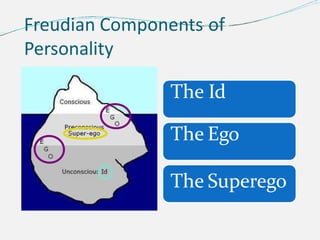
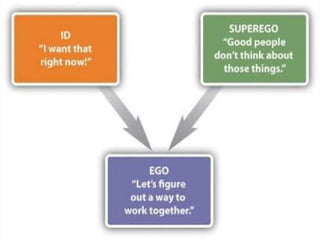
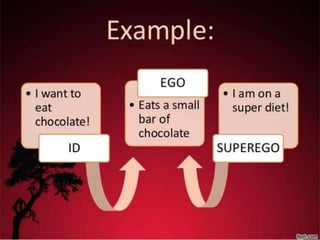
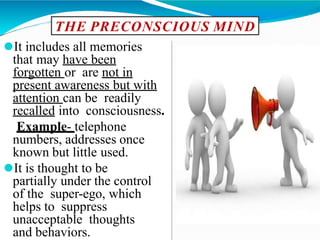
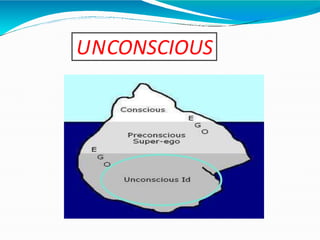
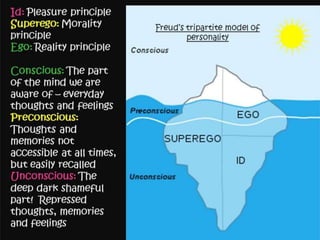
The document provides an overview of personality development, emphasizing the interplay of biological and environmental factors, including influential theories by Sigmund Freud. Freud's psychoanalytic theory identifies three components of personality: the id, ego, and superego, and outlines stages of psychosexual development from birth to adulthood that shape personality. The document also discusses the concept of the conscious and unconscious mind, illustrating how early experiences influence behavior and personal traits.