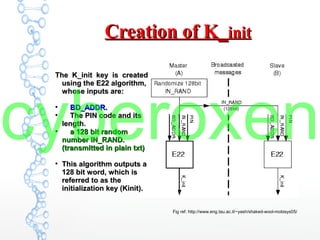
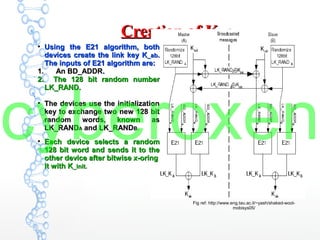
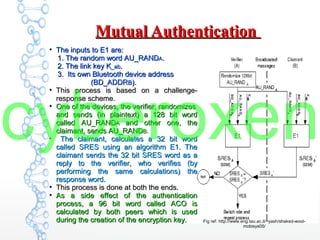
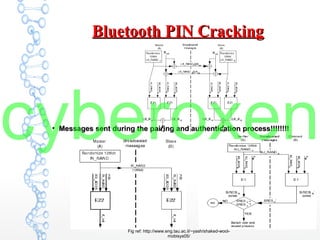
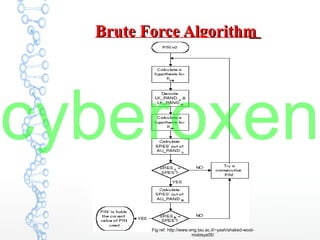
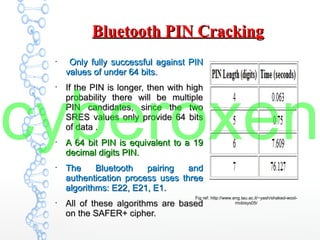
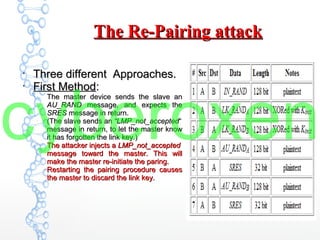
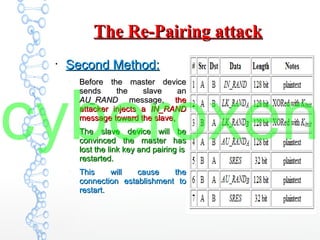
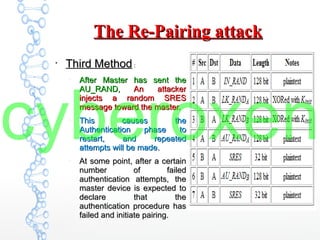
The document provides an in-depth analysis of Bluetooth security, highlighting the pairing process, pin code cracking methods, and vulnerabilities in the Bluetooth protocol. It discusses algorithms used for authentication and encryption key creation, while also detailing potential attacks like re-pairing and brute-force pin cracking. Furthermore, the document emphasizes recommended countermeasures to enhance Bluetooth security, including the use of longer pins and secure pairing practices.