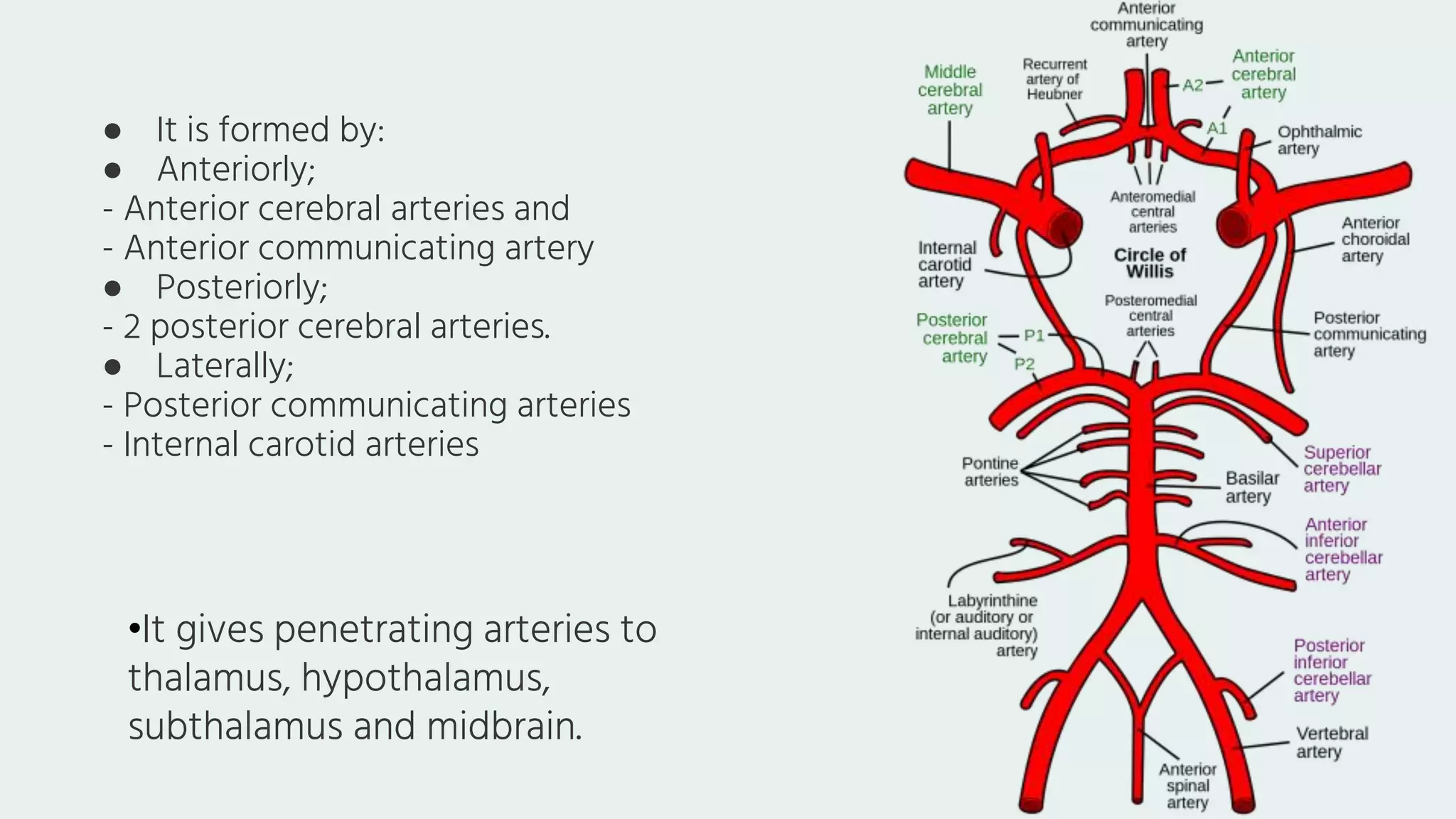
The document summarizes the arteries and veins that supply blood to the brain. It describes the two pairs of large arteries - the vertebral and internal carotid arteries. It details the branches and territories of these arteries, including the circle of Willis where the arteries anastomose. It then outlines the major veins that drain blood from the brain, including the superficial and deep cerebral veins that ultimately drain into the dural venous sinuses.