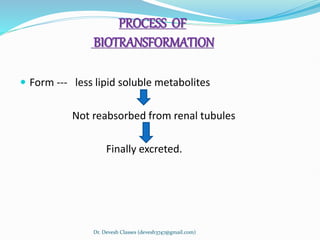
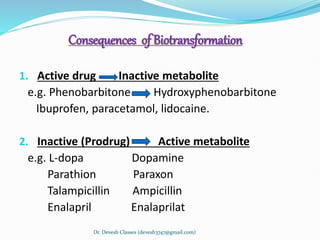
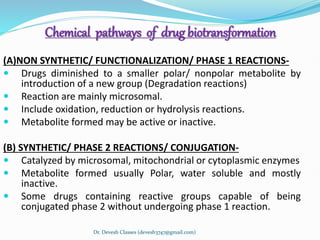
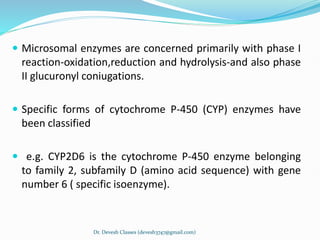
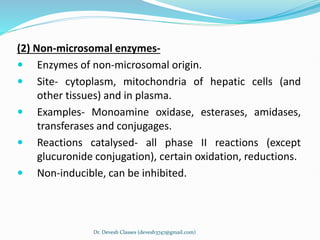
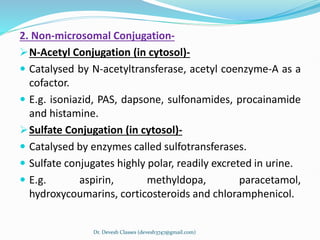
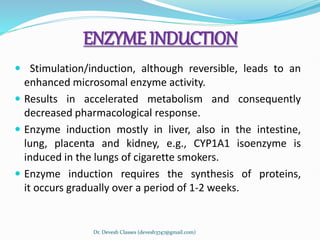
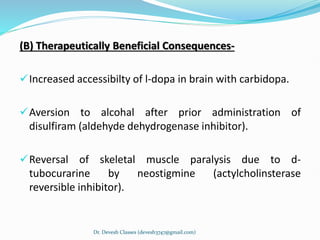
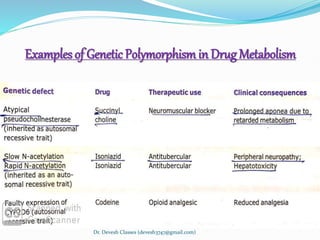
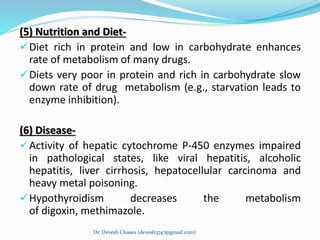
Biotransformation is the enzyme-catalyzed metabolic transformation of drugs within living organisms. It is a major mechanism for drug elimination and occurs mainly in the liver, kidney, intestine, and other tissues. Biotransformation can result in an active drug being converted to an inactive metabolite, an inactive prodrug being converted to an active metabolite, or an active drug being converted to another active metabolite. The drug-metabolizing enzymes involved in biotransformation include microsomal enzymes like the cytochrome P450 system and non-microsomal enzymes. Biotransformation involves two phases - functionalization reactions (Phase I) and conjugation reactions (Phase II).