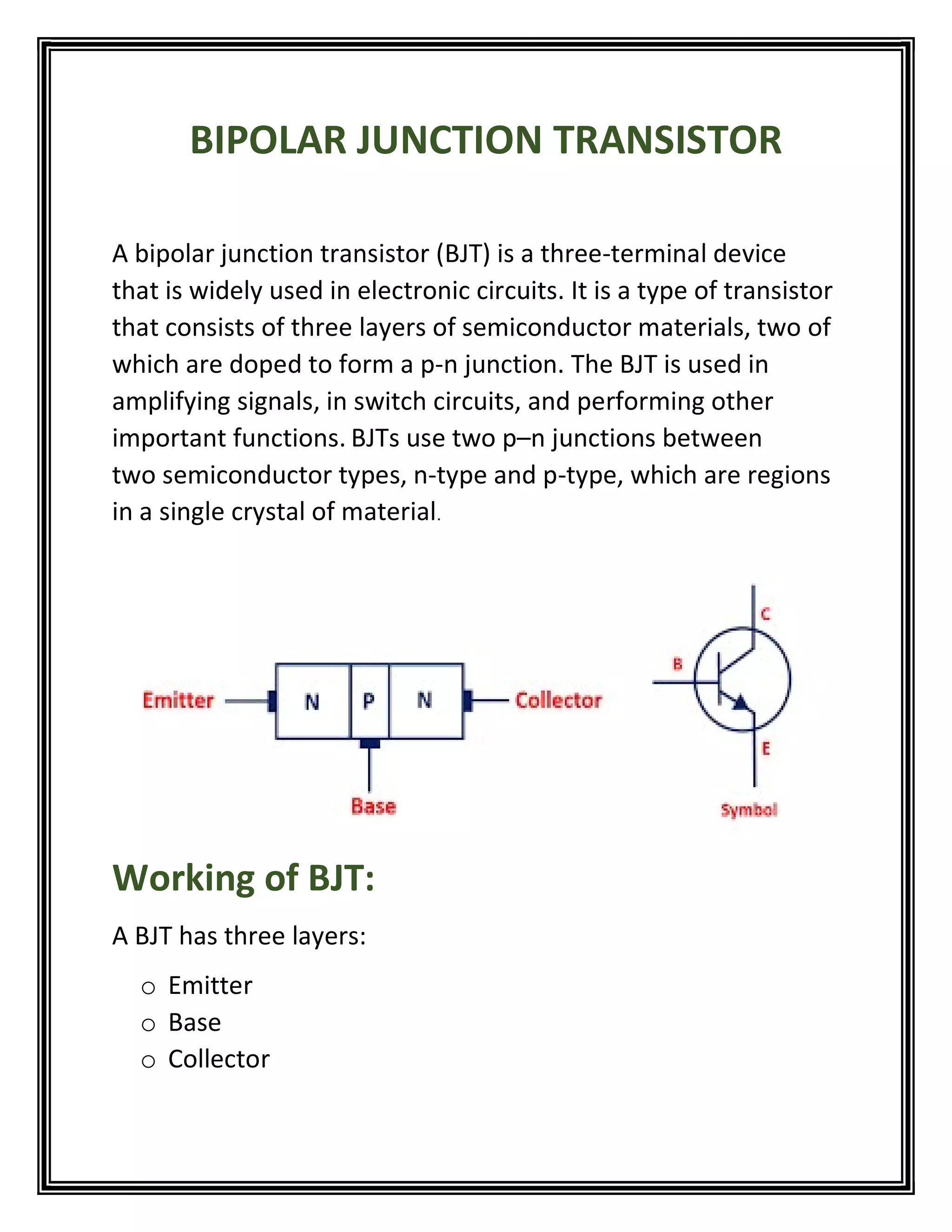
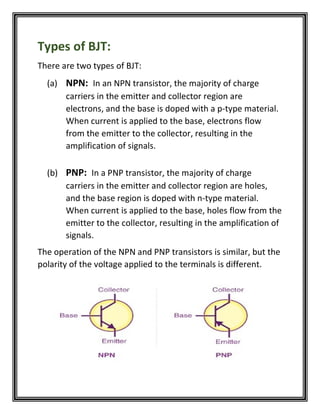
The bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a three-terminal semiconductor device consisting of an emitter, base, and collector layers that is used as an electronic switch and amplifier. It contains a p-n-p or n-p-n junction between the emitter, base, and collector layers. Applying a small voltage to the base controls the flow of current between the emitter and collector, allowing the BJT to amplify signals and be used in applications such as amplifiers, switches, oscillators, temperature sensors, and current regulators.