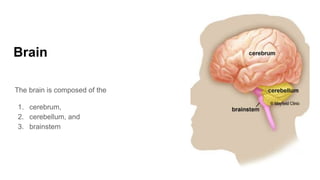
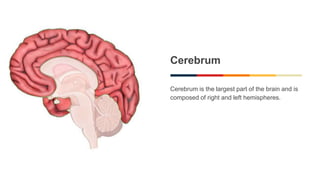
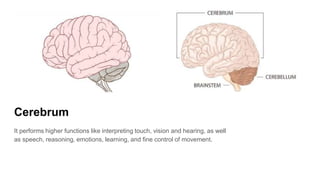
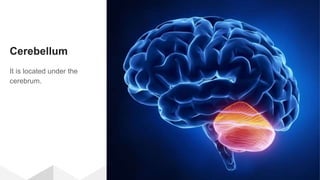
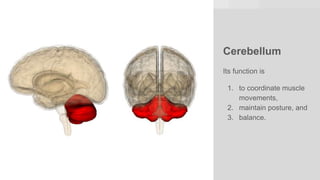
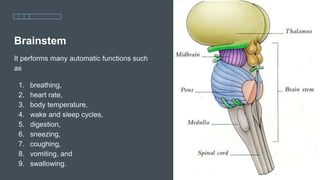
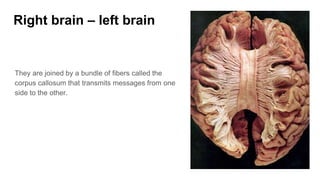
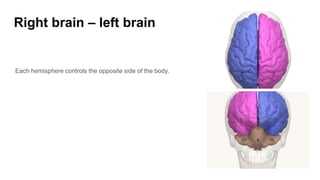
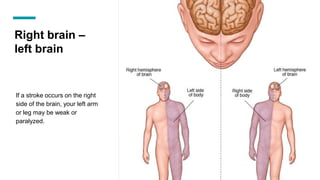
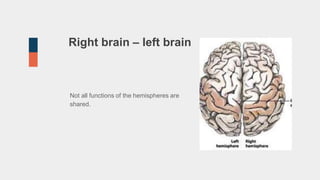
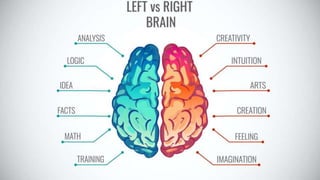
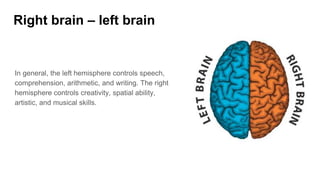
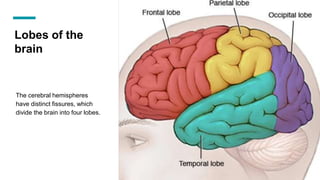
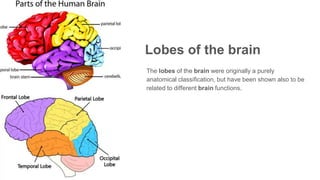
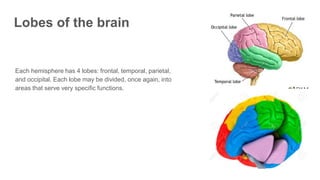
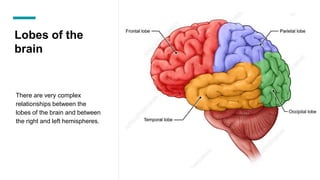
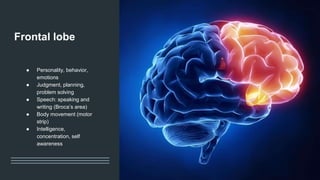
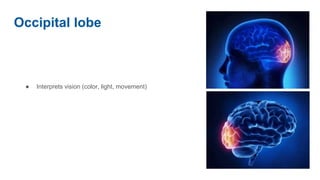
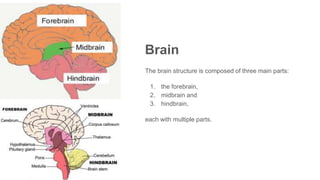
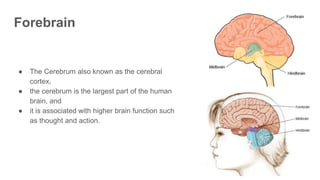
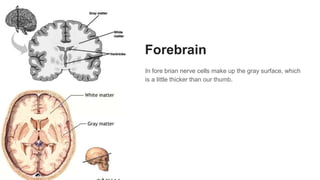
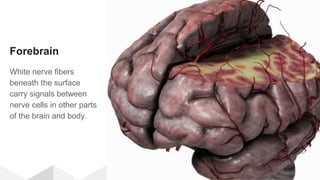
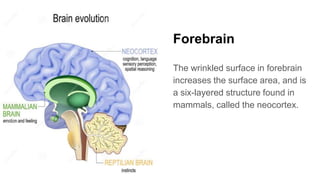
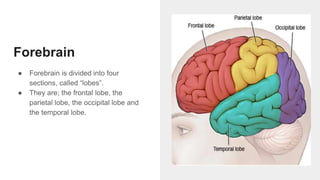
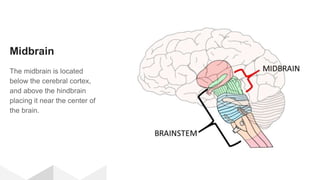
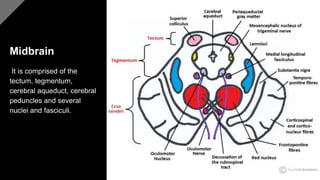
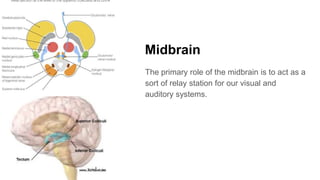
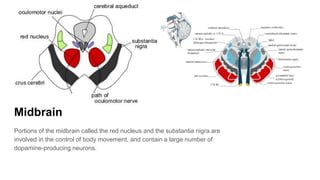
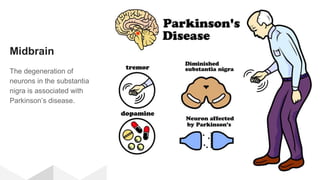
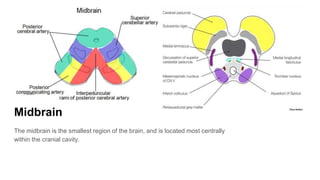
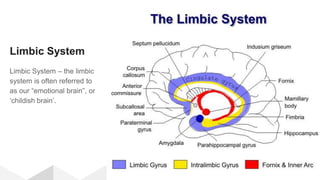
