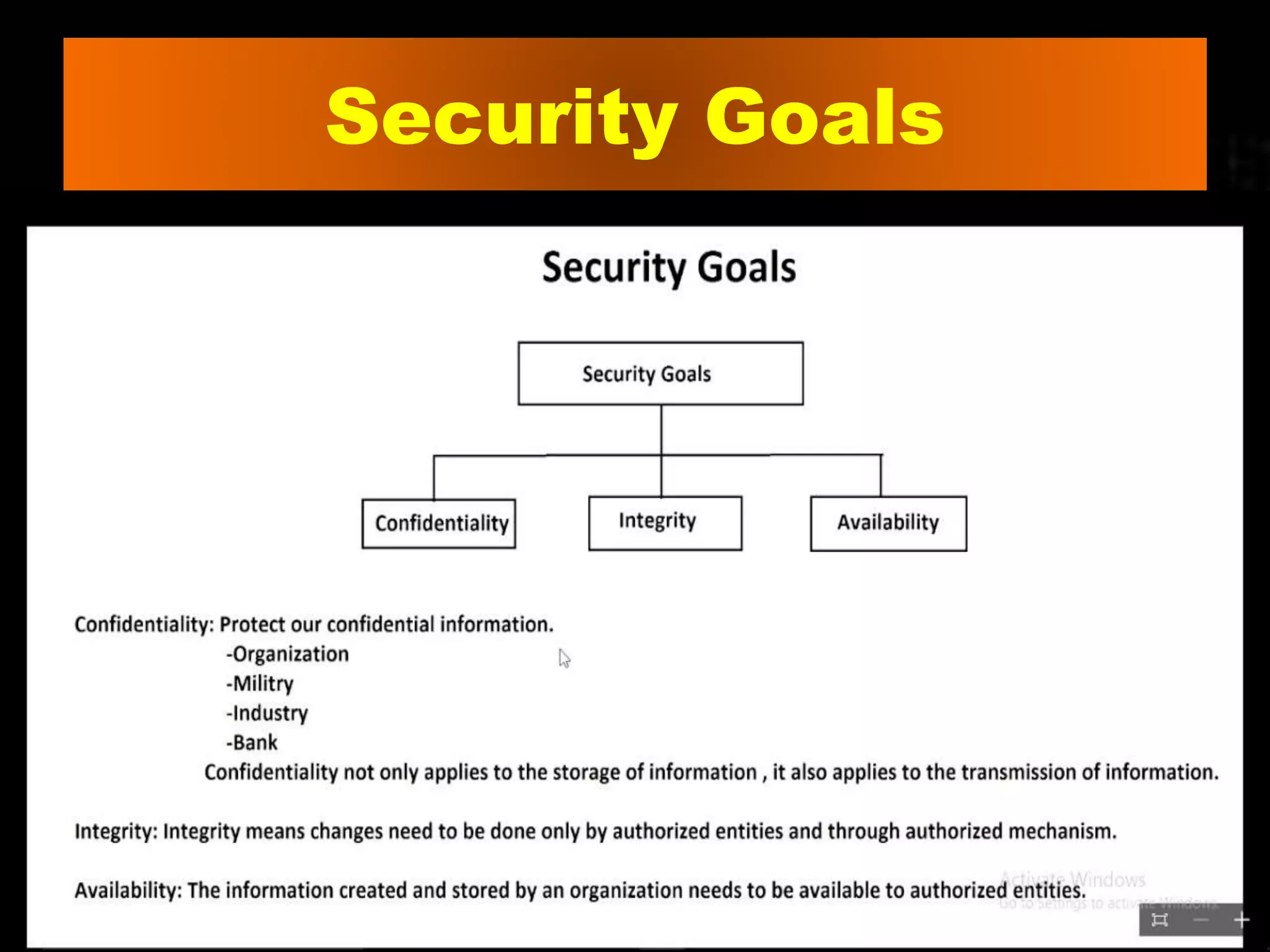
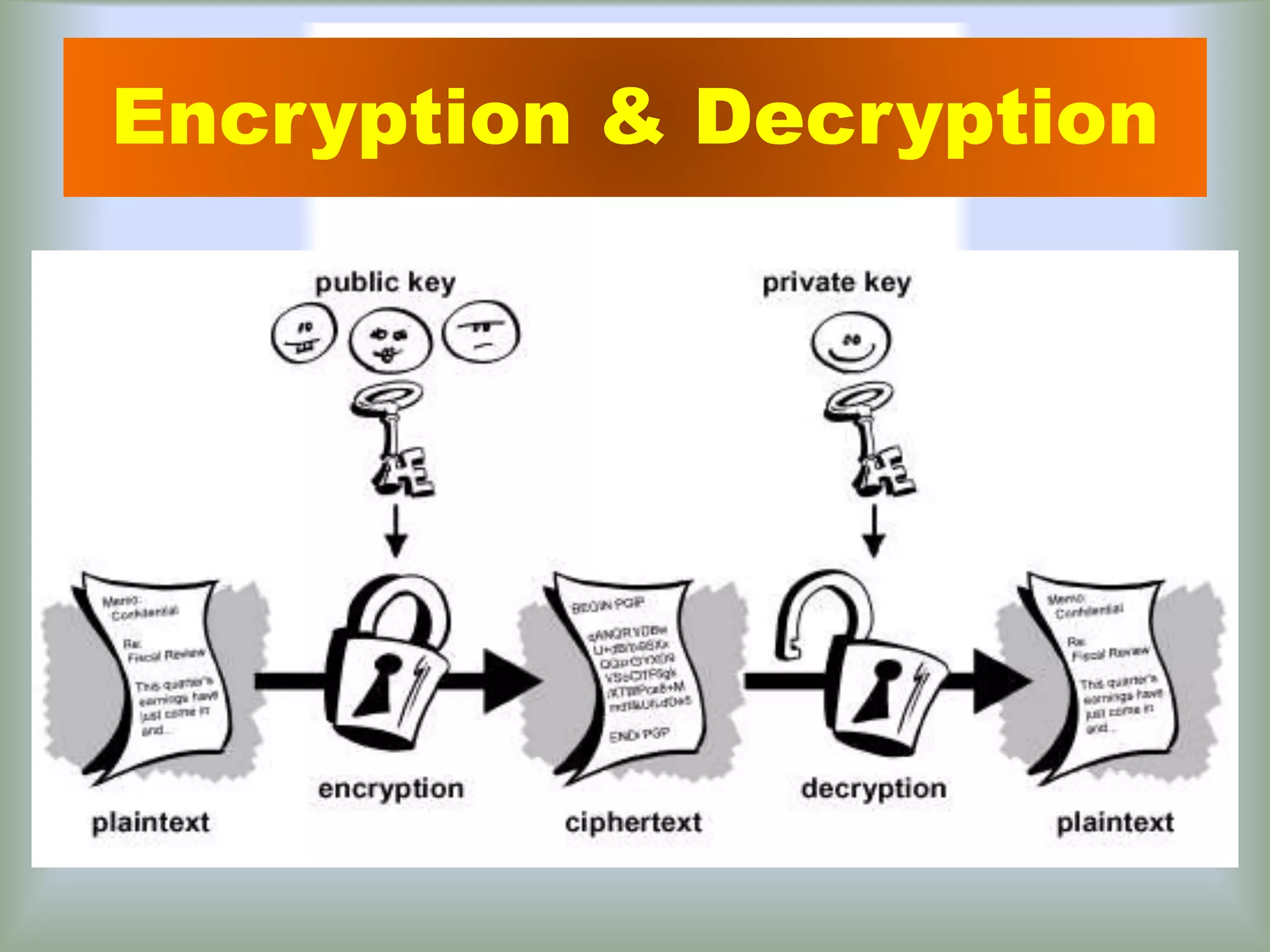
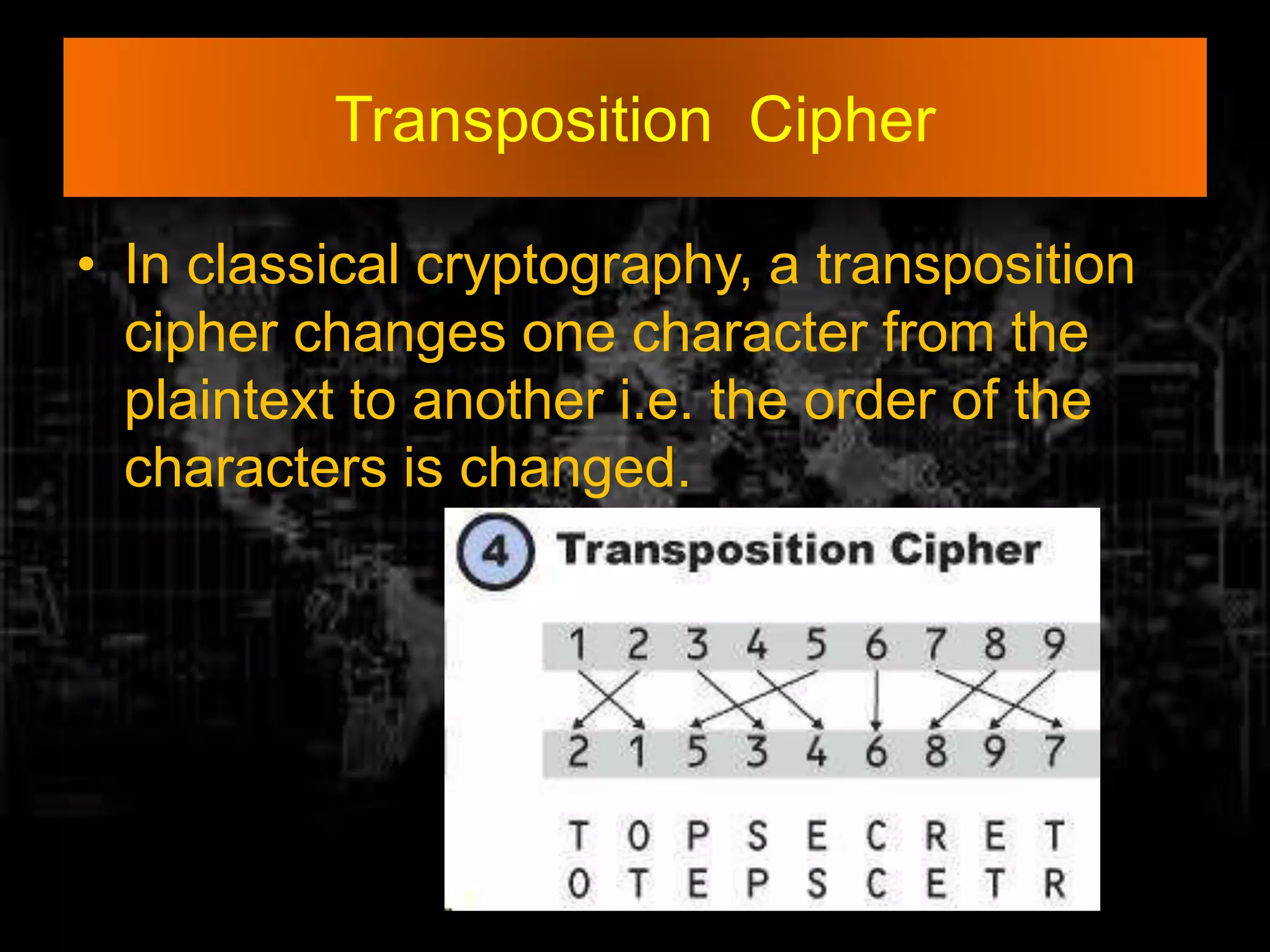
This document provides an overview of cryptography. It discusses security threats and goals, then defines cryptography as using mathematics to encrypt and decrypt data. It describes basic terms like plaintext, encryption, ciphertext, and decryption. The document outlines symmetric and asymmetric key cryptography, and examples of techniques like transposition ciphers, substitution ciphers, stream ciphers, and block ciphers. It concludes that cryptography should be used to implement network security and prevent data leakage through encryption and decryption techniques.