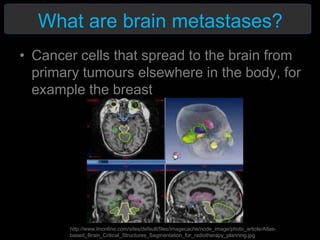
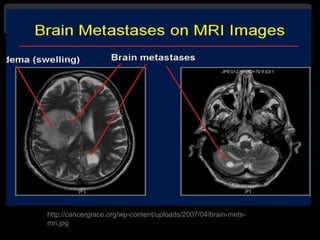
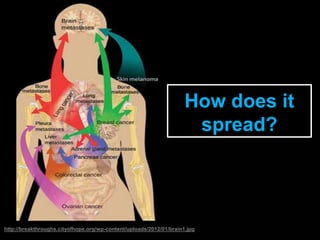
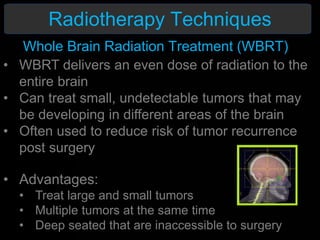
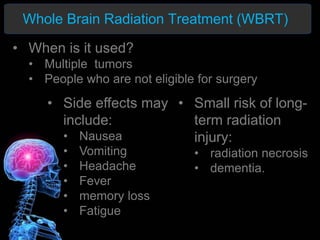
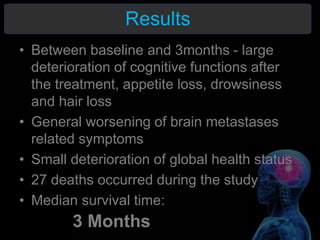
Radiotherapy is a common treatment for brain metastases, but does it improve patients' quality of life? A study of 39 brain metastases patients assessed their quality of life before and after whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) treatment. The results showed a deterioration in cognitive function, appetite, alertness and hair loss in patients after treatment. There was also a small decline in overall health and high mortality. The study concluded that WBRT does not significantly improve quality of life for brain metastases patients. More research is needed to refine treatment approaches.