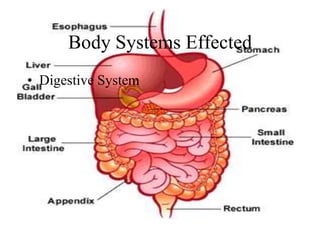
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is characterized by abdominal pain, constipation, and/or diarrhea caused by abnormal contractions of the intestinal muscles. Stress, anxiety, depression, and gastrointestinal infections can contribute to IBS. Symptoms include abdominal bloating, gas, pain relieved by bowel movements, diarrhea, constipation, and feeling of incomplete emptying. Diet, stress management, education, and medication can help treat IBS symptoms. IBS is not contagious and people can recover with treatment.