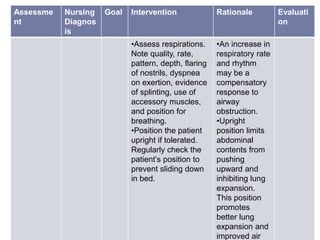
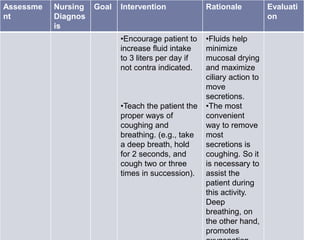
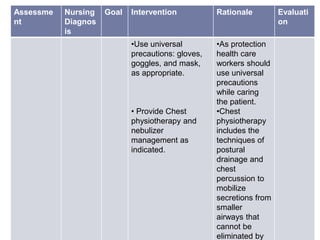
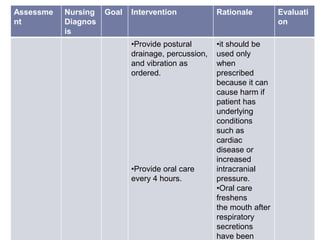
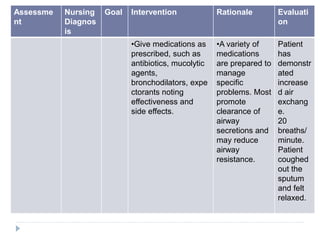
This nursing care plan outlines the steps to address a patient's ineffective airway clearance. It includes assessing the patient's subjective complaints of coughing and fatigue and objective findings of increased respiratory rate. The nursing diagnosis is ineffective airway clearance related to coughing and inability to remove secretions. The goal is for the patient to maintain clear airways. Interventions include positioning the patient upright, teaching coughing techniques, providing chest physiotherapy and medications as ordered. The evaluation found the patient's respiratory rate decreased and they were able to cough up secretions, feeling relaxed.