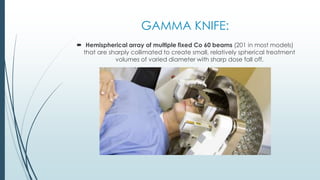
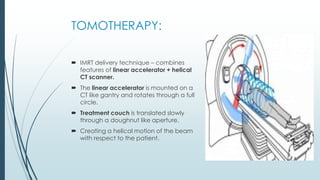
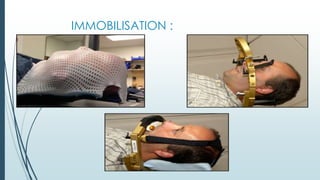
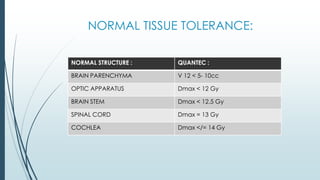
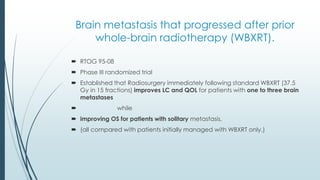
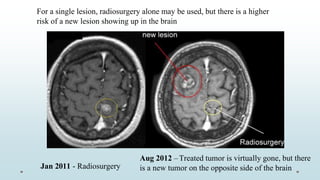
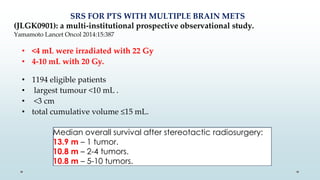
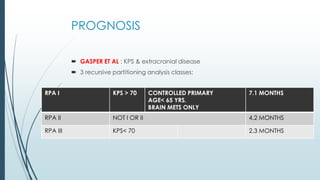
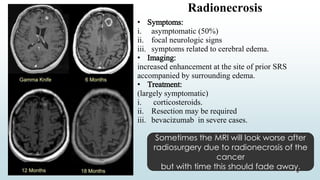
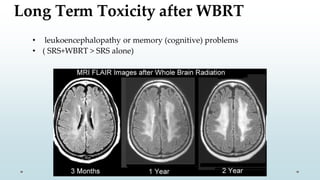
Brain metastasis is a common complication of systemic cancers. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is an effective treatment modality for patients with a limited number of brain metastases and good performance status. SRS provides high local tumor control rates comparable to surgery but is non-invasive. While SRS alone risks new metastases developing elsewhere in the brain, combining SRS with whole brain radiation therapy improves local and distant brain control but increases risks of cognitive decline. Patient prognosis depends on factors like performance status, number and size of metastases, and control of the primary cancer.