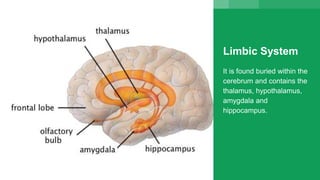
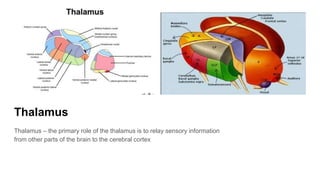
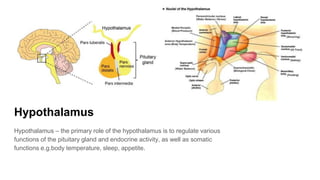
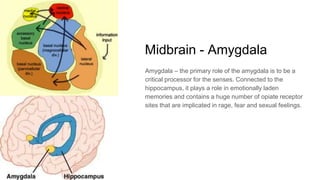
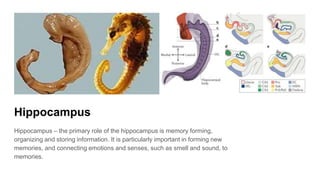
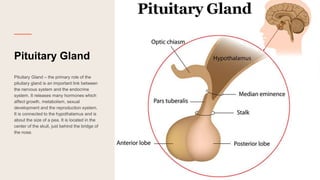
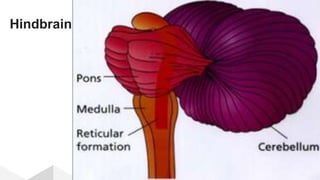
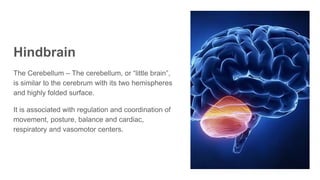
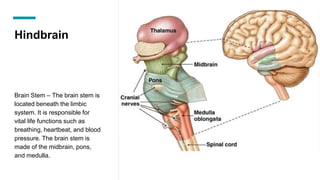
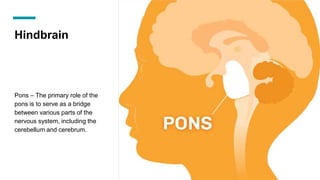
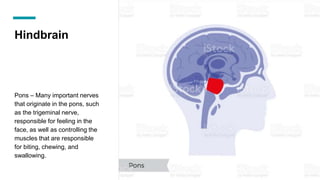
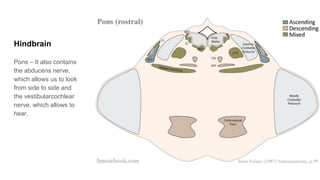
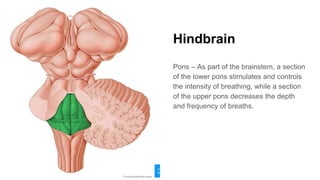
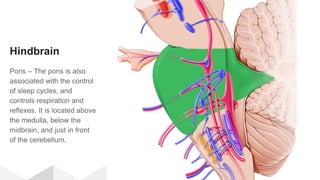
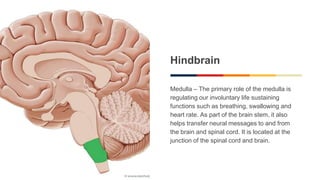
The document discusses the structure and function of the human brain. It is divided into several main sections: the cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem which make up the three main parts of the brain. The cerebrum is the largest part and is divided into four lobes (frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal) which each control different functions. The cerebellum coordinates movement and balance, while the brainstem performs vital automatic functions. The left and right hemispheres each control the opposite side of the body and have slightly different functions. The limbic system controls emotions, and the pituitary gland regulates hormones.