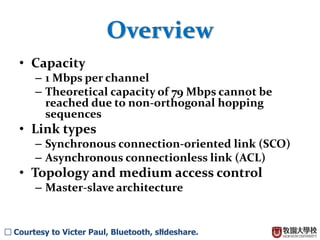
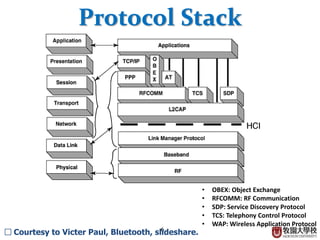
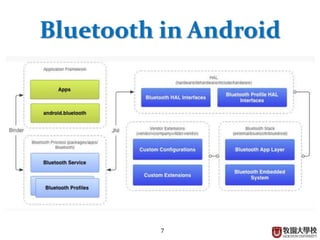
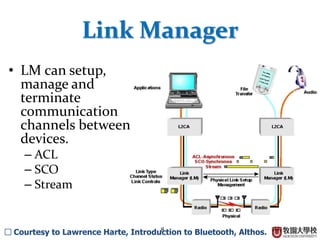
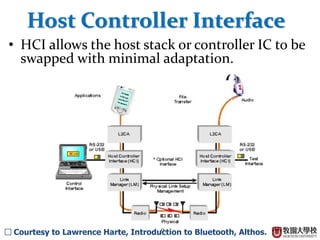
This document summarizes the Bluetooth layer structure. It discusses the link types in Bluetooth including SCO and ACL links. It also outlines the Bluetooth protocol stack including layers like L2CAP, RFCOMM, and SDP. Finally, it briefly explains Bluetooth profiles and how GATT and BR/EDR profiles define possible applications.
![Bluetooth Layer
Structure
Yong Heui Cho @ Mokwon University
Some of slides are referred to:
[1] Victer Paul, Bluetooth, slideshare, 2011.
[2] Erin Yueh, Android Bluetooth Introduction, slideshare, 2009.
[3] Lawrence Harte, Introduction to Bluetooth, Althos, 2008.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/6-160227025317/85/Bluetooth-Layer-Structure-1-320.jpg)