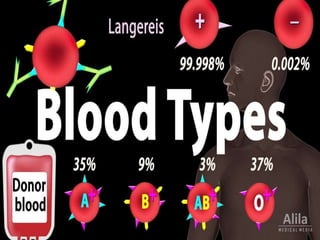
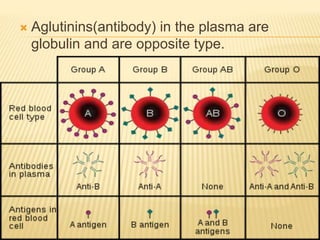
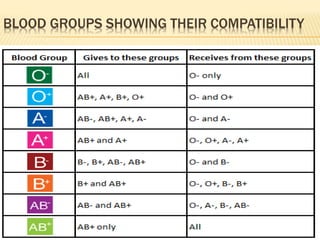
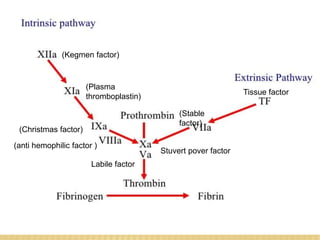
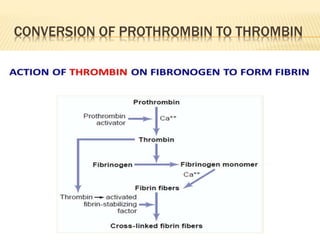
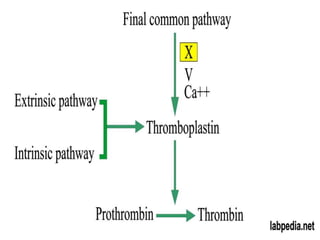
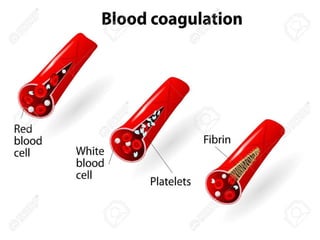
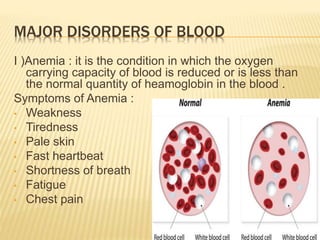
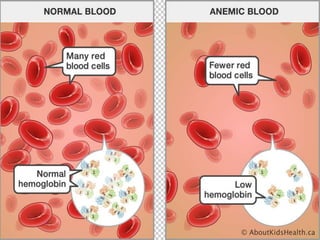
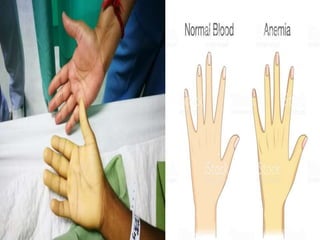
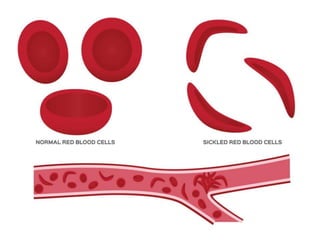
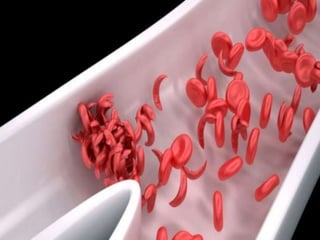
The document discusses blood grouping systems, blood coagulation, and common blood disorders. The two main blood grouping systems are ABO and Rh. It describes the antigens and antibodies involved in ABO blood grouping and compatibility. Blood coagulation involves several coagulation factors and occurs via the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Common blood disorders discussed include anemia, which can be microcytic, macrocytic, or normocytic, and sickle cell anemia.