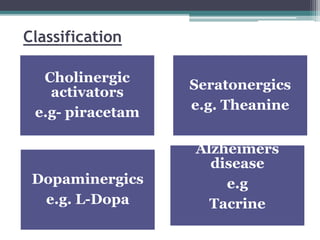
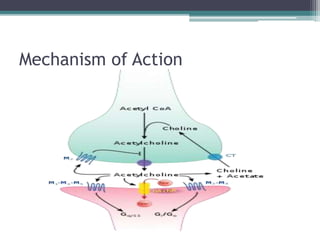
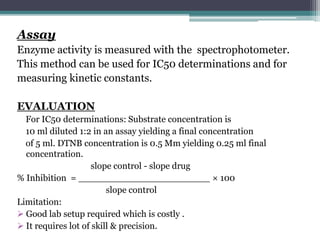
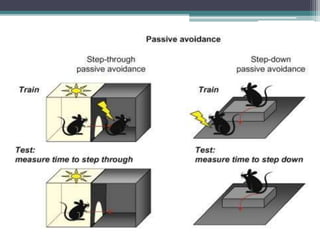
The document presents a comprehensive overview of nootropics, compounds that enhance cognitive functions such as memory and concentration. It details their mechanisms of action, classification, and various screening methods for testing their efficacy, including in vitro and in vivo assessments. Additionally, it highlights the applications of nootropics in treating conditions like Alzheimer's disease and anxiety, along with traditional uses in Ayurvedic medicine.