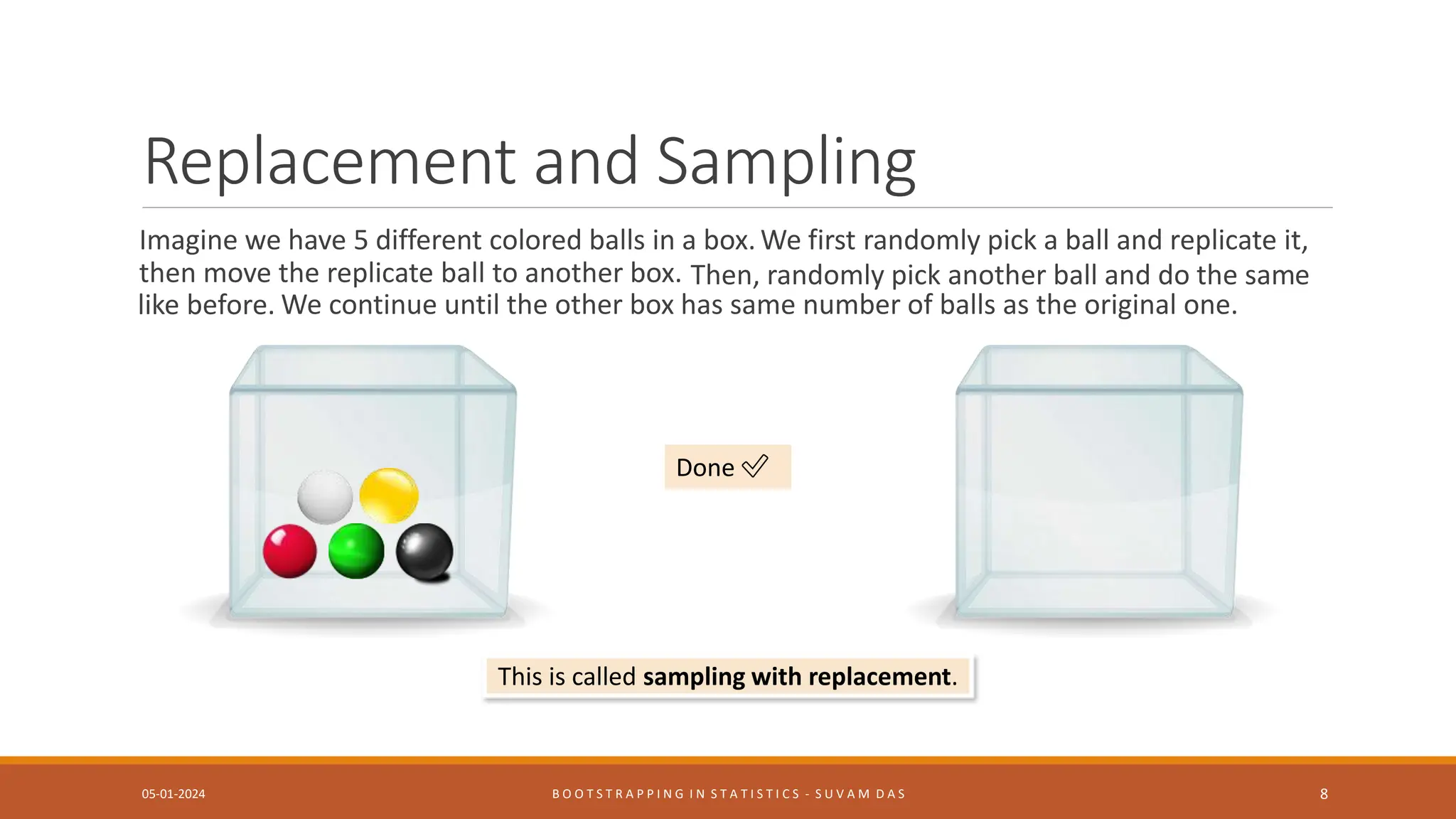
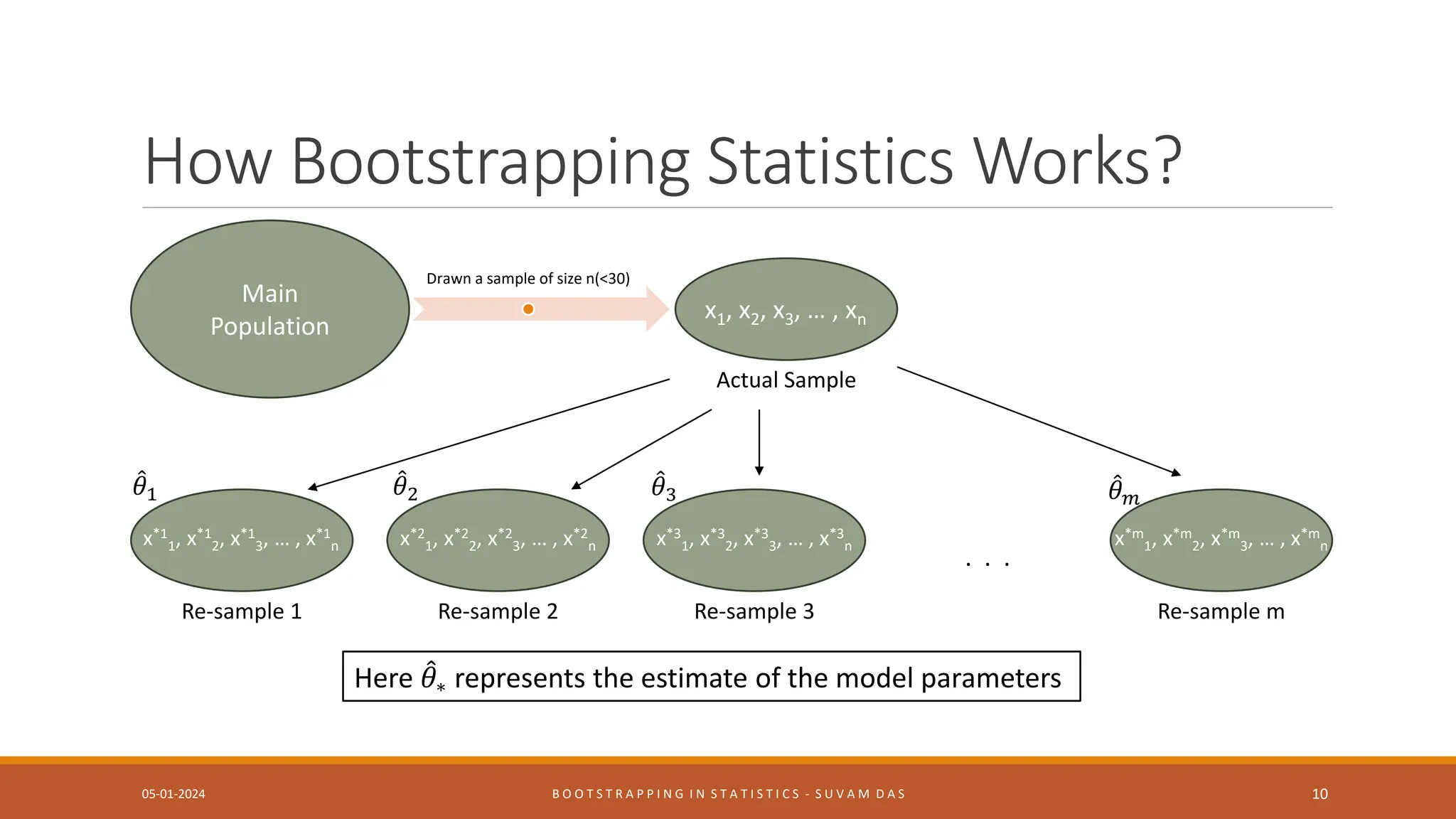
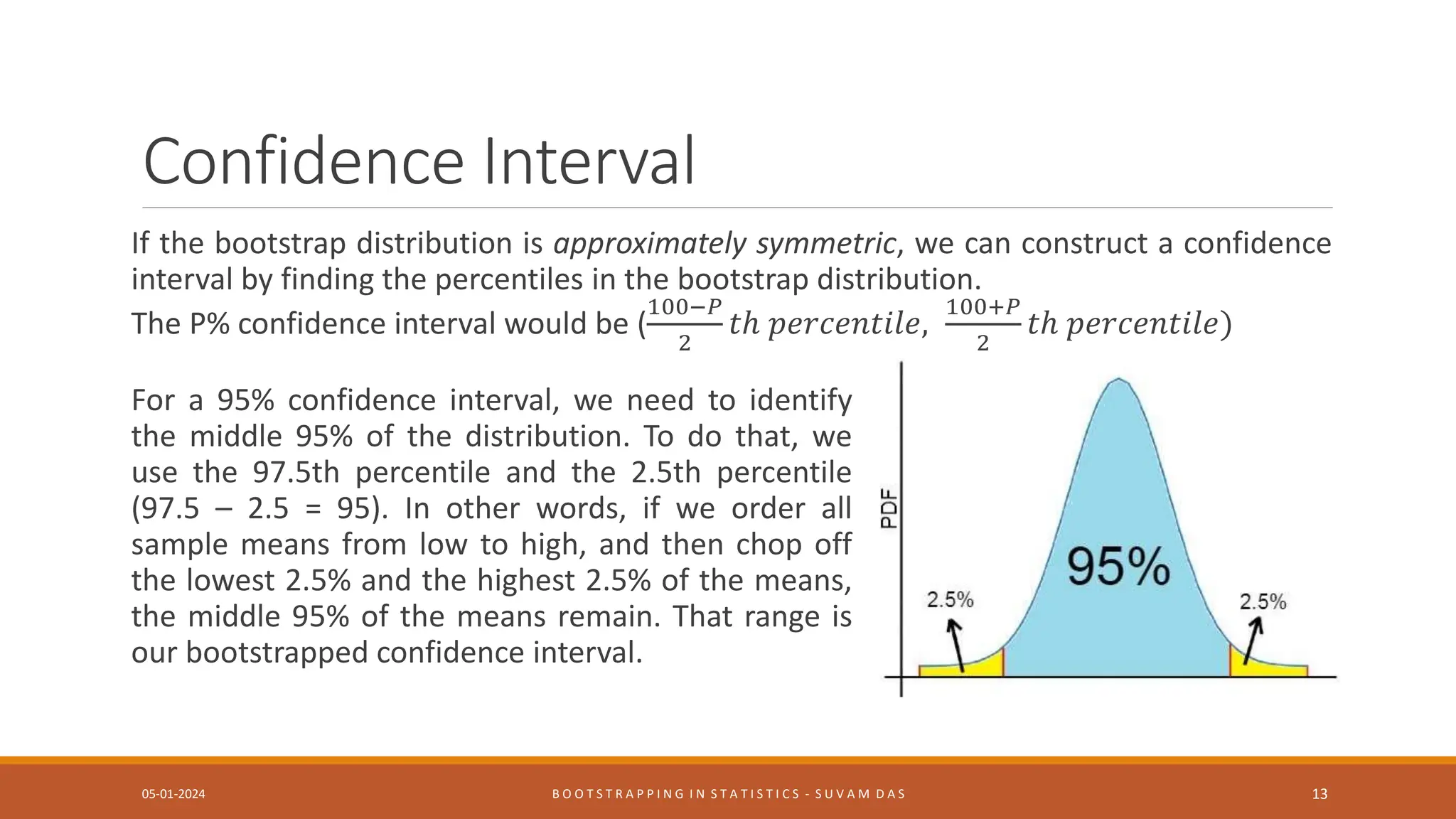
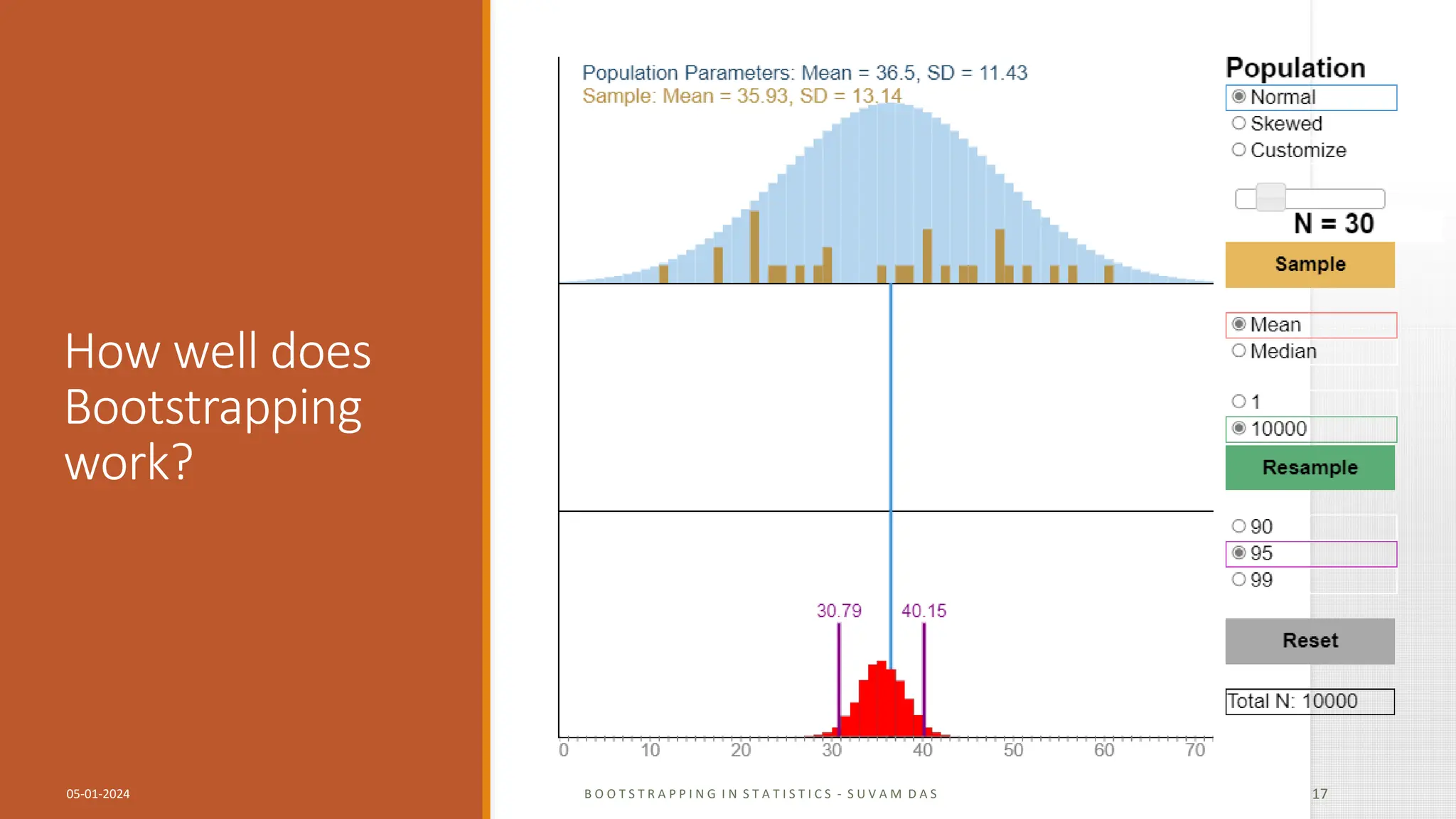
Bootstrapping is a statistical method for estimating properties of a population by resampling from an original sample with replacement many times. It generates multiple simulated samples from a single sample to estimate how well a statistic estimates a population parameter without large sample assumptions. The document discusses what bootstrapping is, when it is useful, how it works by resampling a sample multiple times to estimate properties like confidence intervals, and examples of bootstrapping statistics.